Data Generation for SQL Server
Features and Tools > Tools > Data Generation for SQL Server
Use Toad Data Modeler random data generation to quickly and easily create data for your databases. Data generation is supported for SQL Server 2005 and onwards
To generate data
- Double click any of your entities to open Entity Properties
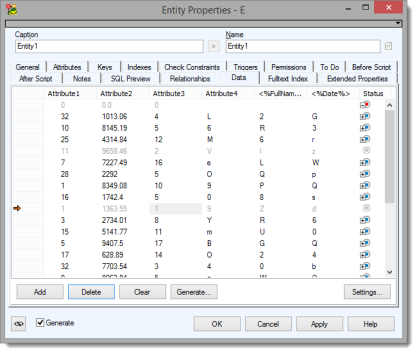
- Setup your Attributes and switch to Data tab to generate your data
- Click Add to add one record, click Generate to add a specified number of new records
To work with records
- Click Delete to remove the selected record and Clear to clear out all your generated data. Cleared data appears grayed out
- Click Settings to disable/enable attributes and adjust minimum and maximum values for generation of data for each column (attribute) for the current model
- Click Settings | Options | Model | Physical Model | Microsoft SQL Server | Generating Data to adjust default data generation settings for all MS SQL Server models. When you change any of these default values it will be carried on to all your SQL Server models
|
|
TIP: Click <%> to add application variables in Attributes in order to use them in your generated data |
Refactoring Utility
Features and Tools > Tools > Refactoring Utility
Toad Data Modeler provides you with a tool that is able to refactor all references to an object when you change its name. For example, let's say you've changed name of an entity. Usually, you would have to go through the rest of the model and change the name in all the places where it is referenced. Refactoring Utility is able to do this automatically, saving your time.
|
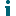
|
Note: The utility refactors text properties only (e.g. AfterScript, BeforeScript, SQL tab, text Views...) |
To open Refactoring Utility
- Click Tools | Refactoring Utility
Fast Parser checkbox - When checked, the Refactoring Utility uses Fast Parser to find broken references. In some cases it might be able to find more inconsistencies than the default Advanced Parser.
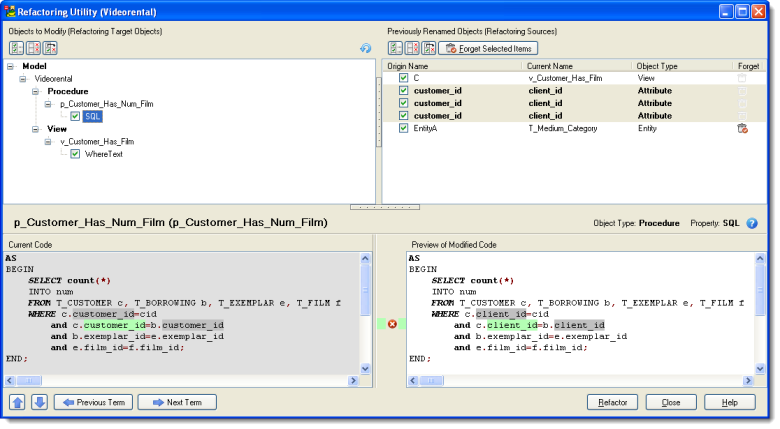
Renamed Objects
In section Previously Renamed Objectst (top-right), you can find objects that were renamed.
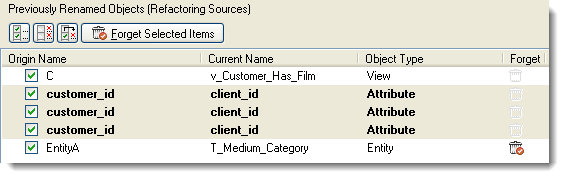
Use checkboxes to select what items you wish to use for current refactoring action.
Renamed objects will stay in section Previously Renamed Objects until you change names in other objects or until you enable icon in column Forget and click the Forget Selected Items button. (In this sample it should be used for EntityA).
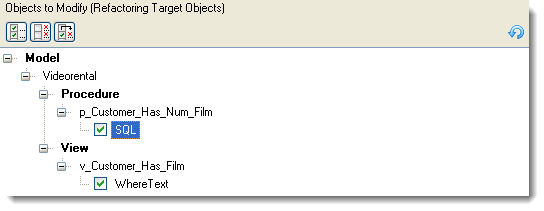
Objects to Modify
In section Objects to Modify, you can find objects and properties that contain old names.
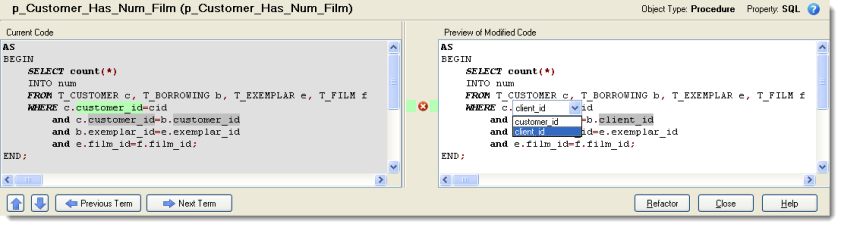
Current and Modified Code Previews
In section Current Code, the body of SQL code is shown. Use buttons Previous Term and Next Term to navigate among names in the same code.
Section Preview of Modified Code displays a preview of refactored code. Click any of the highlighted names and select old or new name or use the icons in middle column to reject suggested changes.
|
|
Note: Renaming from the default name (Entity1, Entity2...) is ignored deliberately. |
Schema/Owner/Database Assignment
Features and Tools > Tools > Schema/Owner/Database Assignment
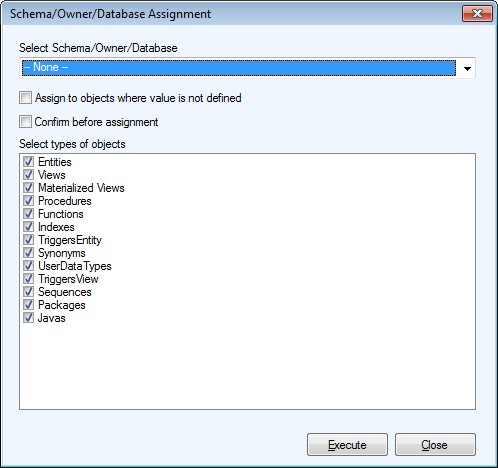
This tool allows you to assign or remove schema/owner/database to/from multiple object groups in your model at once.
To assign a schema/owner to your model
Select Tools | Schema/Owner Assignment.
|
Select Schema/Owner/Database |
Contains existing Schemas/Owners/Users in your model.
Select --None-- from the list to remove the existing schema from objects you mark in the Select types of objects section. |
|
Assign to objects where value is not defined |
Assigns schema/owner to objects, which have none assigned yet. |
|
Confirm before assignment checkbox |
Confirmation dialog for each object where schema is being assigned/removed will be displayed. |
|
Select types of objects area |
Mark objects which should be assigned a Schema/Owner. |
Infer Relationships
Features and Tools > Tools > Infer Relationships
This feature tries to map Primary Keys or Alternate Keys to identically named attributes in other entities.
Conditions:
- Mapping is performed between key and non-key attributes. In other words, if identically named attributes are part of primary key in various tables, e.g. ID column in table Customer and ID column in table Order, the two ID columns will not be mapped and no relationship will be created.
- Names must be identical and data type must be the same, including parameters.
- Non-identifying relationships are created by default. In case you need an identifying relationship, edit the automatically added relationship and change its type to identifying manually.
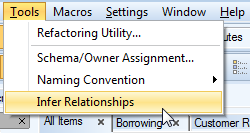
To run the Infer Relationship function
Select Tools | Infer Relationship.
|
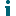
|
Note: Relationships created this way will be marked with a To-Do task prompting you to check whether the relationship has been created correctly.
|
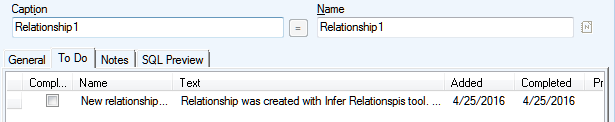
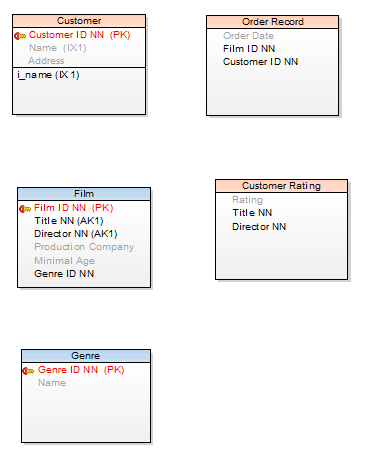
Example:
Model with no relationships. See the Customer ID column in tables Customer and Order Record.
In table Film there is an alternate key with two columns Title and Director. Identically named columns are in table Customer Rating.
Run the Infer Relationship function and see the result:
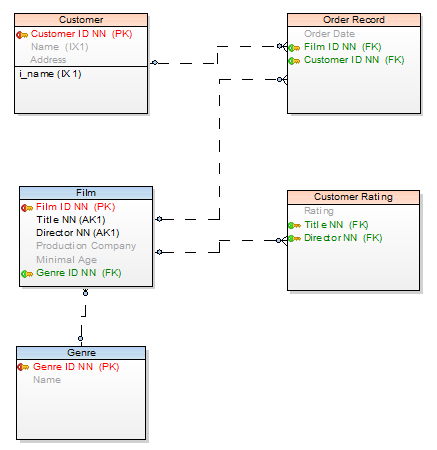
Infer Relationships and Reverse Engineering
The same tool can be used automatically during reverse engineering.
Create a new connection or edit an existing stored connection and check the Infer Relationships checkbox to activate this feature.