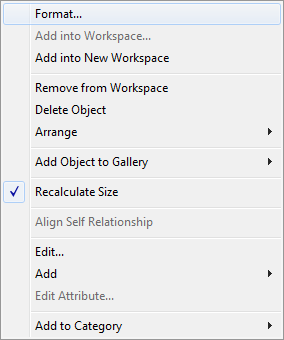
- Right-click the Workspace in your logical model and select Workspace Format.
- Click the Entity tab.
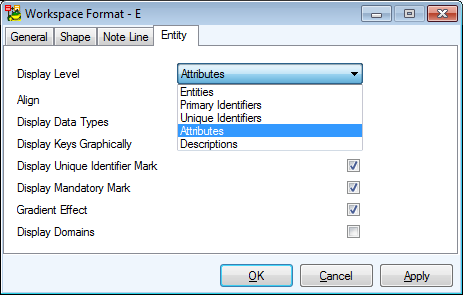
Display Level - Select items you need to display in your logical model - Entities, Primary Identifiers, Unique Identifiers, Attributes, Descriptions.
See the Display Level box on the toolbar (also View menu | Display Level).
To define colors for attributes on your Workspace
Select Settings | Options | Model section | Logical Model | Entity tab | Attribute Colors area.
Toad Data Modeler allows you to design and maintain a logical model giving a complete picture of the business area. Logical model is independent of the database platform and is much simpler than physical model. It uses objects such as inheritance, valid values or M:N relationships. From the Logical ER (LER) diagram, you can build a Physical ER (PER) diagram of the selected database platform (LER to PER conversion).
|
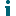
|
Note:
- This topic contains information on objects and functions that are specific for logical modeling. General information and other features applicable in Logical model as well as in Physical model are contained and described in other sections of this Help file. See e.g. the "Model Objects" chapter, "Model Explorer" topic etc.
- See the sample logical model Employee that is included in the installation package for Toad Data Modeler. Default location is: C:\Program Files\Quest Software\Toad Data Modeler\Samples.
|
To create a logical model
Select File | New | Model |Logical Data Model tab.
Benefits of Logical Data Model
Logical Data Model allows you to model inheritances in entity relationship diagrams. Universal Data Model and Physical Data Model do not support this feature.
Specifics of Logical Data Model
- There are three methods how inheritance can be resolved when converting to physical model.
- Attributes do not migrate to child entities.
- It is not possible to define database specific items in Logical Model, for example sequences/autoincrements etc.
- You can define Valid Values in logical model (will be converted to physical model).
Benefits of Super and Sub Types
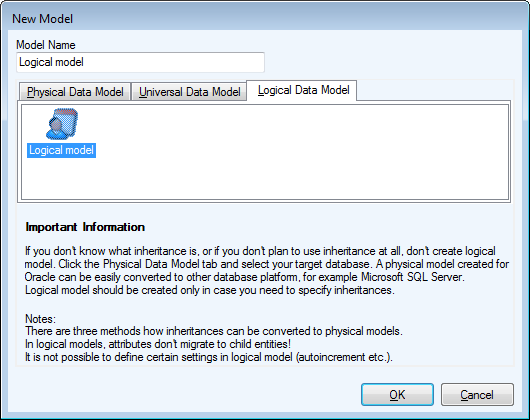
In Logical Model you can define database structure in various ways. See the pictures below. Both of them show a structure modeled in Logical Model and both the models will result in the identical output when converted to Physical Model. The difference is that Model A uses Super and Sub Types while Model B doesn't use inheritance at all.
Model A - Utilizing Super and Sub Types
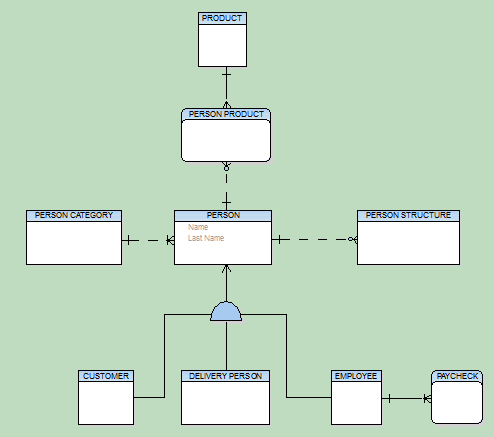
Model B - Lacking Super and Sub Types
This example shows:
- That you can create logical models in different ways and achieve the same result after conversion to physical model.
- That you can be more productive when using inheritance. For example, you only need to change the Last Name attribute once in the first model. Without using inheritance in model B, you have to change it four times.
- How much “readable” the first model is compared to the second one.
- How important is to select appropriate inheritance resolution when converting your logical model to physical.
- That creating logical models without inheritance has minimal benefits compared to using inheritance.
Disadvantage
The main disadvantage of logical modeling is that direct synchronization with existing database is not possible. Only physical models of specific database platforms and versions may be synchronized with an existing database. Therefore, if you want to synchronize your logical model, you need to convert it to the physical model first.