Triggers
Toad Data Modeler allows you to design Entity Relationship Diagrams of specific database platforms, convert physical model from one database platform to another, create an ER Diagram directly from your database (Reverse Engineering feature), update physical models, generate DDL/SQL scripts and Change Scripts, create Dictionary Types, Views, Triggers, Functions, generate detailed documentation to your model (in HTML, RTF, PDF, XSLT formats) and much more.
This chapter describes features and functions related to Physical Data Modeling. Look around each section to get the information you need.
|
|
Note: See the sample physical model Videorental (Oracle 10g db) that is included in the installation package of Toad Data Modeler. Default location is: C:\Program Files (x86)\Quest Software\Toad Data Modeler7.3\Samples. |
Benefits of Physical Data Model
- Detailed definition of database structure, including database specific items, for example:
- Stored procedures
- Functions
- Triggers
- Views
- Materialized views
- Sequences (auto increments) etc.
- Possibility to synchronize local model with existing database.
- Possibility to specify logical names for objects (captions for tables, attributes and other objects).
- Detailed database specific information can be exported to HTML/RTF/PDF or XML/XHTML/CSV reports.
- Automatic generation of SQL code for selected objects (SQL code generation is not available in Logical and Universal Model)
- Automatic migration of PK attributes to child entities (Attributes don't migrate to child entities in Logical Model)
Triggers
To add a trigger
In Entity Properties form, select the Triggers tab and click Add.
To edit a trigger
In Entity Properties form, Triggers tab, double-click the selected trigger or press Edit.
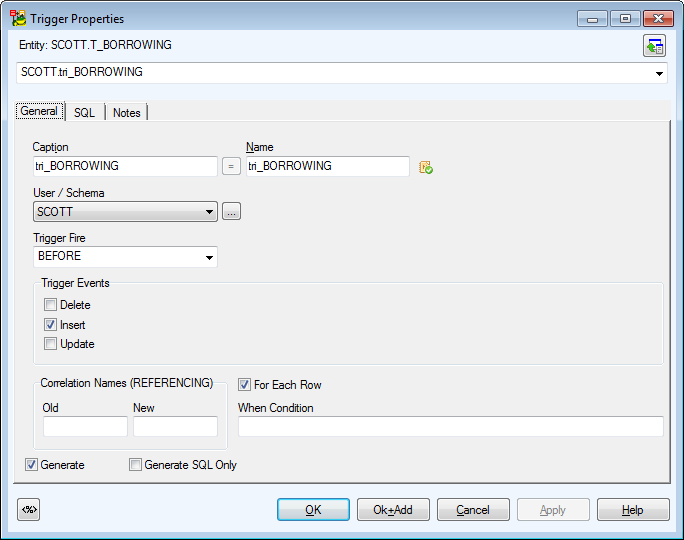
Example: Trigger Properties dialog (Oracle 10g db)
|

|
Above the Object Navigator Box, you can see name of entity the trigger belongs to. If you click the button in top right-hand corner, the parent form will open (Entity Propertiesin this case). |
|
General Tab |
Description |
|
Caption |
Logical trigger name |
| Name |
Physical trigger name |
|
Schema |
Schema selection box |
|
Trigger Fire |
Before, After (database dependent) - select a trigger fire. |
|
Trigger Events |
Delete, Insert, Update - select a trigger event. |
|
Generate |
Select to generate the trigger in final SQL (DDL) script (selected by default.) |
|
Generate SQL Only |
Select to generate the SQL code written in tab SQL only. |
|
SQL Tab |
Write SQL script for the trigger here.
About Templates |
|
Notes Tab |
Space for your notes on the trigger. |
Example: Trigger Properties dialog | SQL tab (Oracle 10g db)

|
|
Note:
- To copy a trigger, press CTRL and drag the trigger over the Triggers folder of a target entity in Model Explorer.
- To move a trigger, drag it over the Triggers tab (folder) of a target entity in Model Explorer.
- To delete a trigger, select it and click Delete on the Triggers tab in the Entity Properties form.
|
Permissions
Toad Data Modeler allows you to design Entity Relationship Diagrams of specific database platforms, convert physical model from one database platform to another, create an ER Diagram directly from your database (Reverse Engineering feature), update physical models, generate DDL/SQL scripts and Change Scripts, create Dictionary Types, Views, Triggers, Functions, generate detailed documentation to your model (in HTML, RTF, PDF, XSLT formats) and much more.
This chapter describes features and functions related to Physical Data Modeling. Look around each section to get the information you need.
|
|
Note: See the sample physical model Videorental (Oracle 10g db) that is included in the installation package of Toad Data Modeler. Default location is: C:\Program Files (x86)\Quest Software\Toad Data Modeler7.3\Samples. |
Benefits of Physical Data Model
- Detailed definition of database structure, including database specific items, for example:
- Stored procedures
- Functions
- Triggers
- Views
- Materialized views
- Sequences (auto increments) etc.
- Possibility to synchronize local model with existing database.
- Possibility to specify logical names for objects (captions for tables, attributes and other objects).
- Detailed database specific information can be exported to HTML/RTF/PDF or XML/XHTML/CSV reports.
- Automatic generation of SQL code for selected objects (SQL code generation is not available in Logical and Universal Model)
- Automatic migration of PK attributes to child entities (Attributes don't migrate to child entities in Logical Model)
Permissions
In Toad Data Modeler, you can assign permissions to the following objects:
- Entity
- Attribute
- User Data Type
- View
- Procedure
- Schema
- Users and User Groups.
This list is dependent on your current database platform and version. For example, some databases do not support assigning permissions to Users.
For every object, different permissions can be set (SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE etc.), depending on current database platform.
Options for permissions are described in the following example. Permissions for attributes, user data types etc. are set in the Properties dialog of particular object | Permissions tab (e.g. Attribute Properties | Properties).
Add Permissions
To be able to add a Permission, it's necessary to define a User or User Group. In case you forget, Toad Data Modeler allows you to define them directly from any Permissions tab of a particular object - click Users or User Groups.
To add a permission for entity
In the Entity Properties form, select the Permissions tab and click Add.
Example: Creating permission for user SCOTT in Entity Properties form:

If you want to change the permission User or User Group, select the permission User (User Group) column, press F2 and choose from the list.
|
|
TIP: This kind of editing properties is usable anywhere in Toad Data Modeler. For more information, see Inplace Editor. |
|
Permissions Tab |
Description |
|
User (User Group) |
Name of user (group) that the permission has been assigned to. |
|
Grantor |
Name of user (group) that assigns the permission. |
|
Permissions: SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, RULE, REFERENCES, TRIGGER |
To edit a permission
In the Entity Properties form | Permissions tab, double-click the selected permission or press Edit .
|
General Tab |
Description |
|
Permissions |
List of all available permissions to a specific object. |
|
Status |
Shows if the particular permission has been assigned or not.
Unchanged - No change has been made.
Grant - Permission has been granted.
Deny - Permission has been denied. (E.g. in Microsoft SQL 2005 models.) |
|
with Grant Option |
Yes/No - Determines if the permission User (Group) can assign the permission to another User (Group). |