|
|
NOTE: Microsoft 365 Advanced Threat Protection default settings may cause issues with Domain Rewrite for inbound messages. Please ensure that Automatic forwarding is set to On in the Outbound spam filter policy for your source or target tenant depending on the rewriting scenario you choose. |
Rewrite with Express Setup Outbound Messages
- When a user sends an email as user@source.com, the Transport Rules in the Source Tenant check whether the message is in scope for Domain Rewrite
- At least one external recipient in To or Cc
- Sender and/or at least one recipient in To or Cc is Domain Rewrite Enabled
- If the message is in scope for Domain Rewrite and there are multiple internal and external recipients, the message will be bifurcated and:
- Copy of the message sent to external recipient will be securely redirected to the Quest Rewrite Service using the Outbound Connector in the Sender Tenant.
- Copy of the message sent to internal recipient is delivered by Exchange Online at the Source tenant with unchanged addresses.
IMPORTANT: Messages directed to internal recipient(s) will not be processed by Quest Rewrite Service.
- When the Domain Rewrite Service receives the message from user@source.com, it processes it by rewriting @source.com to @target.com for every user that has Domain Rewrite enabled. The addresses in
- From, To, and Cc of the email message are rewritten for all external recipients.
- The Domain Rewrite Service securely (via the certificate uploaded during project setup) redirects it to the Rewrite Address Domain Tenant using the Inbound Connector configured in the tenant.
- Exchange Online at the Rewrite Address Domain Tenant sends the message to external recipients as if it was sent by user@target.com, and all addresses of message recipients in To and Cc that have Domain Rewrite enabled appear as @target.com for external recipients.
Rewrite with Express Setup Inbound Messages
- External recipient is not aware about end user’s @source.com address and replies (or create a new email), instead the @target.com address will be used.
- When the reply or a new mail arrives at the @target.com mail domain, the Transport Rules in the Target Tenant check whether any recipients are in scope for Domain Rewrite
- If the message is in scope for Domain Rewrite, it is securely redirected to the Quest Rewrite Service using the Outbound Connector in the Target Tenant
- If the message is in scope for Domain Rewrite and there are multiple internal (recipients in the source tenant) and external recipients (recipients in the @source.com tenant with Rewrite Service enabled), the message will be bifurcated and:
NOTE: Messages directed to internal recipient(s) will not be processed by Quest Rewrite Service.
- Copy of the message sent to external recipient (recipients in the @source.com tenant with Rewrite Service enabled) will be securely redirected to the Quest Rewrite Service using the Outbound Connector in the Source Tenant.
- Copy of the message sent to internal recipient is delivered by Exchange Online at the source tenant with unchanged addresses.
- When the Quest Rewrite Service receives the message addressed to user@target.com, it processes it by rewriting @target.com back to @source.com for every user that has Domain Rewrite enabled
- The Quest Rewrite Service signs the message and securely (via the certificate uploaded during project setup) sends to the Source Tenant using the Inbound Connector
- Source recipient gets the message as if it was addressed to user@source.com

Rewrite with Advance Setup Outbound Messages
- When a user sends an email as user@source.com, the Transport Rules in the Source Tenant check whether the message is in scope for Domain Rewrite
- At least one external recipient in To or Cc
- Sender and/or at least one recipient in To or Cc is Domain Rewrite Enabled
- If the message is in scope for Domain Rewrite and there are multiple internal and external recipients, the message will be bifurcated and:
- Copy of the message sent to external recipient will be securely redirected to the Quest Rewrite Service using the Outbound Connector in the Sender Tenant.
- Copy of the message sent to internal recipient is delivered by Exchange Online to the Source tenant with unchanged addresses.
IMPORTANT: Messages directed to internal recipient(s) will not be processed by Quest Rewrite Service.
- When the Domain Rewrite Service receives the message from user@source.com, it processes it by rewriting @source.com to @target.com for every user that has Domain Rewrite enabled. The addresses in
- From, To and Cc of the email message are rewritten for all external recipients.
- The Domain Rewrite Service a new DKIM-Signature (align with the Rewrite Address domain DKIM) to the message and securely (via the certificate uploaded during project setup) redirects it back to the Original Sender Tenant using the Inbound Connector configured in the tenant.
- Exchange Online at the Original Sender Tenant sends the message to external recipients as if it was sent by user@target.com, and all addresses of message recipients in To and Cc that have Domain Rewrite enabled, appear as @target.com for external recipients.

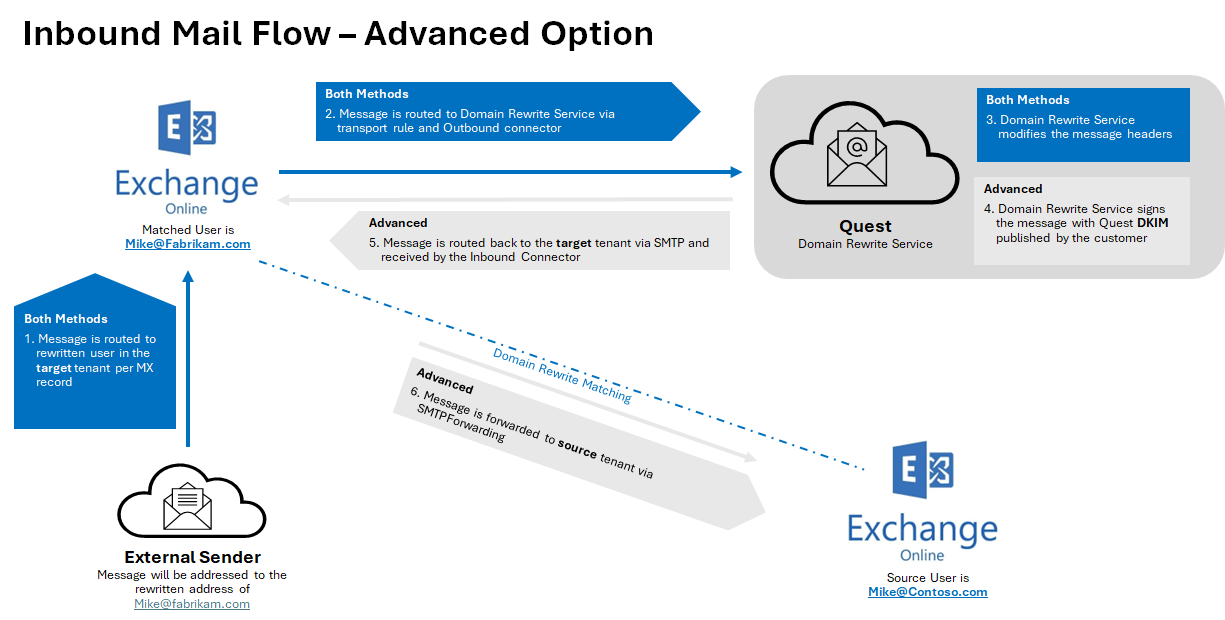
Rewrite with Advance Setup Inbound Messages
- External recipient is not aware about end user’s @source.com address and replies (or create a new email), instead the @target.com address will be used.
- When the reply or a new mail arrives at the @target.com mail domain, the Transport Rules in the Target Tenant check whether any recipients are in scope for Domain Rewrite
- If the message is in scope for Domain Rewrite, it is securely redirected to the Quest Rewrite Service using the Outbound Connector in the Target Tenant
- If the message is in scope for Domain Rewrite and there are multiple internal (recipients in the source tenant) and external recipients (recipients in the @source.com tenant with Rewrite Service enabled), the message will be bifurcated and:
NOTE: Messages directed to internal recipient(s) will not be processed by Quest Rewrite Service.
- Copy of the message sent to external recipient (recipients in the @source.com tenant with Rewrite Service enabled) will be securely redirected to the Quest Rewrite Service using the Outbound Connector in the Source Tenant.
- Copy of the message sent to internal recipient is delivered by Exchange Online at the source tenant with unchanged addresses.
- When the Quest Rewrite Service receives the message addressed to user@target.com, it processes it by rewriting @target.com back to @source.com for every user that has Domain Rewrite enabled
- The Quest Rewrite Service signs the message and securely (via the certificate uploaded during project setup) sends to the Target Tenant using the Inbound Connector
- Exchange Online forwards the rewritten message to @source.com tenant.
- Source recipient gets the message as if it was addressed to user@source.com