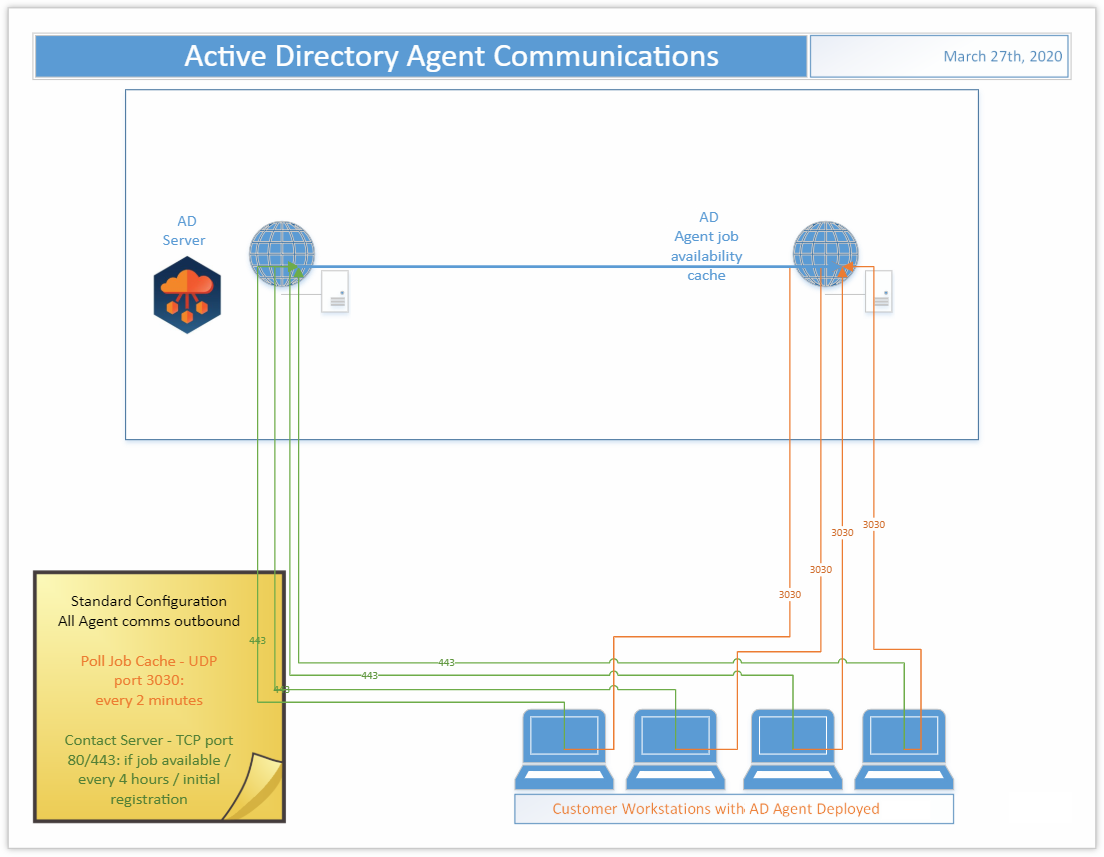
What ports does the agent use to connect?
The Active Directory Agent uses three outbound ports
- TCP 443/80
- UDP 3030
I’ve installed the agent and the device isn’t ready, what do I do?
On startup the Active Directory agent will phone home sometime in the first four hours. This communication offset time is an agent specific random and evenly distributed offset so the initial communications of a large number of devices set up at once will be spaced out and not overload the servers. If your device has the agent installed but you haven’t waited up to four hours yet, wait up to four hours and then re-check the Ready Devices list to see if your device shows up before proceeding to other network troubleshooting operations.
How do I adjust the agent polling interval?
In Active Directory, unlike in Active Directory Pro, the agent polling interval is not end user adjustable. The polling interval is every two minutes over UDP and every four hours over TCP. Should this amount of network traffic be an issue contact Support to investigate reducing the polling interval. Note that reducing the polling interval will cause queued migration actions to take longer to be picked up by the agents.
How many migration actions can I queue at once?
In Active Directory you can queue as many migration actions at once as you would like. There is a hard limit of 600 agents per each two minutes who will be notified by the job availability cache that they have a job waiting for them. Therefore the minimum amount of time which could be required for those queued migration actions to be picked up will be the number of queued migration actions divided by 600 and multiplied by two minutes.
Agent last contact time isn’t updating every two minutes is something wrong?
In Active Directory the Agent last contact time is updated based on the TCP connection with the back end. This will occur if a job is retrieved or every 4 hours as a fall back. It is not expected that the agent last contact time will update every two minutes even if the UDP requests to the job availability cache are functioning correctly.
The machine name was changed during the migration project, will it keep working?
Changing the machine name during a migration project may have unexpected implications. We recommend that you avoid doing so if possible. If not, you will need to delete the device from On Demand Migration Active Directory and reinstall the agent. Use the Status Resets action to reset the registration status of the device, then set the Directory Sync Workflow to reconcile on next run and run it. This will delete the old device from the database. Finally, reinstall the Active Directory Agent on that device and run the Workflow again to read it in.
How do I remove Devices from Active Directory?
To delete registered Devices from Active Directory, first use the Status Resets action to clear their registration status, then run the related Directory Sync Workflow with the setting ‘Reconcile on next run’ enabled. Any unregistered device records in scope of the Workflow will be removed from the database during a reconcile.
Can I migrate to and from GCC/GCCH tenants?
Active Directory supports GCC and GCCH as target environments, in addition to Commercial tenants. Only Commercial and GCC are supported as source environments. To enable GCC/GCCH Device Migration, please contact Quest Support for additional configuration described in the following article: Update GCC/GCCH tenant object's RID value for ReACL. This configuration is required for successfully switching the user profile during cutover.