Quest SQL Optimizer for IBM® DB2® LUW maximizes SQL performance by automating the manual, time-intensive and uncertain process of ensuring that SQL statements are performing as fast as possible. SQL Optimizer analyzes, rewrites, and evaluates SQL statements within multiple database objects, files, or SQL statements captured by the DB2 Event Monitor. With SQL Optimizer, you can analyze and optimize all your problem SQL from multiple sources. SQL Optimizer also provides you a complete index optimization and plan change analysis solution, from index recommendations to simulated index impact analysis, through comparison of multiple SQL access plans.
SQL Optimizer provides you with the following main modules.
SQL Optimizer (including SQL Rewrite and Generate Indexes functions)
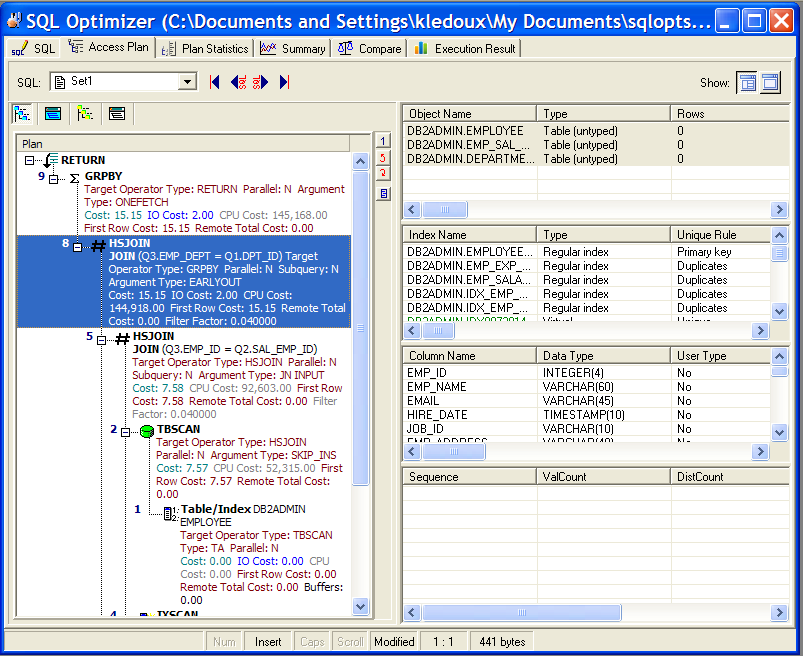
The Access Plan tab in the SQL Optimizer window uses the following panes to display access plan details for the currently selected alternative and information about the objects that the alternative syntax accesses:
Column Values Distribution Statistics
You can rerun the Generate Indexes function to obtain the latest index recommendations.
Note: This process will clear all existing SQL and index-set alternative in this SQL Optimizer session.
To regenerate virtual index sets
Right-click within any of the statistics panes, and select Recommend Virtual Indexes.
You can add your own index sets to this SQL Optimizer session.
To create your own virtual index sets
Right-click within any of the statistics panes, and select Create Virtual Indexes.
Use the pane-control buttons to reorganize the panes.
To display the Access Plan, and the Table, Index, Column, and Column Value Distribution panes
Click .
To display only the Access Plan pane
Click .

The access plan is a combination of steps the DB2 LUW database optimizer chooses to execute a SQL statement. Each node represents how the database optimizer will physically retrieve rows of data from the database or how the data is prepared. By examining the access plan, you can see exactly how the database executes your SQL statement.
The Access Plan pane contains a right-click menu that allows you to perform the following functions:
|
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Sends the access plan in its current view to the printer, to display on the screen (print preview), or to a file. |
|
Copy |
Copies the access plan to the clipboard. |
|
View Plan |
Changes how the access plan is displayed. |
|
Animated Plan Steps |
Highlights one-by-one the access plan steps. |
|
Plan Options |
Opens the Access Plan Options window so you can select the specific detailed information that is displayed in the access plan. You can also choose to display specific information in individual columns. |
|
Get Help on plan_step |
Displays the help text for the currently selected step in the access plan. |
|
Help on Access Plan |
Opens online help for the access plan. |
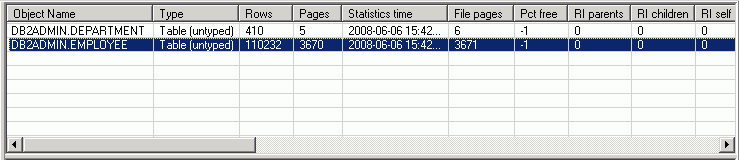
The Object Statistics pane is displayed on the Access Plan tab in the SQL Optimizer window. It lists information for each table, view, or alias referenced in the access plan. If the operation in the selected access plan step accesses a specific object, this object is automatically highlighted in the Table Statistics pane. You can do the following in this pane:
Select an object in this pane to view statistics about its indexes and columns (in the Index and Column Statistics panes, respectively).
Right-click a specific object to update its catalog statistics.
The method in which rows are inserted on pages in the table or view:
|
Value |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Rows appended |
New rows are inserted at the end of the data. |
|
Rows inserted |
New rows are inserted into existing spaces if available. |
The number of check constraints defined on the table or view.
This information is based on the CHECKCOUNT value for the table or view in SYSCAT.TABLES.
The number of columns in the table or view.
This information is based on the COLCOUNT value for the table or view in SYSCAT.TABLES.
Total number of pages allocated for this table.
This information is based on the FPAGES value for the table or view in SYSCAT.TABLES.
The name of the tablespace that holds all the indexes created for the table or view.
This information is based on the INDEX_TBSPACE value for the table or view in SYSCAT.TABLES.
The number of columns that make up the primary key for the table or view.
This information is based on the KEYCOLUMNS value for the table or view in SYSCAT.TABLES.
The number of unique constraints (other than a primary key constraint) defined for the table or view.
This information is based on the KEYUNIQUE value for the table or view in SYSCAT.TABLES.
The name of the tablespace that holds all long data (for LONG or LOB column types) for the table or view.
This information is based on the LONG_TBSPACE value for the table or view in SYSCAT.TABLES.
The preferred lock granularity when DML statements are executed on the table:
|
Value |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Row |
Row-level lock |
|
Lock |
Table-level lock |
|
blank |
Not applicable |
The qualified name of the table or view.
This information is based on the TABSCHEMA and TABNAME values for the table or view in SYSCAT.TABLES.
Total number of overflow records in the table or view. An overflow record is an updated record that is too large to fit on the page in which it is currently stored. The record is copied to another page, and its original location is replaced with a pointer to the new page.
This information is based on the OVERFLOW value for the table or view in SYSCAT.TABLES.
Total number of pages that contain data for the table or view.
This information is based on the NPAGES value for the table or view in SYSCAT.TABLES.
Percentage of each page in the table or view to be reserved for future inserts.
This information is based on the PCTFREE value for the table or view in SYSCAT.TABLES.
The mode used to distribute data in the table or view within a partitioned database:
|
Value |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Hash on partition key |
Hash on the partitioning key |
|
Replicate across partitions |
Replicate table or view data across partitions |
|
blank |
No partitioning. The table, view, or alias exists in a single partition nodegroup with no partitioning key defined. A blank also appears for nicknames. |
The number of referential constraints in which the table or view is a parent (that is, the number of dependent tables of this table).
This information is based on the CHILDREN value for the table or view in SYSCAT.TABLES.
The number of referential constraints in which the table or view is a dependent (that is, the number of parent tables of this table).
This information is based on the PARENTS value for the table or view in SYSCAT.TABLES.
The number of referential constraints in which the table or view is both a parent and a dependent.
This information is based on the SELFREFS value for the table or view in SYSCAT.TABLES.
Total number of data rows in the table or view.
This information is based on the CARD value for the table or view in SYSCAT.TABLES.
The timestamp for the last time a change was made to statistics for the table or view.
This information is based on the STATS_TIME value for the table or view in SYSCAT.TABLES.
Status type for the object from which information is retrieved:
|
Value |
Description |
|
Normal |
Normal status for the table, view, alias, or nickname. |
|
Check |
CHECK PENDING status on the table or nickname. Constraint checking is turned off, and SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE operations are not allowed on the table. |
|
X |
Inoperative view or nickname. This status can occur when the underlying tables of the view or nickname have been dropped. |
The name of the primary tablespace for the table or view.
This information is based on the TBSPACE value for the table or view in SYSCAT.TABLES.
The type of table or view from which information is retrieved:
|
Value |
Description |
|
Table |
Normal table |
|
Hierarchy |
The hierarchy table associated with the implementation of a typed table hierarchy |
|
Summary |
Summary table |
|
View |
Normal view |
|
Alias |
An indirect reference to a table |
|
Nickname |
A reference to a table (data source) in a federated database |
|
Typed table |
Table created from a structured type |
|
Type view |
A view created from a structured type |
The indicator showing whether the table or view has been declared volatile. A volatile table is a table whose contents vary greatly--from empty to large--at any point in time. To generate the access plan for a volatile table, DB2's SQL optimizer tends not to rely on existing table statistics and, therefore, often uses an index scan instead of a table scan. Values for this detail include:
|
Value |
Description |
|
Cardinality of table is volatile |
Table is volatile |
|
blank |
Table is not volatile |