The first step towards success on a project using Migration for Active Directory Express is to understand the product architecture and how this architecture will operate in your environment.
Migration for Active Directory Express consists of the following components:
A directory synchronization engine
A REST based web service
A management interface
A lightweight agent for workstations and member servers
The directory synchronization engine, the web service, and the management interface will all access the same SQL database. In most scenarios, these components will be installed on the same system. In larger or more complex network environments, the components can be distributed across multiple systems.
User workstations, member servers and computers are collectively referred to as Devices in Migration for Active Directory Express. Computers communicate with the Migration for Active Directory Express web service using the Active Directory Agent. The Active Directory Agent is a lightweight application that installs as a service on Windows computers.
To ensure that no firewall exceptions are required, the web service does not “call” the Devices to be migrated. Instead, the Active Directory Agents contact the web service at defined polling intervals, using standard HTTPS or HTTP requests to collect jobs. Jobs include key tasks such as system discovery, updating the operating system, file system, and user profile permissions, and migrating the computer to the new domain.
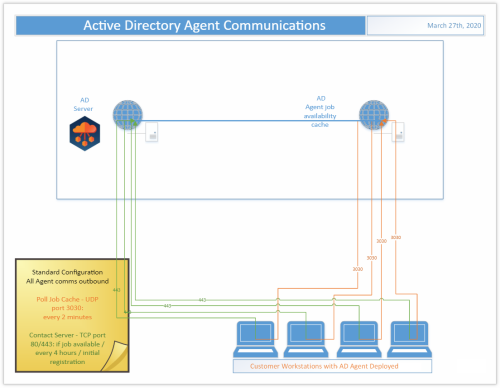
Standard Configuration
In the Standard Configuration for Migration for Active Directory Express, the Agent is deployed to each Device to be migrated. Those Agents communicate outbound to the Active Directory webserver in Azure over ports 80/443 every 4 hours, when a job is available, or when initially registering. They also communicate outbound to the Active Directory Agent job availability cache in Azure over UDP on port 3030 every 2 minutes.
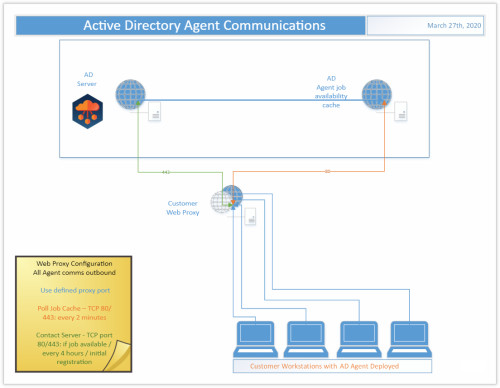
Web Proxy Configuration
In the Web Proxy Configuration for Migration for Active Directory Express, the Agent is deployed to each Device to be migrated and use of a web proxy is enabled. Those Agents communicate outbound through the defined proxy port to the Active Directory webserver in Azure over port 443 every 4 hours, when a job is available, or when initially registering. They also communicate outbound through the defined proxy port to the Active Directory Agent job availability cache in Azure on port 80 every 2 minutes.