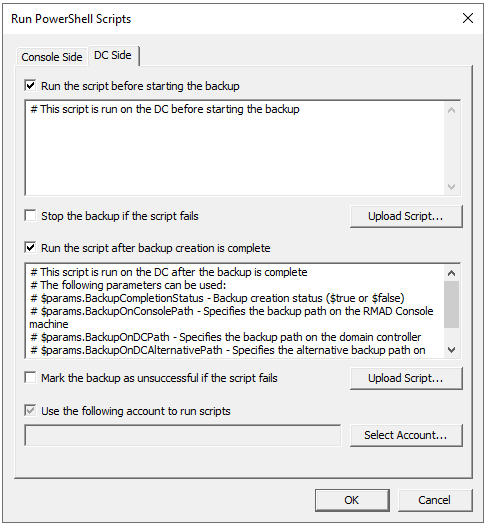
Run Scripts
In the Run PowerShell® Scripts dialog, the following options can be specified:
Run the script before starting the backup - Launches specified PowerShell® scripts before the backup creation process is started.
Stop the backup if the script fails - Stops the backup process if the script cannot be run without errors.
Run the script after backup creation is complete - Launches specified PowerShell® scripts after backup is created.
Mark the backup as unsuccessful if the script fails - If the script fails, the backup process will be shown as failed with error in the RMAD console.
Upload Script - Using this option you can upload an existing PowerShell® script file (.ps1). After the script is uploaded, the contents of the script will be displayed in the dialog and you can edit it if necessary.
Use the following account to run scripts and Select Account - Here you can select an account under which the scripts will be running. For the "Console scripts", by default, the account under which the console is launched will be used. For the "DC scripts", there is no default value, and the user has to select an account. Otherwise, the settings will not be saved.
| NOTE |
If the script is run on a domain controller, we strongly recommend using an account with the minimum rights required only to perform the actions specified in the script. |
Recovery Manager for Active Directory provides an option to set the maximum timeout during which a script can run (the default value is 60 seconds). To change this value, set the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\WOW6432Node\Quest\Recovery Manager for Active Directory\Options\ScriptExecTimeoutInSeconds (DWORD) registry key to <required value>.
Failed script can lead to both Warning and Error results. It depends on the specified settings:
| Option Name | Scenario 1 | Scenario 2 | Scenario 3 | Scenario 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Run the script before starting the backup | ✔ | ✔ | ||
| Stop the backup if the script fails | ✖ | ✔ | ||
| Run the script after backup creation is complete | ✔ | ✔ | ||
| Mark the backup as unsuccessful if the script fails | ✖ | ✔ | ||
| Result | Warning | Error | Warning | Error |
Running scripts can be dangerous - especially on a domain controller. Recovery Manager includes the following security measures for scripts:
Scripts are stored in the Recovery Manager database in an encrypted form.
Scripts are sent from the Recovery Manager console to the Backup Agent using a secure RPC channel.
Scripts are run in memory and no temporary files are created on the disk. When running scripts, the -EncodedCommand parameter of PowerShell.exe is used.
For scripts run on the domain controller, specifying a custom account under which the script will run is required. Using an account with minimum rights is recommended.
All scripts have a timeout when running. If the timeout is exceeded, the script will be forcibly stopped.
The result of the script running is recorded in the Windows Event Log.
Diagnostic logging Specify the logging setting for the Recovery Manager and Backup Agents for all domain controllers in the collection.
The following options are available:
Global settings - Use the default logging settings from the Recovery Manager Console root node: Recovery Manager for Active Directory->Settings…>Logging.
Enable - If you select this option, extended logging will be enabled for all domain controllers within the collection during the backup operation.
Disable - If you select this option, the log will contain only Warnings and Error messages.
The log files will be created in the %ProgramData%\Quest\Recovery Manager for Active Directory\Logs folder:
Agent side (domain controller): ErdAgent.log
Recovery Console: ErdServer.log
Creating a new set of log files Specify the creation of new logs for Recovery Manager and Backup Agents for all controllers in the collection.
Edit HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Quest\Recovery Manager for Active Directory\Diagnostics
Modify or create REG_SZ registry value called LogRotationInterval
The following options are available:
Never - Never create new logs
Daily - Create new logs daily.
Weekly - Create new logs weekly.
Monthly - Create new logs monthly.
| NOTE |
The options on this tab are not supported for BMR backups. |
This tab allows you to override the global (or default) settings used to automatically unpack backups for all Computer Collections.
On this tab, you can use the following elements:
Use global settings. Specifies to use the global settings to automatically unpack each backup upon its creation.
Unpack each backup upon its creation. Allows you to configure settings specific to the Computer Collection to automatically unpack each backup upon its creation. In this option, you can specify the number of recent backup creation sessions from which you want to keep unpacked backups for each domain in the Computer Collection or select the domain controllers you need. Other backups created for the Computer Collection will be automatically deleted.
Do not unpack backups. Specifies not to unpack backups created for the Computer Collection.
For more information on managing unpacked backups, see Unpacking backups.
For a container such as an Active Directory domain, organizational unit, or site added to a Computer Collection, the properties are used to specify an explicit list of the domain controllers or AD LDS (ADAM) instances for which backups are not to be created.
In the Recovery Manager Console tree, select the Computer Collection that holds the container or site.
In the details pane, click the container or site, and then click Properties on the Action menu.
The next subsections provide descriptions for the following: