Reviewing frequently asked questions
You can find the available questions on the FAQts tab of the Infrastructure Environment dashboard.
On this tab, the Categories pane contains several question groups. Selecting a category shows the questions belonging to that category in the Questions pane. From there, clicking a question shows the answer on the right.
Monitoring a partition or VIOS with Foglight for Infrastructure
If you want to monitor a VIOS or a partition with Foglight for Infrastructure, you can quickly create a Host agent. Foglight for PowerVM allows you to monitor the health of the system infrastructure associated with a monitored VIOS or a partition. For complete information about host agents, see Using Foglight for Infrastructure agents.
|
1 |
|
a |
|
b |
|
c |
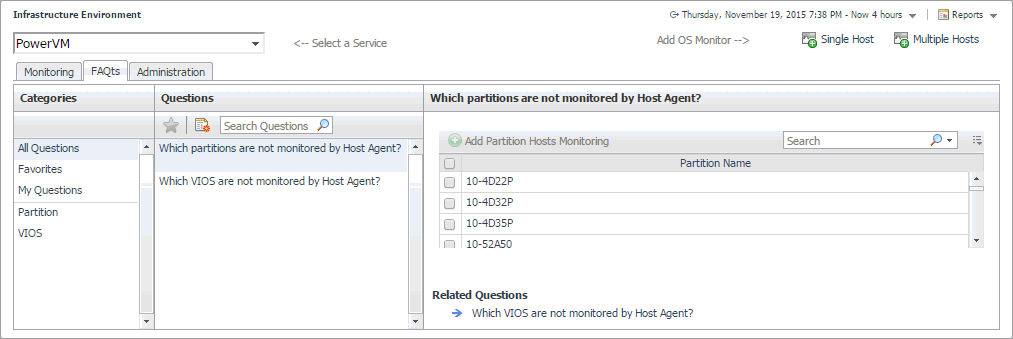
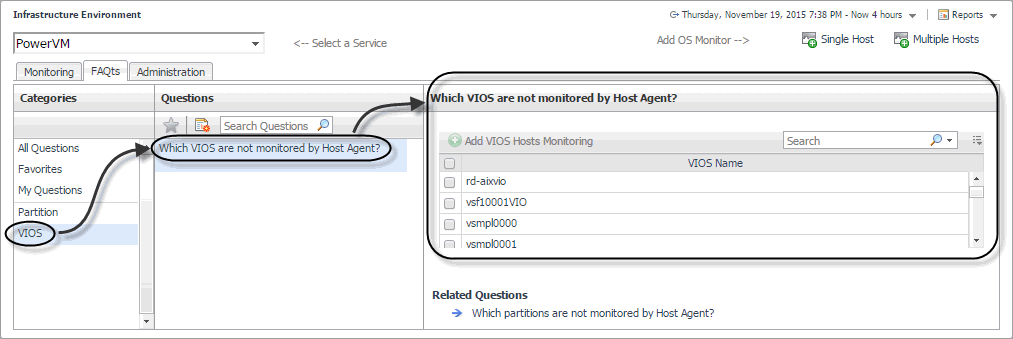
In the Which VIOS are not monitored by Host Agent pane, select a VIOS, and click Add VIOS Hosts Monitoring. |
|
a |
|
b |
|
c |
In the Which partitions are not monitored by Host Agent pane, select a partition, and click Add Partition Hosts Monitoring. |
|
3 |
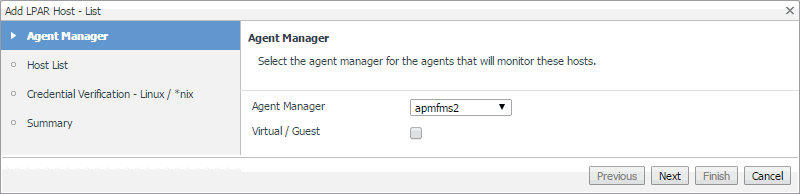
In the Add LPAR Host - List wizard, on the Agent Manager page, select the Agent Manager that you want to associate with the Host agent you are about to create. |
|
a |
Click Agent Manager and select the Agent Manager host that you want to use to associate with the Host agent. The list includes only the Foglight Agent Managers to which the Foglight for Infrastructure agent package is already deployed. |
|
b |
Ensure that the Virtual / Guest check box is cleared. |
|
c |
Click Next. |
|
4 |
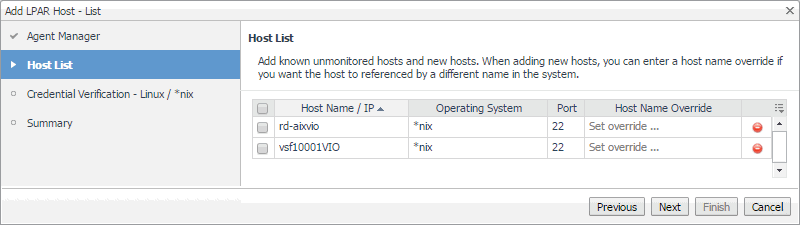
In the Add LPAR Host - List wizard, on the Host List page, review the list of VIOS or partition instances that you selected for monitoring. |
|
a |
By default, the VIOS or partition name is used as a host name. If you want to display one or more of these components under a different name in the browser interface and reports, click the Host Name Override column, and type a new name when prompted. |
|
b |
Click Next. |
|
5 |
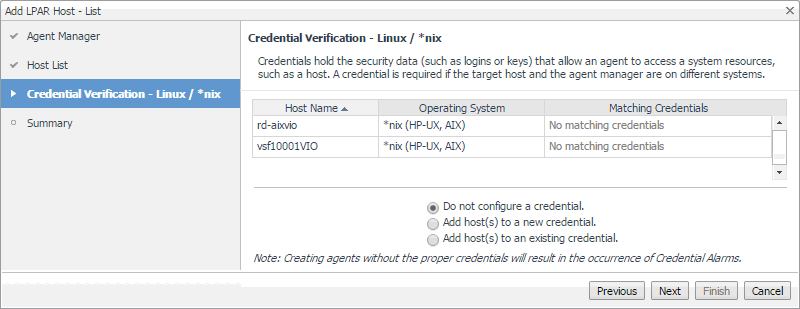
On the Credentials Verification page, select one of the following options: |
|
• |
Do not configure a credential: Select this option if you want to configure the credential for this component at a later time. Click Next and continue to Step 8. |
|
• |
Add host(s) to a new credential: Select this option if you want to create a new credential for this component. This option is suitable if none of the existing credentials have the connection details needed to access the new host. Click Next and continue to Step 6. |
|
• |
Add host(s) to an existing credential: Select this option if you want the Host agent to use an existing credential to access this component. This option is suitable if an existing credential has the security data needed to access this component (such as user name and password), but you need to edit its resource mappings to include this component. Click Next and continue to Step 7. |
|
• |
For complete information about Foglight credentials, see the Administration and Configuration Help. |
|
a |
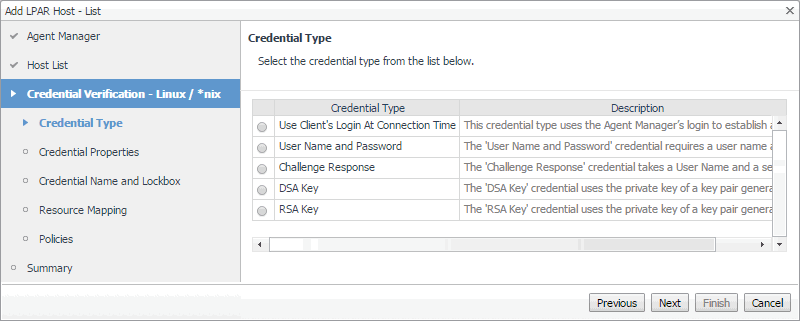
On the Credential Type page that appears, select the desired credential type. |
|
b |
|
c |
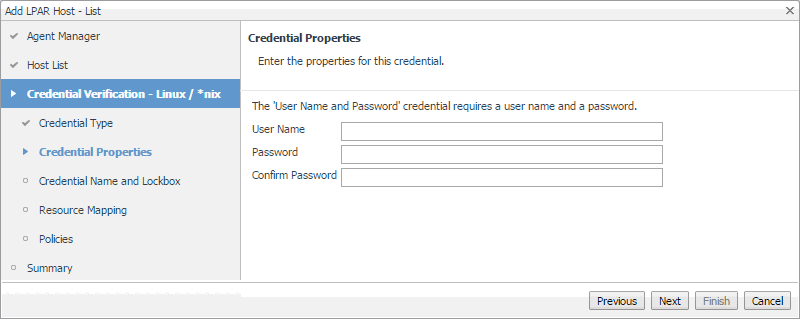
On the Credential Properties page, provide the required information. The level of required data depends on the selected credential type. For example, a User Name and Password credential needs a user name and a password, while a Challenge Response credential requires a user name along with a question/response pair. |
|
d |
|
e |
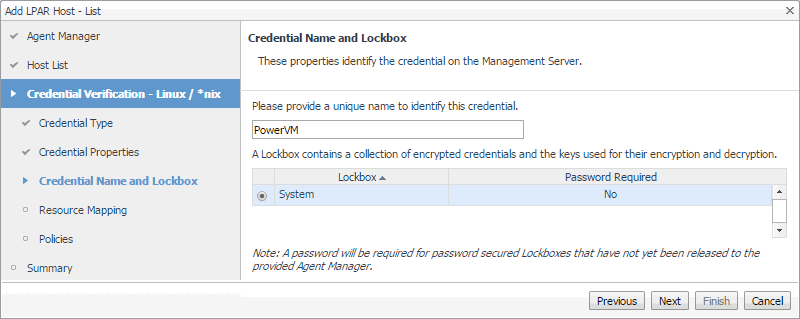
On the Credential Name and Lockbox page, provide a name to identify the credential, and select a lockbox in which you want to keep the credential. A lockbox can be used to group credentials for access and/or security. The default System lockbox is sufficient for smaller installations. |
|
f |
|
g |
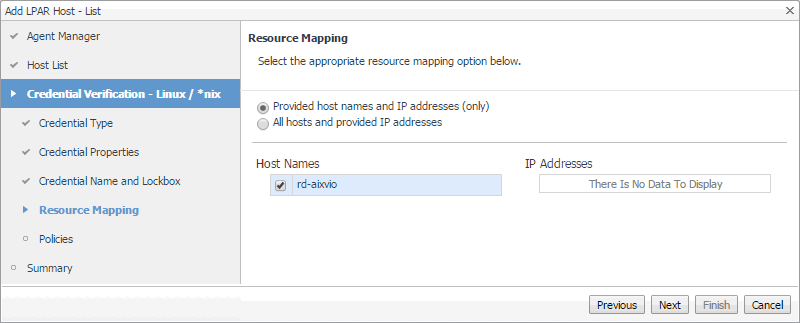
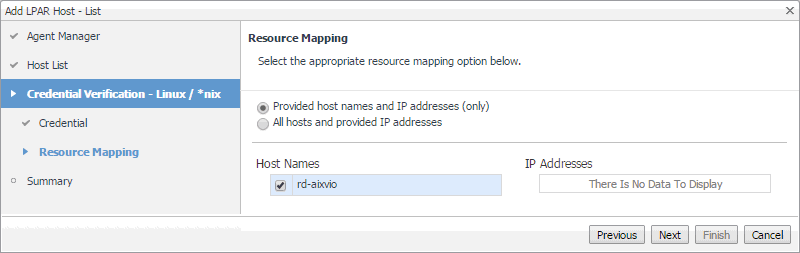
On the Resource Mapping page, ensure that the VIOS or partition components that you want to associate with this credential are selected. |
|
h |
|
i |
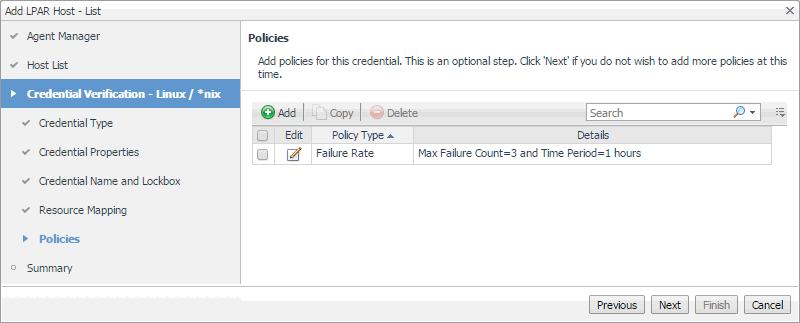
Optional—On the Policies page, define one or more policies for this credential. A policy defines the number of times a credential can be used, the number of allowed authentication failures, the time range during which the credential is valid, or the length of time the credential data can be cached on the client. For example, you can specify the number of times the credential can be used, or the time period during which it can be used. For complete information about the available credential policies, see the Administration and Configuration Help. |
|
a |
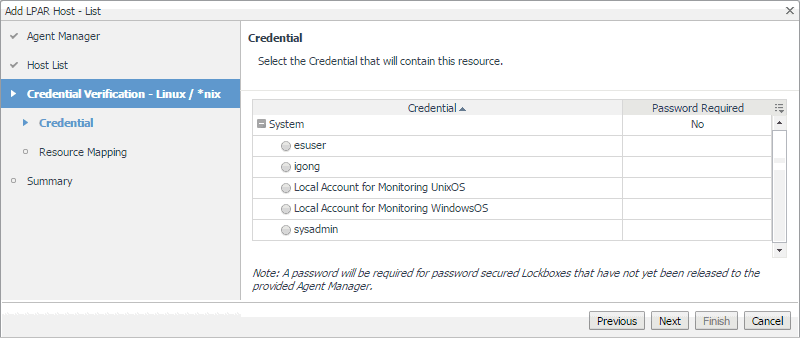
On the Credential page that appears, select an existing credential that you want the Host agent to use to access this component. |
|
b |
|
c |
On the Resource Mapping page, ensure that the VIOS or partition components that you want to associate with this credential are selected. |
|
8 |
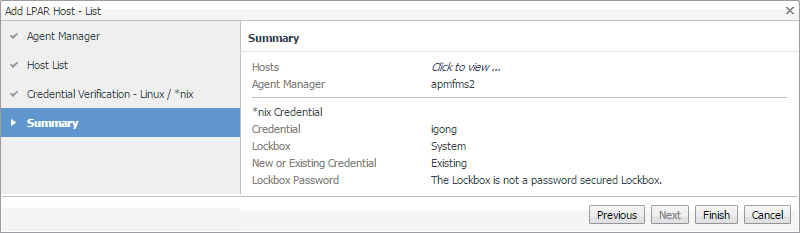
On the Summary page that appears, review the information about the monitored component, selected Agent Manager, and the credential. |
|
9 |
Click Finish. |
Advanced system configuration and troubleshooting
This contains platform-specific configuration information for configuring Foglight® for Infrastructure on Windows® when using Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) or Windows Remote Management (WinRM) for remote monitoring access.
For more details, see the following topic:
Advanced system configuration for WinRM
The advanced configuration for non-administrative users includes the following steps:
To add a non-administrative user to the above user groups:
To grant the WinRM RootSDDL permission to a non-administrative user:
To grant the permission to the namespace for the current non-administrative user:
|
9 |
The following sample demonstrates how to grant permission to the SCMANAGER service:
|
3 |
Add “(A;;CCLCRPRC;;;S-1-5-32-558)” between “D:” and “(A;;CC;;;AU)”, and execute the sc sdset command to grant the permission to the SCMANAGER service. For example, execute the following command: |