Quest SQL Optimizer for IBM® DB2® LUWmaximizes SQL performance by automating the manual, time-intensive and uncertain process of ensuring that SQL statements are performing as fast as possible. SQL Optimizer analyzes, rewrites, and evaluates SQL statements within multiple database objects, files, or SQL statements captured by the DB2 Event Monitor. With SQL Optimizer, you can analyze and optimize all your problem SQL from multiple sources. SQL Optimizer also provides you a complete index optimization and plan change analysis solution, from index recommendations to simulated index impact analysis, through comparison of multiple SQL access plans.
SQL Optimizer provides you with the following main modules.
SQL Optimizer (including SQL Rewrite and Generate Indexes functions)
The Index Usage Analyzer identifies unused indexes by analyzing access plans from SQL statements in your database applications. It examines their access plans and reports any indexes in the database that are not used. You can use this module to quickly identify the indexes in databases that are not contributing to the performance of the database applications. These unused indexes can then be deleted to free up space and improve the speed of the database applications and maintenance.
The Index Usage Analyzer identifies:
Tables that are referenced in the SQL statements
Indexes in each table that are used in the access plans, and the number of referenced SQL for each index
Indexes in each table that are not used in the access plans
The selected SQL statements that the Index Usage Analyzer analyzes are from SQL that you have saved in the SQL Repository or SQL statements from the SQL Scanner.
Quest SQL Optimizer for IBM® DB2® LUWmaximizes SQL performance by automating the manual, time-intensive and uncertain process of ensuring that SQL statements are performing as fast as possible. SQL Optimizer analyzes, rewrites, and evaluates SQL statements within multiple database objects, files, or SQL statements captured by the DB2 Event Monitor. With SQL Optimizer, you can analyze and optimize all your problem SQL from multiple sources. SQL Optimizer also provides you a complete index optimization and plan change analysis solution, from index recommendations to simulated index impact analysis, through comparison of multiple SQL access plans.
SQL Optimizer provides you with the following main modules.
SQL Optimizer (including SQL Rewrite and Generate Indexes functions)
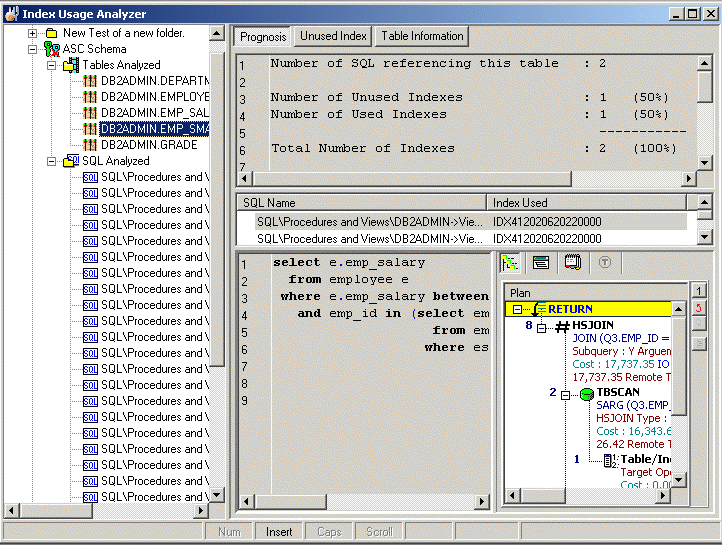
The Index Usage Analyzer window displays the information about the SQL statements that are saved in the Index Usage Analyzer. The display in the right section of the window depends on what is selected in the left pane.
Always displays a tree diagram of the Analyzers and the folders they are stored in.
The right pane displays a variety of different information depending upon what is selected from the tree diagram in the left pane.
You can display information for the following: