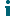The Dashboard page contains graphics that show key information about the current state of the DR Series system. This page automatically refreshes every 30 seconds.
To use the Dashboard page, follow these steps.
- Click Dashboard in the left navigation menu of the DR Series system GUI.
NOTE: When you first log on to the DR Series system GUI, you view the Dashboard page by default.
- You can view the following graphs:
- Capacity—displays total used space, free space, and used and encrypted space in GBs and TBs.
- Storage Savings—displays a total savings in percentage (combining both deduplication and compression) over a time period (for example, every hour, which is the default).
- Throughput—displays the throughput volume (reads and writes) in Mebibytes/second (MiB/s) based on time (for example, every hour, which is the default).
- System—displays information about memory and CPU usage.
- At the bottom of the Dashboard page, you can also view the System Summary section, which lists key information about the current DR Series system, including:
- Total number of files in all containers
- Number of containers
- Number of containers replicated
- Active bytes–the total bytes before optimization.
- Advanced data protection—the status of the data integrity check.
- Cleaner status—The current cleaner status as one of the following states:
- Pending—displayed when there is any scheduled window set and the current time is outside the scheduled window for the Cleaner operation.
- Running—displayed when the Cleaner operation is running during a scheduled window.
- Idle—displayed only if there is no Cleaner operation running during a scheduled window.
- To change the time display in the graphs, click Zoom within the graph you want to view, and then select the time increment as hour, day, week, month, or year.
- To quickly view the state of the system, click the System Health Indicator icon, in the upper right corner of the DR Series system GUI. This icon appears green or red depending on the system state and displays the following information:
- System State—displays the status value optimal, warning (a non-critical error has occurred), or actionable state (in which a critical error is detected.) To view more information about the System State, go to the Dashboard > Usage page, which displays current detailed status information for the system.
- Hardware State—displays the status value optimal, warning (a non-critical error has occurred), or actionable state (in which a critical error is detected.) To view more information about the Hardware State, go to the Dashboard > Health page, which displays current detailed status information for the hardware and expansion shelf enclosures (if installed).
- Alerts—displays the number of alerts that have occurred. You can click this number to view the alert(s).
- Events—displays the number of events that have occurred. You can click this number to view the event(s).