|
Scenario
You want to create a macro that will add a prefix to all attributes in your model.
Solution: You will create a macro Add Prefix. The macro will be available via right-click menu on the Workspace. You want to create a user form where you will define the prefix and decide if you want to apply the change in Caption of attributes too. |
- Open Script Explorer.
- Right-click the Macros item and select Add New Macro.
- Right-click the new item and select Properties.
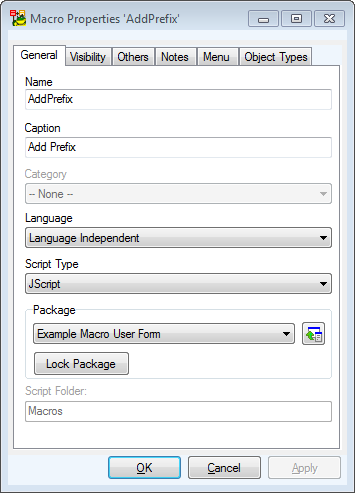
- On tab General, define properties of the macro.
|
|
Important: Name of macro mustn’t contain spaces and other forbidden characters. The name must start with a character (not number). Then you can use characters, numbers or possibly '_'. The rules don’t refer to caption. Caption can be any title you want. |
- On tab Visibility, select where you want to apply the macro – Physical Model.
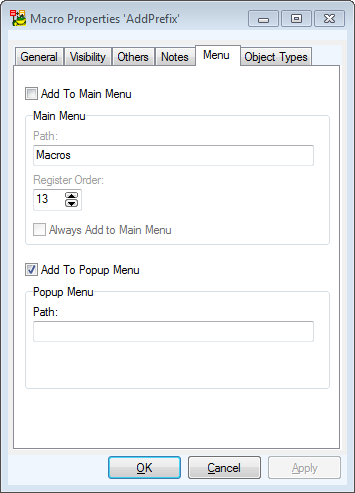
- On tab Menu, define whether you want to display the macro in:
- Macro menu,
- pop-up menu,
- both places.
Parameter Path specifies position in main menu (or pop-up menu). Example: 'Test\My Items'.
In this example, you decide to display it only in pop-up menu.
Path box is empty as 'Macros' item is set as default.
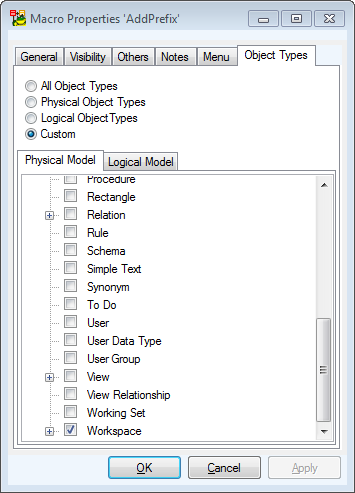
- On tab Object Types, select in which object pop-up menu you want to display it. Select Workspace.
Confirm OK.
- Double-click the macro in Script Explorer to open Script Editor. Modify the default code.
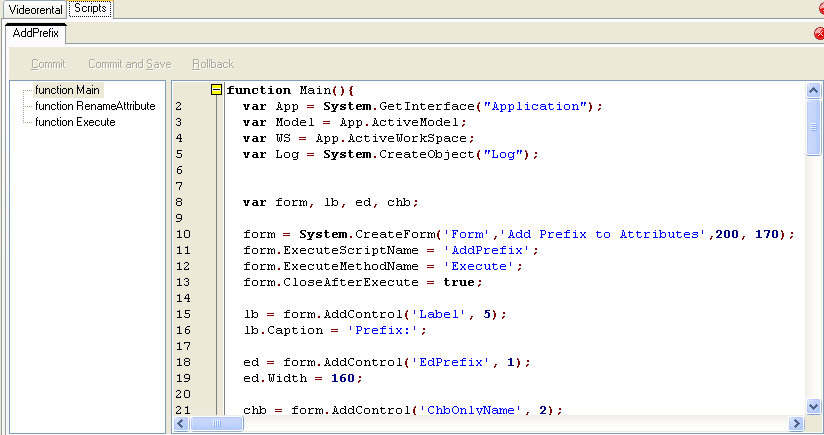


- Click Commit and Save.
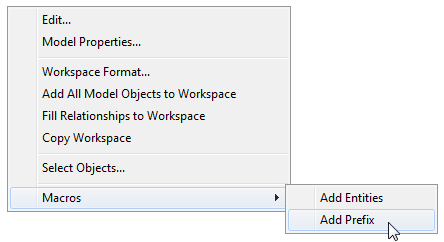
- Right-click the Workspace |Macros |Add Prefix to open the user form.
Toad Data Modeler implements the concept of metamodels. Metamodels are accessible only in Expert Mode (via Package Explorer).
Metamodel is a graphical representation of objects, classes, methods and relationships between them in a specific Package.
Using metamodels, you can create your own classes, methods and properties and define relationships between those items and items that are created in the application by default.
|
|
Important: It is recommended to only use lower and uppercase letters for naming your objects in metamodels (no numbers and special characters). |
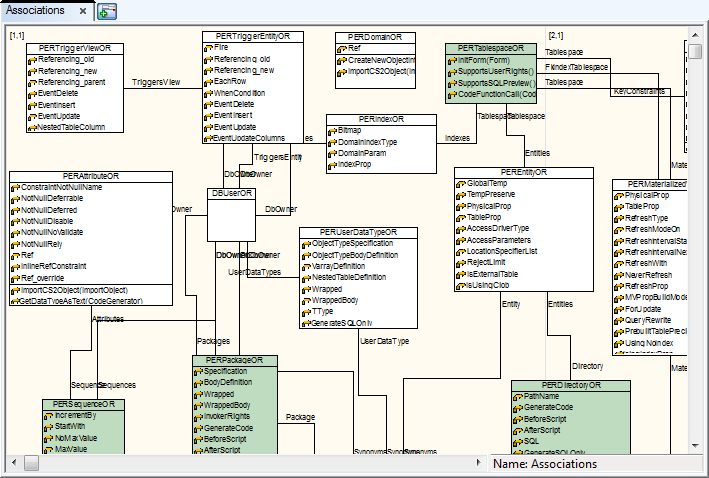
Example: The metamodel of Oracle package
Open Metamodels
- Open
 (or select Expert Mode Menu | Customization | Package Explorer).
(or select Expert Mode Menu | Customization | Package Explorer).
- Select a package.
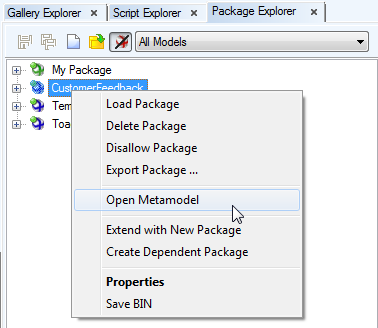
- Right-click the package and select Open Metamodel.
Toad Data Modeler implements the concept of metamodels. Metamodels are accessible only in Expert Mode (via Package Explorer).
Metamodel is a graphical representation of objects, classes, methods and relationships between them in a specific Package.
Using metamodels, you can create your own classes, methods and properties and define relationships between those items and items that are created in the application by default.
|
|
Important: It is recommended to only use lower and uppercase letters for naming your objects in metamodels (no numbers and special characters). |
Example: The metamodel of Oracle package

Open Metamodels
- Open
 (or select Expert Mode Menu | Customization | Package Explorer).
(or select Expert Mode Menu | Customization | Package Explorer).
- Select a package.
- Right-click the package and select Open Metamodel.

- Right-click the work area and select Add Class.
- In the Class Selection dialog, select a class and define settings on tab Settings.
Result: The selected class will be added to your metamodel and you will be able to modify it.