Oracle's Real Application Clusters (RAC) architecture harnesses the processing power of multiple interconnected computers (nodes) to access a shared Oracle database. It does so via the following components:
The following diagram, adapted from Oracle Real Application Clusters by Murali Vallath [Elsevier Digital Press, 2004] illustrates some of the basic components of an Oracle RAC cluster.
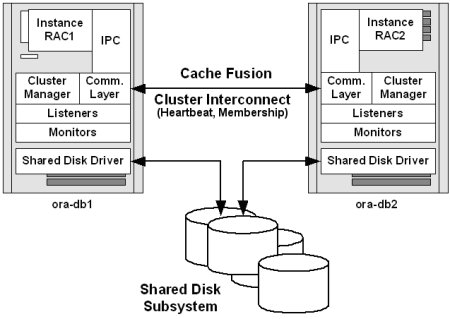
Other terms displayed in the diagram include:
|
Term |
Description |
|---|---|
|
IPC (Interprocess Communication Protocol) |
Oracle RAC uses IPC to coordinate concurrent processes, enabling the cluster to handle many user requests at the same time. |
|
Cluster Manager |
The cluster manager provides cluster integrity by using the interconnect to process heartbeat messages between nodes. |
|
Communication Layer |
The communication layer manages communication between nodes in the cluster. |
|
Heartbeat and Membership |
The heartbeat messaging system determines which nodes are currently members of the cluster. |
|
Listeners |
Listener processes establish communication paths between the database instances in a cluster. |
|
Monitors |
Various monitor processes verify listener and instance processes. |
|
Shared Disk Driver |
To improve performance and availability, database files in Oracle RAC systems must be stored on multiple disks that are shared by all the nodes in the cluster, and all nodes must be able read and write to those disks. The shared disk driver on each node provides this access to all the disks in a shared disk subsystem. |
Oracle RAC is ideal for data warehouse applications. More generally, large enterprises use Oracle RAC for databases where the following factors are important.