Performance monitoring with the Hyper-V Environment dashboard
A typical virtual environment contains a set of physical servers and virtual machines. A physical server can be a part of a cluster, and can have one or more virtual machines associated with it. You can view the overall state of these components on the Hyper-V Environment dashboard.
Accessing the Hyper-V Environment dashboard
When you navigate to the Hyper-V Environment dashboard for the first time, the Monitoring tab appears. This tab provides an overall summary of your virtual environment.
To access the Hyper-V Environment dashboard:
|
3 |
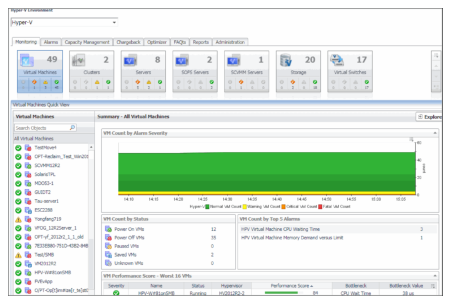
On the navigation panel, under Homes, click Hyper-V Environment. The Hyper-V Environment dashboard appears in the display area.  The Hyper-V Environment dashboard shows summary information about the clusters, servers, and virtual machines in your environment, and additional information about each specific component. |
|
4 |
Select the Clusters, Servers, Virtual Machines, SOFS Servers, SCVMM Servers, Storage, or Virtual Switches tile from the top left. |
Monitoring tab
The Monitoring tab allows you to select a monitoring object or a group of objects, such as clusters, servers, virtual machines, virtual switches, or volumes, and review the data associated with your selection. For example, selecting all servers identifies the top three consumers of CPU, memory, network, and disk resources and shows the related alarm states. Selecting a specific server shows the CPU, memory, network, and disk usage for the selected server, along with high-level hardware and software configuration.
Gauge charts
he data of CPU, memory, network, and disk usage are represented using a spinner (also known as rotating wheel) which is divided into four severity levels, including Normal (in green), Warning (in yellow), Critical (in orange), and Fatal (in red).
The severity of CPU Load is calculated based on the following formula: (utilization current average - utilization period average)/utilization period standardDeviation. If this value is:
The severity of Network I/O is calculated based on the following formula: (transferRate current average - transferRate period average)/transferRate period standardDeviation. If this value is:
The severity of Memory Load is calculated based on the following formula: (currentPressure current average - currentPressure period average)/currentPressure period standardDeviation. If this value is:
The severity of Disk usage is calculated based on the following formula: (diskTransferRate current average - diskTransferRate period average)/diskTransferRate period standardDeviation. If this value is:
|
• |
Summary: Includes the following embedded views: |
|
• |
SCVMM Inventory: Includes the following embedded views: |
|
|
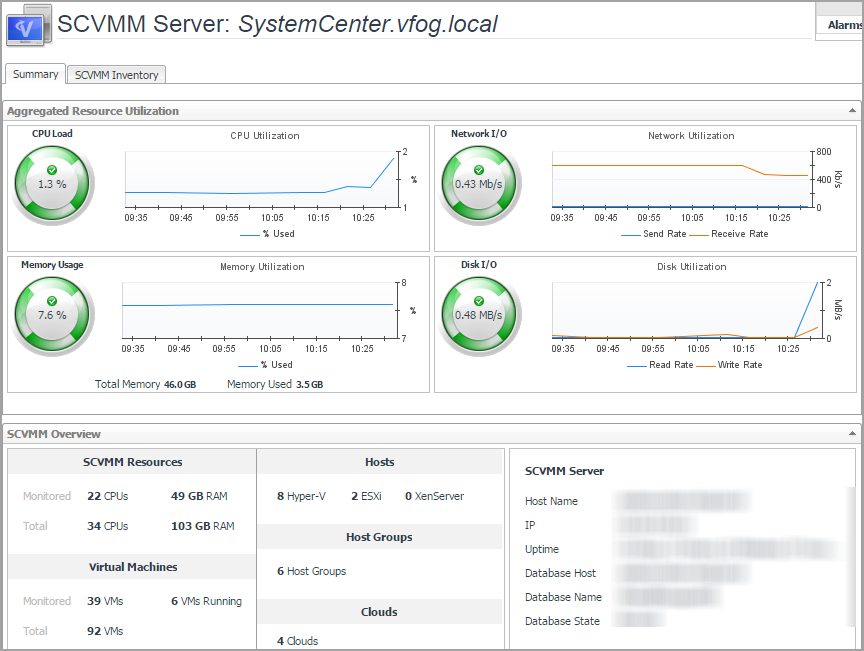
Indicates the overall information of the selected SCVMM server. |
|
|
SCVMM Resources. Shows the CPU and memory information.
|
• |
Monitored: Shows the number of CPU and memory of Hyper-V servers that are managed by the selected SCVMM server and are also monitored by the Hyper-V agents. |
|
• |
Total: Shows the numbers of CPU and memory that are managed by the selected SCVMM server. | |
|
|
Virtual Machines. Shows the VM related information.
|
• |
Monitored: Shows the number of VMs/running VMs that are managed by the selected SCVMM server and are also monitored by the Hyper-V agents. |
|
• |
Total: Shows the total number of virtual machines that are managed by the selected SCVMM server. | |
|
|
Hosts. Shows the list of hosts available in the selected SCVMM Server. |
|
|
Host Groups. Shows the number of host groups available in selected SCVMM Server. |
|
|
Clouds. Shows the number of clouds available in the selected SCVMM Server. |
|
|
SCVMM Server. Shows the state of the selected SCVMM Server, including Host Name, IP, Uptime, Database Host, Database Name, and Database State.
If there are no IP and Uptime metrics displayed in the SCVMM Server area, this should be caused by one of the following:
|
 The Hyper-V Environment dashboard shows summary information about the clusters, servers, and virtual machines in your environment, and additional information about each specific component.
The Hyper-V Environment dashboard shows summary information about the clusters, servers, and virtual machines in your environment, and additional information about each specific component.