When a backup is created, a checksum is calculated for the backup file and saved in the backup file. An integrity check recalculates the checksum and compares it to the checksum stored in the backup file.
NOTE: Regular BMR backups don't have checksum enabled by default. Only Secure Server BMR backups have checksum enabled by default.
The Checksum calculation is enabled by modifying the registry: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\WOW6432Node\Quest\Recovery Manager for Active Directory\Options\
create a new DWORD key ChecksumCalculationMode
The various values for enable/disable Checksum Calculation are:

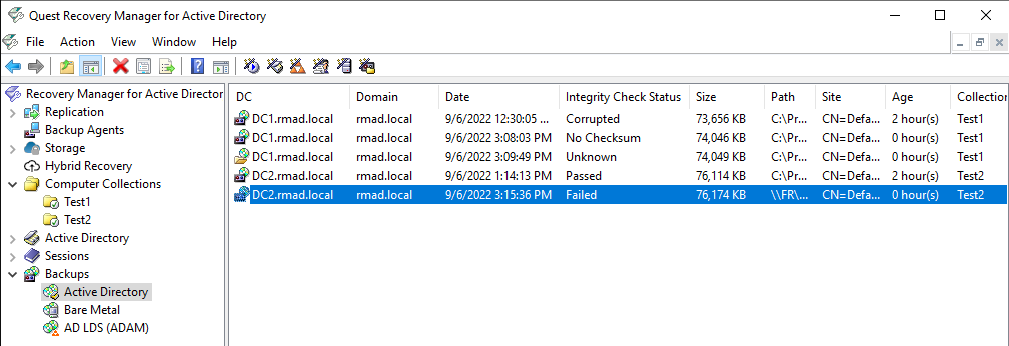
In the Recovery Manager for Active Directory console, click the Backups node then click the Active Directory, Bare Metal, or AD LDS (ADAM) node.
Click a backup you want to check the integrity on.
An automatic integrity check will be performed on the import.
The following statuses can be displayed after the integrity check has finished:
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| Passed | The newly calculated checksum value matches the previously calculated checksum stored in the backups file. |
| Unknown | The integrity check was not performed. |
| Running | The integrity check is in progress. |
| Failed | The backup is not accessible (wrong credentials) or may have been moved from the path. |
| No Checksum | The previously calculated checksum could not be read. This could be due to the backup being created by a previous version of the product. The backup also may have been damaged in such a way that the checksum was also affected. |
| Corrupted | The newly calculated checksum value does not match the previously calculated checksum stored in the backup file. |
NOTE: Integrity checks are recorded as a Windows Eventlog event on the console during the integrity check. The events can be found in Applications and Services Log | Recovery Manager for Active Directory. If Email is configured, then email notifications are sent for integrity checks that are performed either after creating a backup (controlled by the Run an integrity check after creating a backup setting); or after creating a scheduled backup for the previous N sessions (controlled by the Check the integrity of previously created backups after a scheduled backup setting). The integrity check results are combined with the backup creation results and sent as a single message. If the Send notification upon errors or warnings only setting is selected, then an notification will only be sent if the integrity check report contains the results Backup file is corrupted or Integrity check failed. If all integrity checks are successful, no email notification will be sent.
To manually perform an integrity check on any backup already in the Active Directory, Bare Metal, or AD LDS (ADAM) nodes:
Click a backup you want to perform the integrity check on.
Right click and select Check Integrity.
One of the statuses above will be displayed after running the manual integrity check.
The following backup types are supported for integrity check after the backup registration:
Active Directory backups (.bkf)
AD LDS (ADAM) backups (.bkf)
Bare Metal backup (.vhd, .vhdx)
Offline Active Directory Database files (.dit) are ignored.
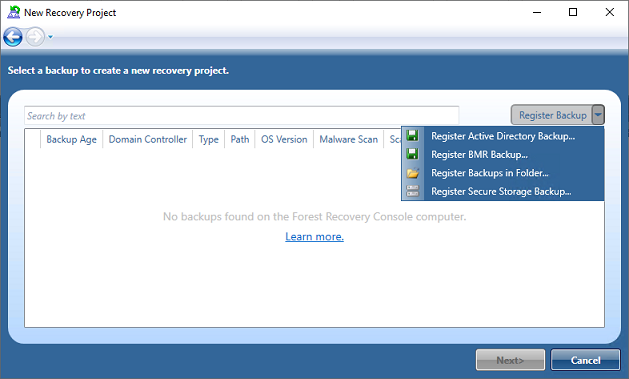
The registering of backups from New Recovery Project dialog in Forest Recovery Console, will automatically execute an integrity check when backups are registered using Register Active Directory Backup…, Register BMR Backup… and Register Backups in Folder… options.
The result of the integrity check is available in the Media Cataloging dialog box.

Registering backups from Select Backup dialog in Forest Recovery Console automatically execute an integrity check for both Active Directory Backup and BMR Backup selection.

The result of the integrity check is available in the Media Cataloging dialog box.
Automatic execution of backup integrity checks from the RMAD Console and Forest Recovery Console can be configured in the registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\WOW6432Node\Quest\Recovery Manager for Active Directory\Options
IntegrityCheckOnBkfRegistration (REG_DWORD), can be 0 or 1 (default), allows to run integrity check for AD and ADAM (AD LDS) backups at registration.
IntegrityCheckOnBmrRegistration (REG_DWORD), can be 0 (default) or 1, allows to run integrity check for BMR backups at registration.
The registering of backups can be done via PowerShell® as a parameter has been added to the Add-RMADBackup cmdlet to allow an integrity check to be performed after the backup has been registered in the Active Directory database.
Add-RMADBackup -Path 'C:\MyBackups\2023-03-03 19-23-11.bkf' -CheckIntegrity
The result of the integrity check is available directly in PowerShell or can be viewed in the RMAD Console:
NOTE: IntegrityCheckOnBkfRegistration and IntegrityCheckOnBmrRegistration registry settings do not affect the integrity check with Add-RMADBackup cmdlet.
A list of the backups can be exported to a file for other processing or record keeping.
Exported lists can be saved in one of the following formats:
Text (Tab delimited) (*.txt)
Text (Comma delimited) (*.csv)
Unicode Text (Tab delimited) (*.txt)
Unicode Text (Comma delimited) (*.csv)
In the Recovery Manager for Active Directory console, click the Backups node then click the Active Directory, Bare Metal, or AD LDS (ADAM) node.
Right click and select Export List…
In the Export List dialog, select a location to save the file, enter a file name, and click Save .
The Properties dialog box for a registered Active Directory, Bare Metal, or AD LDS (ADAM) backup provides detailed information about the backup, such as the backup creation date, backup size, and a list of the Active Directory® components the backup includes.
In the console tree, expand the Backups node, and then select Active Directory, Bare Metal, or AD LDS (ADAM).
In the details pane, select the desired backup, and then click Properties on the Action menu.
The General tab displays general information about the selected backup.
On this tab, you can use the following elements:
Backup description: The description of the backup including server name and date and time of when the backup was created.
Domain: The domain of the server.
Created: The date and time when the backup was created.
Backup location: The location where the backup is stored on the RMAD server (scroll to right to read a long location).
Encryption: The encryption status of the backup.
Original size: The original size of the data before backup.
Backup size: Size of the backup file.
Compression ratio: The compression ration of the backup file compared to the original size.