Each On Demand migration project needs a source or target tenant with Exchange Online. These are Commercial tenants. For users in the United States deployment region, On Demand Migration offers two options depending on the type of Microsoft 365 tenant that you want to add:
- Commercial or GCC Tenant - choose this option if you want to add either a Microsoft 365 commercial tenant hosted on the Azure public cloud or a Microsoft 365 GCC (Government Community Cloud) tenant with moderate cyber-security and compliance standards hosted on the Azure Government cloud.
- GCC High Tenant - choose this option if you want to add a Microsoft 365 GCC High tenant with advanced cyber-security and compliance standards like NIST 800-171, FedRAMP High and ITAR hosted on the Azure Government cloud.
|
|
NOTE: When you create a migration project, a GCC or GCC High tenant can be used as the target tenant only. Currently, only the On Demand Migration module supports GCC and GCC High tenants. |
For more information about adding, removing and managing tenants, see Managing your Azure tenants and on-premises domains in the On Demand Global Settings Current User Guide.
Adding a tenant
- Log in to On Demand using the credentials you used to sign up for On Demand.
- If you have multiple organizations you must select an organization. If you have a single organization it will be automatically selected.
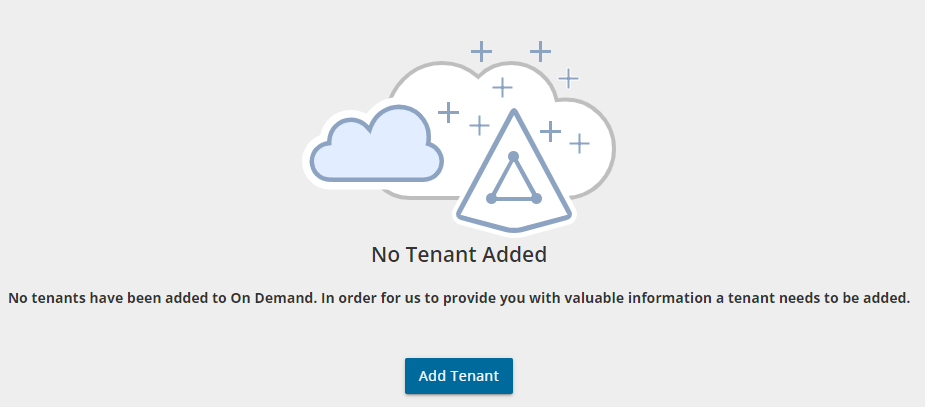
- If there are no tenants in your organization, click Add Tenant.
-or-
In the navigation panel on the left, click Tenants. The Office 365 Tenants page opens. Then click Add Tenant.
- The Add Tenant page opens.
- Enter your Microsoft Entra ID Global Administrator credentials for the target tenant and click Next. A page opens with the list of permissions that you must grant.
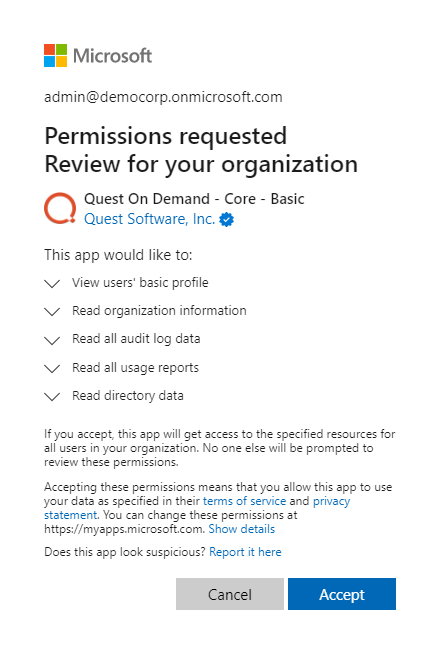
- Click Accept to grant consent to the initial Core - Basic permission set to the On Demand service principal.
- The Office 365 Tenants page opens with the tenant added as a new tile.
In this topic:
On-Premise connectivity requirements
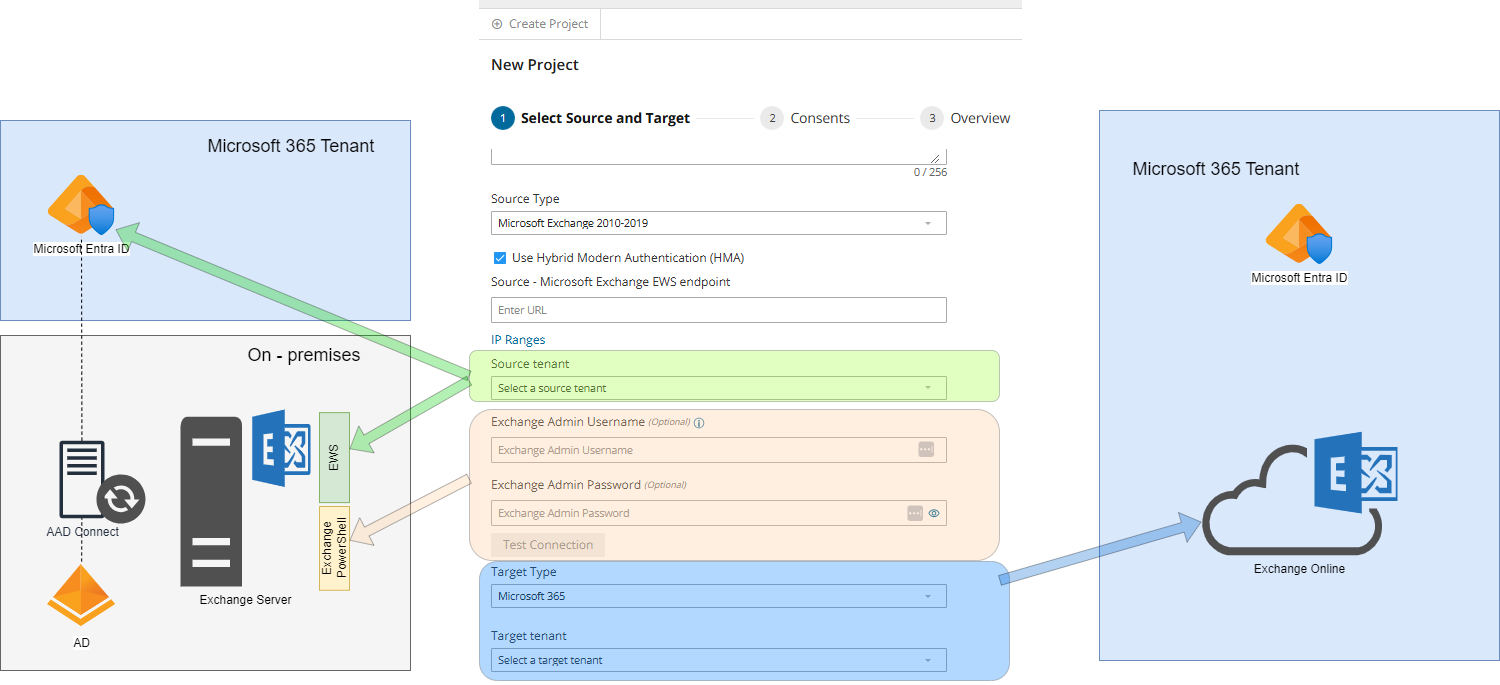
ODMHE uses EWS and PowerShell for mailbox migration. EWS is used for the mailbox content migration (folders and messages), PowerShell is used during the discovery process and to migrate Delegates, Auto-replies, Forwarding. Both endpoints must be configured and enabled on the Exchange on-premises server.
EWS endpoint
EWS endpoint URL must be provided during project creation or through the connection dialog in form of http(s)://server-name/EWS/Exchange.asmx.
PowerShell endpoint
PowerShell endpoint address is derived from the EWS URL http(s)://server-name/EWS/Exchange.asmx > http(s)://server-name/powershell
Protocols and Ports
The decision which protocol to use: HTTP or HTTPS, is made when providing the EWS endpoint. The same protocol will be used for PowerShell. To connect to a remote computer, the remote computer must be listening on the port that the connection uses.
For EWS and PowerShell, the default ports are
Authentication
ODMHE currently supports two authentication methods for Exchange on-premises.
Basic Authentication
Requires to provide Exchange admin credentials as described in the On-Premise connectivity requirements section.

Hybrid Modern Authentication (HMA)
Available for Office 365 hybrid deployments where Microsoft Exchange 2010 SP2 - SE on-premises server is linked to a M365 tenant. The tenant must be added to Quest On Demand, and the necessary consents must be granted as described in the Consents for Quest On Demand section.
When HMA is configured then modern authentication (OAuth2) is used for connection to the EWS endpoint for content migration.
Since HMA does not support the remote PowerShell protocol, you must also provide basic authentication credentials (username and pasword).
IP Addresses
ODMHE uses a predefined range of IP addresses which should be allowed in your environment. The following OnDemand components use these IP ranges:
- ODMHE Worker function - connects to EWS endpoint for source mailbox validation and retrieving mailbox ID.
- ODMHE API function - validates EWS connectivity.
- ODM Migration engine - connects to EWS endpoint for source mailbox content migration
- ODM PowerShell API - connects to remote PowerShell
Contact Quest Technical Support for the list of IP addresses.
On-Premise Exchange admin account requirements
ODMHE requires an Exchange admin account for exchange on-premises. It can be specified in the project creation wizard and later updated with the connection dialog.
|
|
NOTE: The Exchange admin account does NOT need to have a mailbox on Exchange on-premise. |
ODMHE uses the explicit credentials of an administrator account to:
- discover mailboxes.
- migrate the mailbox content (folders and messages) with EWS, and migrate Delegates, Auto-replies, Forwarding with PowerShell when basic authentication is used.
- migrate Delegates, Auto-replies, Forwarding with Powershell when HMA (Hybrid Modern Authentication) is used.
Permissions needed
For content migration from or to Exchange on-prem these exchange roles must be assigned to migration user:
For PowerShell based migrations (Discovery, Delegates, Auto-replies, Forwarding) from or to Exchange on-premise, these Exchange roles must be assigned to the migration user.
- Active Directory Permissions
- ApplicationImpersonation
- Mail Recipients
Consents for Quest On Demand
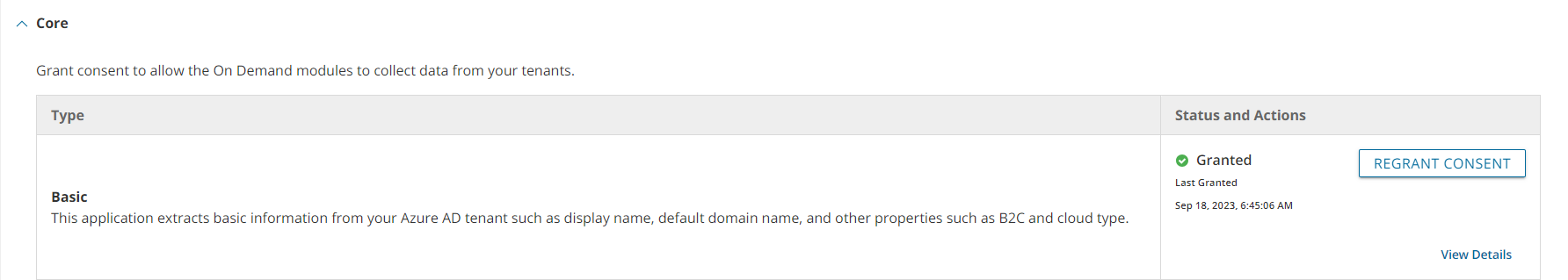
The ability for On Demand service principals to access and operate with assets requires explicit permissions. The Tenant Administrator grants these permissions through consents. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is supported for tenant administrators when granting consents.
Each tenant that is added has granted consent to the initial Core - Basic permission set to the On Demand service principal. Additional consents are required to work with different features of On Demand Migration for Hybrid Exchange.
Granting Consent
- Click Tenants from the navigation pane.
- Select a tenant and click Edit Consents from the tenant tile.
- Click Grant Consent or Regrant Consent for the permissions type. Then click Accept in the Microsoft consents dialog.

This section lists the minimum consents and roles required by the On Demand Migration service principals.
|
|
NOTE: Consents are required only for M365 or HMA tenants. They are not required for on-premise Microsoft Exchange Server. |
For initial tenant setup
| Add and configure tenants, and grant consent |
Core-Basic consent from both Source and Target tenant administrator accounts.
Global Administrator role from both source and target tenant administrator accounts. |
For Mailbox migration
| All tasks |
Migration - Basic - Minimal consent from Source tenant administrator accounts.
Migration - Basic - Full consent from Target tenant administrator accounts.
Migration - Basic is a legacy permission set and should be replaced with either the Minimal or Full permission sets. |
| Migrate mailboxes |
Migration - Mailbox Migration - Minimal consent from Source tenant administrator accounts.
Migration - Mailbox Migration - Full consent from Target tenant administrator accounts.
Migration - Mailbox Migration is a legacy permission set and should be replaced with either the Minimal or Full permission sets. |
When you have granted the consents, verify that the service principals were successfully created in the target tenant as described in the steps below:
- Log in to the Azure admin portal.
- Open the Microsoft Entra ID service page.
- Click Manage > Enterprise applications from the navigation pane. Then click All applications.
- Filter the list if necessary and verify the list of service principals. Your list may differ from the image below.
Microsoft service throttling limits the number of concurrent calls to a Microsoft service to prevent overuse of resources. These limits are set by the Microsoft services and are dependent on the service type along with the operations that are being completed by On Demand for the service. In addition, any throttling limits are subject to change by Microsoft.
Microsoft Graph
Microsoft Graph is designed to handle a high volume of requests. If an overwhelming number of requests occurs, throttling helps maintain optimal performance and reliability of the Microsoft Graph service. For more information, see https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/graph/throttling. Microsoft enforce throttling limits for Microsoft Graph based on tenant size, including requests-per-minute and requests-per-day. Microsoft does not provide a method for modifying these limits.
Handling ODM Throttling
Quest On Demand Migration follows best practices provided by Microsoft when experiencing throttling. These include reducing the number of operations of requests, reducing the frequency of calls and avoiding immediate retries, since all requests accrue against the usage limits for the application.
For requests that an application makes, such as On Demand Migration, including Microsoft Graph, CSOM, or REST calls, Microsoft can return error codes including HTTP status code 429 ("Too many requests") or 503 ("Server Too Busy") which result in the requests to fail. In both cases, a Retry-After header is included in the response indicating how long the calling application should wait before retrying or making a new request.
Upgrading Throttling Policies
Exchange Web Services (EWS) are throttled by Microsoft whenever large quantities of data flows through the EWS platform. The On Demand Migration service throughput can be improved by upgrading the following throttling policy parameter setting to Unlimited:
- EwsMaxBurst - Defines the amount of time that an EWS user can consume an elevated amount of resources before being throttled. This is measured in milliseconds. This value is set separately for each component.
- EwsRechargeRate - Defines the rate at which an EWS user's budget is recharged (budget grows by) during the budget time.
- EwsCutoffBalance - Defines the resource consumption limits for EWS user before that user is completely blocked from performing operations on a specific component.
Tenant administrators can upgrade the throttling policies by making a service request with Microsoft.
To complete a migration project, a lightweight user desktop application called Desktop Update Agent (DUA) must be configured and deployed by administrators and run on users workstations. DUA provides enhanced support, helps ensure the success of cross-tenant migration projects, makes agent delivery easier, and status reporting more informative.
DUA features:
- Ability to manage user’s application reconfigurations activities from a single view within On Demand Migration.
- Support for Microsoft 365 application license reset.
- Support for various client authentication mechanisms.
For more information about downloading, administration and use of DUA, see the Quest On Demand Migration Update Agent Guide.