To view SQL information
Create a scan job using the Add Scanner Jobs wizard. See Scan SQL for more information.
Select a group in the Scanner node in the Task pane.
Select a scan job from the Group node.
Select the SQL Information tab.
Click the following to view the information that displays for each pane.
|
SQL name |
Name of the SQL statement. |
|
SQL Classification |
Statement type as classified by SQL Optimizer. Types include Simple, Complex, or Problematic. |
|
Classification Rules |
Applicable SQL classification rules. Rules used for the classification process are set in the SQL Classification Options page. See SQL Classification Options for more information. |
| Error Message |
Details of errors encountered during scanning. Note: This field is only shown for SQL statements classified as Invalid. |
|
Note: SQL Classification information only displays for the original SQL statement. | |
| SQL Name | Name of the SQL statement. |
| Conversion | Applicable SQL conversion details. See About SQL Conversion for more information. |
| Original SQL | SQL script for original SQL statement. |
| SQL Name | Name of the SQL statement. |
| Temp Table Dependency | SQL script used to create temporary tables in SQL Scanner. |
The execution plan displays the steps a database takes to execute a SQL statement. You can use the execution plan to determine if a statement is efficient.
The following displays a sample execution plan in tree plan format:
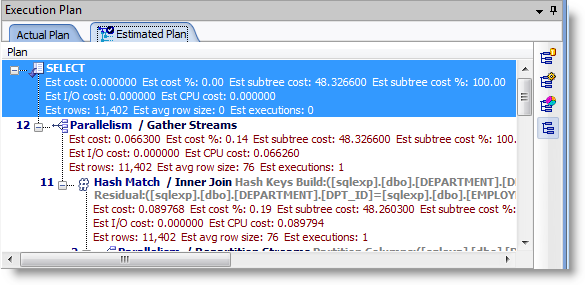
Each step of the tree indicates how SQL Optimizer retrieves rows of data. The first line of the execution plan displays the SQL statement type, such as SELECT. The remaining lines represent an operation. The operations are numbered in the order of execution to make the plan easier to read.
SQL Optimizer executes each child operation before the parent operation. For some SQL statements, SQL Optimizer executes the parent operation once it retrieves a single row from the child operation. Other SQL statements require that SQL Optimizer retrieve all rows from the child operation before it executes the parent operation.
The annotated execution plan includes the following information for each step:
Execution order number
Join syntax (annotated)
Filter syntax (annotated)
Object name
Table access
Index scan
Cost
Partition name
The execution plan displays the steps a database takes to execute a SQL statement. You can use the execution plan to determine if a statement is efficient.
The following displays a sample execution plan in tree plan format:

Each step of the tree indicates how SQL Optimizer retrieves rows of data. The first line of the execution plan displays the SQL statement type, such as SELECT. The remaining lines represent an operation. The operations are numbered in the order of execution to make the plan easier to read.
SQL Optimizer executes each child operation before the parent operation. For some SQL statements, SQL Optimizer executes the parent operation once it retrieves a single row from the child operation. Other SQL statements require that SQL Optimizer retrieve all rows from the child operation before it executes the parent operation.
The annotated execution plan includes the following information for each step:
Execution order number
Join syntax (annotated)
Filter syntax (annotated)
Object name
Table access
Index scan
Cost
Partition name
To copy an execution plan
| » | Right-click the execution plan and select Copy. |
Note: You can paste execution plans displayed as a Tree Plan or Plain Language Plan in text or bitmap format. Applications such as Microsoft Word allow you to choose the format using the Paste Special option. You can use text applications such as Notepad to paste execution plans in text format or graphic applications such as MS Paint to paste execution plans in bitmap format.