A collection is a group of mailboxes that should be migrated within the same time period and to the same target mailbox store. Mailboxes can be placed in a collection directly or through a recipient container or distribution list (DL). Where possible, use containers to populate collections. This will ensure that the newly-created mailboxes are included in synchronization automatically.
However, if the mailboxes you plan to synchronize in a Remote Users Collection are in the same container as normal users’ mailboxes, it is better to use distribution lists to populate both the Remote Users Collections and normal collections. This will ensure that mailboxes of the remote users will not be synchronized in normal collections and vice versa.
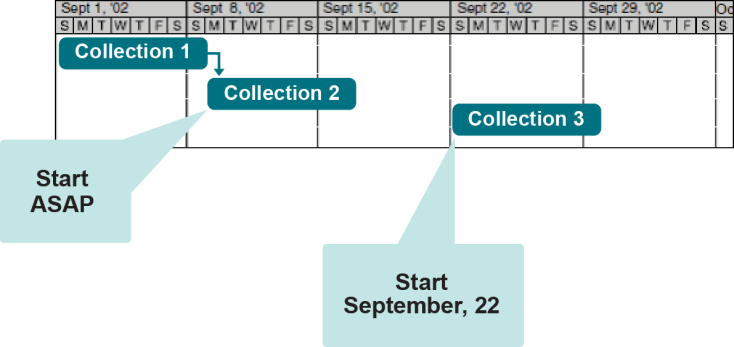
Multiple collections may be associated with each job. Each collection has a priority number starting from 1, which is the highest priority. The collections are processed by the agent in sessions according to their priority number. The agents start processing with the collection that has the highest priority. The collection priority can be changed.
Mailbox synchronization jobs and collections for the entire migration should be set up at the start of the project. Each collection has settings that control when the mailboxes that belong to it are synchronized.
If you plan to use one collection for a source server, create and populate mailbox collections to organize the migration of mailbox content as appropriate for your needs—for example, by department, by projected migration date, and so on.
The All mailboxes collection cannot be used as a Remote Users Collection. Usually jobs are split into collections in order to achieve the following goals:
Populating Remote Users Collections
You should add to Remote Users Collections those remote and laptop users who:
You should not add to the Remote Users Collection any user who:
Considerations
You should also consider the following before adding users to a Remote Users Collection:
Migrating Remote Users Collection
To determine the optimal number of mailboxes to be added to each Remote Users Collection, you can evaluate how many mailboxes can be migrated per night (in, say, 8 hours). It is recommended that you build a lab similar to your production environment and test how many mailboxes the Mail Source Agent can process during the time interval you specify.
Our testing has shown that the Mail Source Agent can process 26 mailboxes, 150 MB each, of a Remote Users Collection per hour. However, please note that agent performance tightly depends on the server and network capacity, mailbox size, and many other factors, and therefore these figures are for approximation only.
To add the mailboxes of remote and laptop users to a Remote Users Collection and start synchronizing the collection:
|
|
NOTE: During synchronization of a remote user’s mailbox, the Mail Source Agent removes the corresponding target mailbox (if any) and recreates it. When the Mail Source Agent logs on to the mailbox in order to process it, the mailbox becomes unavailable for the user for the time it is being processed by the agent. |
When the time interval specified for the agent to process the Remote Users Collections is over, check whether the mailboxes of the Remote Users Collections have been synchronized and switched by the Mail Source Agent. When the users log on, EMWProf will start updating their profiles, and after update the target mailboxes will become the active users’ mailboxes.
Synchronization of the Calendar folders of the remote users’ mailboxes will be performed by the Calendar Synchronization Agent during the entire period of migration, but you should start calendar synchronization for such mailboxes only after the switch. This is to prevent the CSA from creating mailboxes on the target before they are processed by the Mail Source Agent. The calendar agent will transfer calendar data from the source mailbox to the target mailbox.
In inter-org Exchange migration you may want to split mailboxes across multiple servers or storage groups or stores (databases), or consolidate mailboxes onto fewer Exchange servers.
Splitting Servers or Stores
Each job specifies a source-target server pair. This facilitates splitting mailboxes across multiple servers. Mail agents process jobs one at a time. To migrate from one server to multiple servers, create separate jobs.
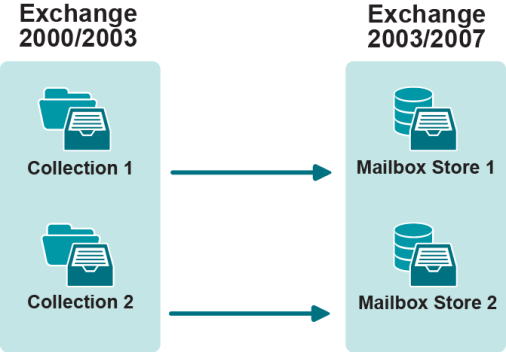
To migrate mailboxes to multiple stores, create separate collections and specify the appropriate target store in the collection’s properties.
Consolidating Servers
It is simple to consolidate multiple source Exchange servers into one target Exchange server. Each source-target server pair will have a job. Data received from multiple jobs is handled in serial by the agent running on the target server, while source mailboxes are processed in parallel by the multiple agents running on the source servers.
The following are the important issues to consider when synchronizing calendars and free/busy data: