Investigating Latency
 |
 |
Investigating Latency
The Foglight Cartridge for Sybase assists your investigation into latency with the RS_LatencyTabular table view and the RS_Latency_Graph view.
To start with the RS_Latency_Tabular table view:
To view more detailed information:
Generating SybaseMDA Reports
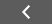 |
 |
Generating SybaseMDA Reports
The Foglight for Sybase report templates can be found in the following location, when listed by module: SybaseMDA >Reports.
Figure 49. Reports
The cartridge comes equipped with the following report templates:
Cache Activity Report
 |
 |
Cache Activity Report
Change Tracking Summary Report
 |
 |
Change Tracking Summary Report
This report takes two special input parameters:
The change occurs at 10:00. stepMinutes is set to 15 and beforeAfterMinutes is set to 10 minutes. As a result, two periods appear: 9:35-9:50 and 10:10-10:25.