The Code Finder searches database objects and files for a specific text string. Each occurrence of the specified text is listed and the database objects or files where it is found.
Open Database Object or File in SQL Worksheet
The Code Finder window is divided into three sections: search criteria, where to search, and the search result.
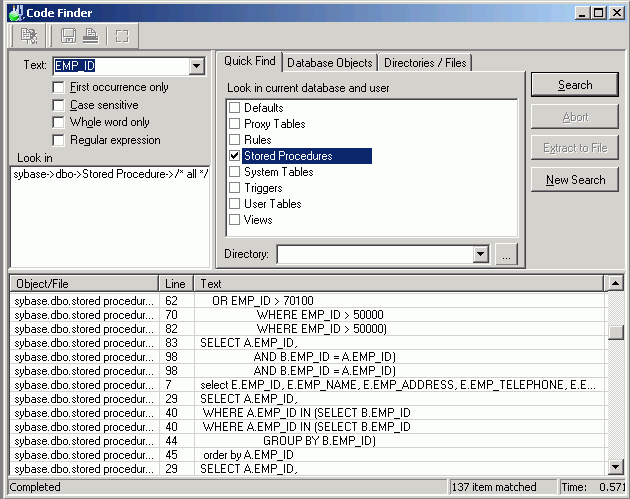
The search criteria displays on the top left pane. Review the following for additional information:
|
Item |
Description |
|
Text |
Specify text. |
|
First occurrence only |
Specify whether to search for only the first occurrence of the text in the database object or file. If this option is not selected, all occurrences of the text displays. |
|
Case sensitive |
Specify whether to search for the text in exact case that you enter it. |
|
Whole word only |
Specify whether to search for words only |
|
Regular Expression |
Specify whether to recognize regular expressions in the search string. |
Select where you want to search. Review the following for additional information:
| Item | Description |
|
Look in |
Displays the list of selected objects and files to search. |
|
Quick Find |
Allows the selection of the database objects belonging to the current database and user (Tables, Views, Procedures, Triggers, Rules, Defaults) and/or the selection of all files belonging to the selected directory. |
|
Database Objects |
Allows the browsing and selection of database objects from different databases and users. |
|
Directories/Files |
Allows the browsing and selection of directories or files. . |
The lower pane displays the list of items that matches the search criteria. Review the following for additional information:
| Item | Description |
|
Name |
Database object or file name. |
|
Line |
Line number of matched specified text. |
|
Text |
Line of text showing the matched specified text. |
Open Database Object or File in SQL Worksheet
To display the Code Finder window
Click 
Enter a search text or use the down arrow next to the input field to select from a list of previously entered search text. The First occurrence only, Case sensitive, Whole word only andRegular expression checkboxes lets you refine the search.
Select the Quick Find tab to select objects belonging to the current database and user. Or, select the Database Objects tab. Expand the object and select user, object type or object name and click Add. The selected object displays in the Look in pane on the top left indicating that the selected objects will be searched. No duplicate objects can be selected.
Select the Directories/Files tab. Select the directory and enter a file mask or click the down arrow to select from a list of previously entered file marks. If blank, *.* is used indicating that all files will be searched. To search in the sub-directory, select Include sub-directories checkbox. Click Add to select the directory and files. No duplicate files can be selected.
To start searching
Click Search.
To stop the search
Click Abort.
Open Database Object or File in SQL Worksheet
Regular expressions are characters that customize a text search string. They formulate a more complex search.
You must select the Regular expression checkbox to use these advanced search features.
| Type of Search |
Search Characters |
Location of character in the search string |
Explanation | ||||||||
|
Text at the beginning of line |
^ (circumflex) Example:^select |
Beginning | A circumflex at the beginning of the text search string finds the text only if it is the first non white space text on a line | ||||||||
|
Text at the end of line |
$ (dollar sign) Example:error$ |
End | A dollar sign at the end of the expression matches the end of a line. | ||||||||
|
Single character wildcard |
. (period) Example:f.r matches "for" and "‘far" |
Any place | A period represents any character. | ||||||||
|
Class of character |
: (colon) Example:SQL:a finds SQLSTATE or SQLTABLE SQL:d Finds SQL1 or SQL3 |
Any place |
A colon matches a class of characters described by the character following the colon.
| ||||||||
|
Search for Regular Expression characters |
\ (backslash) Example: \^ searches for ^ \\ searches for \. |
Any place | A backslash before a wildcard character searches for actual character and does not use the character as a wildcard. | ||||||||
|
Search for multiple characters in one position |
[...] (characters within square brackets Example:r[au]n finds run or ran |
Any place | Characters enclosed in square brackets matches any one character that displays in the brackets, but no others. Nesting of brackets is not supported. | ||||||||
|
Search for any character but the specified characters in one character position |
[^] (circumflex within square brackets) Example: r[^oa]n finds run, r n, rin, etc but not ron or ran. |
Any place | A circumflex at the start of the string in square brackets means NOT. The expression matches any character except the characters in the string and the carriage return (ASCII 0x0D) or line feed (ASCII 0x0A). | ||||||||
|
Search for a range of characters in one character position |
[-] (hyphen within the square brackets) Example: SQL[1-3] finds SQL1, SQL2 and SQL3 |
Any place |
A hyphen within the square brackets signifies a range of characters. Note: the range must be in a progressive order, i.e. "[a-x]" matches any character from a through x while "[x-a]" does not match anything. |