When Spotlight® on SAP ASE is unable to locate a valid user license, the application opens in freeware mode. The limitations of this mode are:
Spotlight® on SAP ASE can only connect to one machine.
There is no balloon help available for components on the Home Page.
No drilldowns are available to display detailed information.
The words "Freeware Mode" display on the status bar at the bottom of the Spotlight console.
Within these limitations, Spotlight retains all the features available in the fully licensed version.
When you install the trial version of Spotlight® on SAP ASE, it comes with a 30-day license key. During the 30 days of the trial period, Spotlight retains all the features available in the fully licensed version.
After the trial period, the license expires, and Spotlight® on SAP ASE reverts to freeware mode.
For a graphical representation of the SAP ASE architecture, see ASE graphic.
Adaptive Server Enterprise (ASE) is a full featured, mature relational database management system. It is a highly scalable RDBMS that is widely used in enterprise class installations.
The general structure, or architecture, of Adaptive Server shares many similar concepts used by the family of RDBMS servers from other vendors, but it does have some of its own terms and unique implementations, as described in the following sections.
Any host machine can have one or more named "dataserver" (or "server" for short) instances of Adaptive Server installed and running on it. All client code that communicates with Adaptive Server will need the host name, server name, and port address it is listening on, to address it properly (in addition to a valid login/password).
A server will consist of one or more "engines" (separate operating system processes providing identical services but performing independent and parallel DB tasks, while appearing to any connected client as one server entity) with the number of engines depending on the server configuration. The number of engines defined is usually directly related to the SMP capacities of the host machine.
Access to Adaptive Server is maintained locally at the server. A login is created that a client can then use to access Adaptive Server.
Exceptions:
On Windows NT/2000, Adaptive Server can be configured to use native security.
Starting with ASE v12.5, Adaptive Server can be configured to use LDAP.
A login does not by itself provide access to an underlying database on the server.
Each named server will have a number of "databases." They can be categorized into two types: system and user-defined databases.
A database is defined as a collection of segregated tables and indexes. For example, the system database named "master" contains all the tables and indexes needed to run, configure, and administer the server as a whole.
Each database has "users" defined that can access the database. A DBA will provide access to a database by creating or assigning a user that the server login can use while in the respective database.
Once a client connects to a server, it can switch context to any of the databases (security permitting). Any SQL query can reference tables outside the current database using the proper SQL syntax.
A "device" is a logical or physical unit of storage on which a database is created.
A database device is sub-divided into logical units of storage for the database, called "segments." A user-defined segment can also be created so that one or more tables or indices can be placed, or segregated, onto a new segment apart from the default segments (typically done for application performance and tuning).
Adaptive Server populates and maintains tables with server-specific information (i.e., setup, security, configuration). Most system tables reside on the master database, but each database contains a smaller set of system tables as well.
The system tables are the primary source of all information about Adaptive Server that Spotlight retrieves.
Open/Server that handles the backup tasks for one or more Adaptive Servers.
This section describes the features of the Spotlight on SAP ASE user interface. The features may be of the following kinds:
Features that are specific to Spotlight on SAP ASE.
Spotlight applications all operate in the same way. They differ only in the kind of information they collect and display. The features that are specific to Spotlight® on SAP ASE tell you what is happening in the system(s ) that you are currently connected to. The supplied information is displayed in:
The main Spotlight on SAP ASE page, including individual panels, components, and specific menu and toolbar options.
The specific drilldowns accessible from that page.
The individual alarms that relate to Spotlight on SAP ASE.
The Spotlight on SAP ASEOptions window.
Features that are common to all Spotlight applications.
These are the features that allow you to manage (and customize) the behavior of Spotlight® on SAP ASE and any other Spotlight applications installed on your computer. These features are described in detail in the section Concepts and features in Spotlight Basics. They include:
A standard set of menu, toolbar, connection and help options.
A set of editors (Console options, Metric and Properties) for customizing the behavior of the current Spotlight connection.
Features that allow you to configure and use Spotlight.
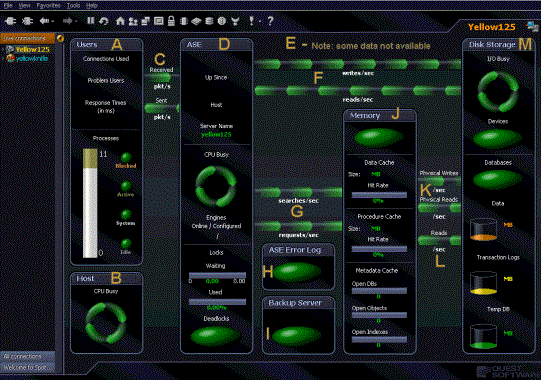
The main Spotlight on SAP ASE window provides a quick and intuitive view of the activity of an ASE instance.
The Spotlight on SAP ASE window helps you locate system bottlenecks quickly. Related server statistics are grouped together on panels that are connected by a series of graphical flow and icons. Spotlight on SAP ASE updates these flows in real time so that you can see how quickly data is moving through the system. The icons change color as their values move through the range of thresholds.
The following graphic shows the main features of the Spotlight on SAP ASE window. The list at the bottom of this page identifies each element, and provides a link to display more information.
|
| |