Map Source and Target Columns
When source and target column names are different, you can specify an explicit column mapping in the configuration file, to ensure that Post applies row data to the correct target columns.
Guidelines for using column mapping
-
To use column mapping, you must map every column in a source table to a column in the target table, even if only some source and target names are different. When some columns are mapped but not others, the entry is considered to be a column partition for vertically partitioned replication, and data changes for non-listed columns are not replicated.
- If the spelling case is different between the source and target column names, enclose them within quotes.
- You can use horizontally partitioned replication and column mapping for the same source table, but you cannot combine column mapping with vertically partitioned replication.
- A target table can have more columns than the source table, but there must at least be a target column for every source column.
- ALTER TABLE to add a column to a table that is configured with column mapping is not supported.
Configure column mapping
The following syntax creates a column map. For more information, see Configure SharePlex to Replicate Data.
| datasource_specification |
|
|
| src_owner.table (src_col,src_col,...) |
tgt_owner.table (tgt_col,tgt_col,...) |
routing_map |
| datasource_specification |
The datasource specification. For more information, see Database Specifications in a Configuration File. |
| src_owner.table and tgt_owner.table |
The specifications for the source and target tables, respectively. For more information, see Create a Configuration File. |
|
(src_col,src_col,...) |
A list of the source columns.
Follow these rules to specify a column list:
- A column list must be enclosed within parentheses.
- Separate each column name with a comma. A space after the comma is optional.
- The maximum length of a column list is 174820 bytes (the maximum line length allowed in a configuration file).
|
| (tgt_col,tgt_col,...) |
A list of the target columns.
- List the target columns in the same logical order as their corresponding source columns. This is required regardless of the actual order of the target columns in the table, so that SharePlex builds the correct map in the object cache. For example, a change to the second column in the source list is replicated to the second column in the target list.
- The syntax rules for the source list also apply to the target list.
|
| routing_map |
The routing map. For more information, see Routing Specifications in a Configuration File. |
Configuration example
This example contains no case-sensitive columns.
|
Datasource o.oraA |
|
|
|
sales.prod (ID,name,vendor) |
mfg.prod (UPC,product,supplier) |
sysB@o.oraB |
This example contains case-sensitive columns.
|
Datasource o.oraA |
|
|
|
sales.prod (ID,"name",vendor) |
mfg.prod (UPC,"product",supplier) |
sysB@o.oraB |
SharePlex provides the following scripts to automate the building of a configuration file to specify Oracle source objects.
- config.sql: configure all tables and optionally all sequences in the database.
- build_config.sql: configure multiple or all tables in a schema
Supported databases
Oracle
Use config.sql
The config.sql script enables you to build a configuration that lists all of the tables, and optionally all of the sequences, in all of the schemas of a database. This script saves time when establishing a high-availability replication strategy or other scenario where you want the entire database to be replicated to an identical secondary database.
Conditions for using config.sql
To run config.sql:
-
Change directories to the config sub-directory of the SharePlex variable-data directory. The config.sql script puts configurations in the current working directory, and SharePlex configurations must reside in the config sub-directory.
cd /vardir/config
- Log onto SQL*Plus as SYSTEM.
-
Run config.sql using the full path from the util sub-directory of the SharePlex product directory.
@ /proddir/util/config.sql
Refer to the following table when following the prompts:
| Target machine |
The name of the target machine, for example SystemB. |
| Source database SID |
The ORACLE_SID of the source (primary) Oracle instance, for example oraA. Do not include the o. keyword. The ORACLE_SID is case-sensitive. |
| Target database SID |
The ORACLE_SID of the target (destination) Oracle instance, for example oraB. Do not include the o. keyword. The ORACLE_SID is case-sensitive. |
| Replicate sequences |
Enter y to replicate sequences or n not to replicate sequences. |
| SharePlex oracle username |
The name of the SharePlex user in the source database. This entry prevents the SharePlex schema from being replicated, which would cause replication problems. If a valid name is not provided, the script fails. |
Note: The name assigned by SharePlex to the configuration is config.file. If you run the script again to create another configuration file, it overwrites the first file. To preserve the original file, rename it before you create the second one.
Next steps:
-
If any tables or owners are case-sensitive, open the configuration file with the edit config command in sp_ctrl, then use the text editor to enclose case-sensitive table and owner names within double-quote marks, for example “scott”.“emp”. The script does not add the quote marks required by Oracle to enforce case-sensitivity.
sp_ctrl> edit config filename
-
To ensure that the configuration is in the correct location, issue the list config command. If the name of the configuration is not shown, it was created in the wrong directory. Find the file and move it to the config sub-directory of the variable-data directory.
sp_ctrl> list config
Use build_config.sql
The build_config.sql script enables you to build a configuration that contains multiple (or all) tables in a schema. It is an interactive script that prompts for each component of the configuration step by step. Instead of entering the information for each object and the routing individually, you can use a wildcard to select certain tables at once, or you can select all of the tables in the schema.
Conditions for using build_config.sql
- Source and target table names must be the same.
- The script does not support sequences. Before you activate the configuration that the script builds, you can use the edit config command in sp_ctrl to add entries for sequences.
- The script does not support partitioned replication. You can use the copy config command to copy the configuration that the script builds, then use the edit config command to add entries for the tables that use partitioned replication. Activate the new configuration, not the original.
- The script does not configure objects in the SYS, SYSTEM, and SharePlex schemas. These schemas cannot be replicated since they are system and/or instance-specific.
- You can run build_config.sql for different schemas, then combine those configurations into one configuration by using a text editor. Make certain to eliminate all but one Datasource:o.SID line, which is the first non-commented line of the file. Do not move the file out of the config sub-directory.
- You can use the edit config command to make any other changes as needed after the configuration is built.
To run build_config.sql:
-
Change directories to the config sub-directory of the SharePlex variable-data directory. The build_config.sql script puts configurations in the current working directory, and SharePlex configurations must reside in the config sub-directory.
cd /vardir/config
- Log onto SQL*Plus as SYSTEM.
-
Run build_config.sql using the full path from the util sub-directory of the SharePlex product directory.
@ /proddir/util/build_config.sql
Refer to the following table when following the prompts.
| Target machine |
The name of the target machine, for example SystemB. |
| Source database SID |
The ORACLE_SID of the source (primary) Oracle instance, for example oraA. Do not include the o. keyword. The ORACLE_SID is case-sensitive. |
| Target database SID |
The ORACLE_SID of the target (destination) Oracle instance, for example oraB. Do not include the o. keyword. The ORACLE_SID is case-sensitive. |
| Owner of the source database tables |
The owner of the source tables. |
| Owner of the target database tables |
The owner of the target tables. |
| Table name to include (blank for all) |
Do one of the following:
- Press Enter to accept the default, which selects all tables that belong to the source owner.
- Enter a wildcard (%) character and a string to select certain tables, for example %e_salary%.
- Enter an individual table name.
|
| Name of the output file to create |
A name for the configuration. The script gives the file a .lst suffix, for example Scott_config.lst. |
Next steps:
-
If any tables or owners are case-sensitive, open the configuration with the edit config command in sp_ctrl, then use the text editor to enclose case-sensitive table and owner names within double-quote marks, for example “scott”.“emp”. The script does not add the quote marks required by Oracle to enforce case-sensitivity.
sp_ctrl> edit config filename
-
To ensure that the configuration is in the correct location, issue the list config command. If the name of the configuration is not shown, it was created in the wrong directory. Find the file and move it to the config sub-directory of the variable-data directory.
sp_ctrl> list config
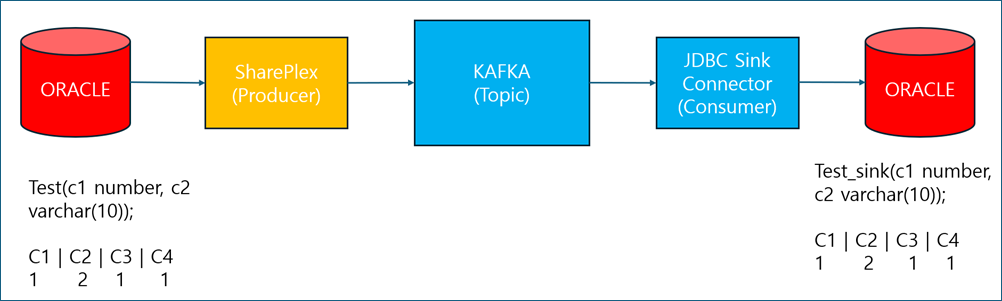
SharePlex supports data replication in an AVRO format with schema registry and JDBC sink connector.
Supported source and target
Oracle to Kafka
Pre-requisites:
-
Enable supplemental logging for all columns.
-
Tables in replication should have key(s) defined.
-
Set the SP_OCT_REDUCED_KEY parameter to 0 to ensure that the before-image of all columns, except for LONGs/LOBs, is available with each UPDATE or DELETE record.
-
For a basic implementation, both key and value schemas must be used to minimize or eliminate the need for transformation in the JDBC sink connector.
-
Each table should have a corresponding Kafka topic, with a separate JDBC sink connector configured for each table.
-
The table name should match the Kafka topic name. The naming convention for Kafka topics should follow the format schema.tablename.
-
SharePlex supports the Kerberos (SASL_PLAINTEXT) and SASL PLAIN authentications for Oracle to Confluent Kafka replication with AVRO format.
Data replication procedure in AVRO format
-
SharePlex captures data from the source Oracle database and replicates it to Kafka.
-
A JDBC Sink Connector reads the data from the Kafka topic and replicates it to the target Oracle database.
Schema registry and format
Kafka property schema.registry.url with default value empty will be introduced. It need to be set with its proper value using target x.kafka set kafka schema.registry.url = <url value>.
Using the JDBC Sink connector
Kafka topic configuration
-
Each table should have a separate Kafka topic, and each topic must have a corresponding JDBC Sink Connector.
-
The Kafka topic name should match the table name, following the naming convention schema.tablename.
Support for Delete and Update operations
Delete operations: To enable delete operations with the JDBC Sink Connector, the record key is required. It can be retrieved directly from the Kafka topic using the key schema, or extracted from the value schema using built-in transformations if the key schema is not used. The delete.enabled parameter must be enabled in the JDBC Sink Connector configuration.
Update operations: Since updates are not represented in "before" and "after" values, updates on key columns are handled with two events: first, a delete event with the old key values, followed by an insert event with the new key values.
LOB columns and field filtering
LOB columns: LOB columns cannot be part of keys in SharePlex. If a non-LOB column is updated, the data for LOB columns will not be available in the before or after image. In such cases, a placeholder value _splex_default will be used (excluding binary LONGs/LOBs mapped to AVRO bytes such as LONG RAW, BLOB). These columns can be conditionally filtered out using the ReplaceField transform with predicates.
Following is an example of transform and predicate configuration for JDBC Sink connector:
transforms.col_clob.type = org.apache.kafka.connect.transforms.ReplaceField$Value
transforms.col_clob.exclude = COL_CLOB
transforms.col_clob.predicate = col_clob
transforms.col_long.type = org.apache.kafka.connect.transforms.ReplaceField$Value
transforms.col_long.exclude = COL_LONG
transforms.col_long.predicate = col_long
predicates.col_clob.type = de.denisw.kafka.connect.jmespath.MatchesJMESPath$Value
predicates.col_clob.query = COL_CLOB == '_splex_default'
predicates.col_long.type = de.denisw.kafka.connect.jmespath.MatchesJMESPath$Value
predicates.col_long.query = COL_LONG == '_splex_default'
Filtering fields: Filtering specific fields is not supported by built-in transforms alone. The kafka-connect-jmespath plugin, an add-on, must be installed to enable this functionality.
Supported DDL operations
SharePlex supports the DDL operations like `ALTER TABLE ADD or DROP COLUMN`. The schema evolves based on these operations. However, schema changes should not be automatically replicated to the target using the JDBC Sink Connector to avoid incorrect datatype creation. Thus, auto.create and auto.evolve settings in the JDBC Sink Connector should be disabled. Changes must be applied manually to the target table, and the connector should be restarted afterward.
Configuring Kafka properties
The Kafka property schema.registry.url (default value empty) must be set correctly using target x.kafka set kafka schema.registry.url = <url value>.
The AVRO property datetime_logical (default is `yes`) determines whether datetime datatypes are mapped to AVRO logical datatypes or to AVRO strings. If set to `no`, formats need to be specified according to Oracle DB's NLS formats (Examples: NLS_DATE_FORMAT, NLS_TIMESTAMP_FORMAT).
AVRO property datetime_logical with default yes will be introduced. If set to yes, datetime datatypes will be mapped to respective AVRO logical datatypes otherwise will be mapped to AVRO string datatype. If it is set to no, respective data formats need to be set. These formats need to be derived from Oracle DBs NLS formats like NLS_DATE_FORMAT, NLS_TIMESTAMP_FORMAT and NLS_TIMESTAMP_TZ_FORMAT. Formatting keywords are case insensitive.
The following keywords can be part of these formats, which can be in uppercase or lowercase:
-
DD: Represents a two-digit date value (example: 25).
-
MM: Represents a two-digit month value (example: 12).
-
MON: Represents a three-letter month value (example: JAN).
-
YYYY: Represents a four-digit year value (example: 2024).
-
YY: Represents the last two digits of the year value (example: 24).
-
HH: Represents a two-digit hour value. If AM/PM is not present, it will be represented in a 24-hour format; otherwise, in a 12-hour format (example: 10).
-
MI: Represents a two-digit minute value.
-
SS: Represents a two-digit seconds value.
-
F: Represents a fractional value; the number of digits will depend on the source datatype precision (example: 123456).
-
AM/PM: Represents the meridian indicator (example: AM).
-
Z: Represents the time zone. It can be in the form of an offset value or a region name, depending on what is received from the source (example: +05:30 or ASIA/CALCUTTA).
Example of setting parameters for AVRO formatting
JDBC Sink connector configuration example
Once the Kafka topic and key-value AVRO schemas are created, configure the JDBC Sink Connector. Below is an example configuration file that can be uploaded to Confluent Kafka Control Center's Connect section:
File name: `connector_DEMO_BASIC_DT_config.properties`
Content:
name = DEMO_BASIC_DT
connector.class = io.confluent.connect.jdbc.JdbcSinkConnector
key.converter = io.confluent.connect.avro.AvroConverter
value.converter = io.confluent.connect.avro.AvroConverter
topics = <schema name>.DEMO_BASIC_DT
connection.url = jdbc:oracle:thin:@10.250.14.177:1521:p19c
connection.user = <user name>
connection.password = <password>
dialect.name = OracleDatabaseDialect
insert.mode = upsert
delete.enabled = true
table.name.format = ${topic}
pk.mode = record_key
pk.fields = COL_SMALLINT, COL_INT
quote.sql.identifiers = never
value.converter.schema.registry.url = http://localhost:8081
key.converter.schema.registry.url = http://localhost:8081
If column names are different on Oracle source and Oracle target, then need to add transform for that particular column in Control Center
Example: "transforms.col_char.renames": "COL_CHAR:col_char"
Limitations:
-
An UPDATE on a key column results in a DELETE operation followed by the INSERT. If the UPDATE does not include data for LOB columns, those columns will become empty.
-
The Confluent kafka-connect-jmespath predicate plugin, used for filtering fields, does not support the AVRO BYTES datatype. Therefore, binary LONGs/LOBs (such as LONG RAW and BLOB) mapped to AVRO BYTES cannot be filtered out. When such columns lack data, they are populated with the value _splex_default during updates, which must be filtered out using appropriate transform and predicate configurations.
-
Commit operations are not directly posted as commits. They are handled by the JDBC Sink Connector and are configurable with JDBC Sink Connector configurations, which commits after a configurable limit is reached.
-
TRUNCATE operations are not supported by the JDBC Sink Connector. The Poster will ignore any TRUNCATE transactions.
-
DateTime Handling with AVRO parameter datetime_logical set to yes using the Target command datetime_logical = yes:
-
Timestamp precision is supported up to milliseconds.
-
Timestamps with timezones do not retain timezone information and must be mapped to TIMESTAMP.
-
DATE and TIMESTAMP can store values only after 01-Jan-1970. If earlier values are received, processing stops with an error.
-
If an Oracle Date datatype includes TIME, the JDBC Sink Connector will fail to insert the record in the Oracle target database when datetime_logical is set to `no` and the date format includes time. |


