Recovery Manager for Active Directory (RMAD) provides the facility to create backups of the Active Directory® components on domain controllers, including the Active Directory® database and Windows Server® Bare Metal Recovery (BMR) backups.
Both types of backups can be created for any Active Directory® domain controller available on the network. Backup creation is a task that can be performed on a regular basis without interrupting the operation of the domain controller.
RMAD lets you organize domain controllers into collections, and establish a backup scheduling frequency and “allowed hours” during which the backup process may run. Based on the frequency of updates to the directory data store, you can configure a backup schedule for each collection.
Depending on the requirements of your enterprise, you can configure a retention policy to specify how many backups are retained: for example, all saved backups or a number of the most recent backups. Different policy settings can be specified for different domain controller collections.
For Active Directory® backups, it is not necessary to maintain a single, centralized repository: several repositories, perhaps based on the site topology, can make your deployment more WAN-friendly. To minimize bandwidth consumption, RMAD employs agents that compress the data to be backed up, before sending it across the network.
RMAD allows backups to be encrypted and protected with a password, to prevent unauthorized access. This password is used to generate a passphrase with which the backup is encrypted.
For Active Directory® backup encryption, the product uses Microsoft’s implementation of the AES-256 algorithm from RSA, Inc. (Microsoft Enhanced RSA and AES Cryptographic Provider), with the maximum cipher strength. The use of the Microsoft Enhanced RSA and AES Cryptographic Provider ensures that backups are encrypted with 256–bit cipher strength
You can have RMAD keep unpacked Active Directory® or AD LDS (ADAM) backups in any appropriate location on your network.
Unpacked backups can be reused for subsequent starts of the Online Restore Wizard or Group Policy Restore Wizard. The use of unpacked backups accelerates the backup data preparation step of those wizards, because the unpacking process may be a lengthy operation.
RMAD makes it possible to use Active Directory® or AD LDS (ADAM) backups created with third-party backup tools. Before using this feature, unpack the backup to an alternate location with the corresponding third-party backup tool, and then register the database file (ntds.dit or adamntds.dit) using the Online Restore Wizard or Online Restore Wizard for AD LDS (ADAM), respectively.
When backing up Global Catalog servers, you have the option to force RMAD to collect group membership information from all domains within the Active Directory® forest. This option ensures that group membership spanning multiple domains is fully backed up.
It is recommended that you restore objects from Global Catalog backups that were created with this option. Otherwise, restored objects may not retrieve their membership in some local groups, because even Global Catalog servers do not store full information about group memberships. For example, information about membership in domain local groups is only stored in the home domains of those groups.
In an Active Directory® environment, each domain controller maintains its own Active Directory® database. Therefore, a backup of the Active Directory® database is domain controller-specific. To completely back up Active Directory®, you must back up the directory database on every domain controller.
To restore deleted or corrupted objects, it is recommended to back up at least two domain controllers for each domain for redundancy. If you intend to restore cross-domain group membership information, then it is also necessary to back up a global catalog server.
Another reason for backing up the directory database on every domain controller is loose consistency. Replication of changes made to Active Directory® does not occur immediately. The replication process first accumulates all changes, and then provides them to the participating domain controllers. As a result, the directory database on any domain controller is normally in a state of loose consistency. The directory object data on individual domain controllers differs to some extent, given that replication updates are either in transit between domain controllers, or waiting to be initiated.
The age of the backup must also be considered. Active Directory® prevents the restoration of data older than the "tombstone lifetime" - a setting specified in Active Directory®. Because of this, an Active Directory® backup should be created at least once within the tombstone lifetime. However, it is strongly recommended that backups of the directory database be created more often than this.
Backups created with Recovery Manager for Active Directory can be stored in multiple locations. Primary storage of backups allows for backup files to be saved on a distributed network, or on selected computers with physically restricted access. Recovery Manager considers these locations as primary storage and is referred to as Tier 1 storage.
Recovery Manager for Active Directory provides options for primary storage in local and remote locations. Local storage is refers to storage on the Recovery Manager console computer, where remote storage is storage on the backed up domain controller or other remote servers on network shares. These locations are remote due to not being on the Recovery Manager console computer. See the Local Storage tab and Remote Storage tab. For both local and remote storage locations, a primary backup path can be provided and an alternate backup path.
Primary storage is for the original backup files to be saved to the a safe location. For primary storage, the backup agent creates the backup file, compresses the data and then the file is saved to the configured storage locations. In the diagram below see line number 1 to view the process that is taken to save the backup file to primary storage locations. The RPC protocol is used to save backups files to the console computer. For saving to remote storage locations SMB protocols are used.
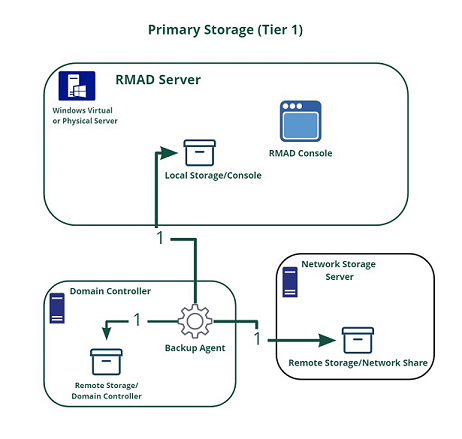
The figure illustrates how Recovery Manager for Active Directory creates and saves backup files to primary storage locations.
| NOTE |
For Recovery Manager for Active Directory 10.1 or higher: Make sure that you use the Backup Agent version supplied with this release of Recovery Manager for Active Directory. |
Recovery Manager for Active Directory employs a Backup Agent to back up remote domain controllers and AD LDS (ADAM) hosts. This is because some backup APIs provided by the operating system cannot be used to access a target domain controller or AD LDS (ADAM) host from the Recovery Manager Console. Therefore, Backup Agent must be installed on a remote domain controller or AD LDS (ADAM) host in order to gain access to its specific objects. RMAD can automatically install Backup Agent before starting a backup, and remove it upon the completion of backup operation. Alternatively, you can preinstall Backup Agent manually. For more information on the advantages of using preinstalled Backup Agent, see Using preinstalled Backup Agent below.
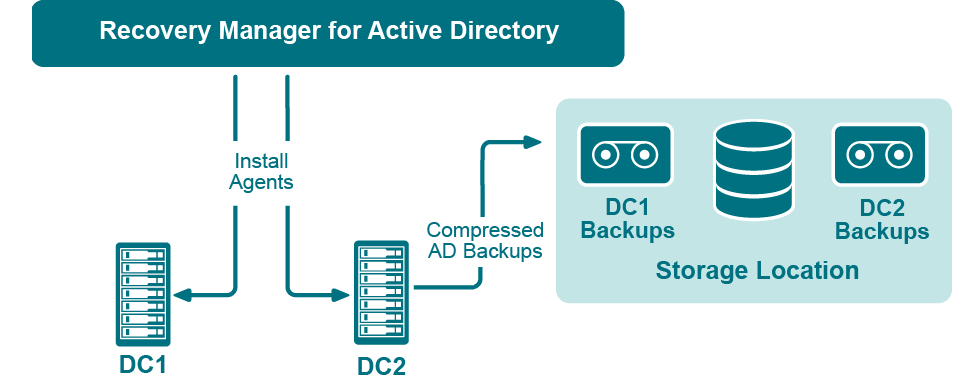
The Recovery Manager for Active Directory (RMAD) employs a Backup Agent when creating backups. The Backup Agent is installed on domain controllers DC1 and DC2 and compresses the data and transfers the compressed data to storage location.
Since Backup Agent compresses the data before sending it over the network, the network load is decreased significantly. The average compression ratio is 7:1. The use of Backup Agent also provides increased scalability and performance by allowing the creation of backups on multiple domain controllers in parallel.
RMAD allows to run Backup Agent in the security context of a specific user account. Since RMAD needs administrative access to the domain controller in order to run Backup Agent, the account under which RMAD is running must belong to the Administrators group on that domain controller or AD LDS (ADAM) host, providing administrative access to the entire domain. If RMAD cannot be started under such an account, separate credentials (user logon name and password) should be specified, so that Backup Agent is run under an account that has sufficient privileges.
RMAD allows you to back up Computer Collections using Backup Agent manually preinstalled on each target domain controller. This method enables you to
Perform a backup operation without having domain administrator privileges. It is sufficient if RMAD runs under a backup operator's credentials.
Reduce network traffic when backing up the Computer Collection.
Back up domain controllers in domains that have no trust relationships established with the domain in which RMAD is running, solving the so-called “no trust” problem.
Recovery Manager for Active Directory (RMAD) enables the recovery of a portion of the directory or the entire directory, in the event of corruption or inadvertent modification. The granular, object-level, online restore may also be used to undelete directory objects. These powerful, security-sensitive functions of RMAD should only be performed by highly trusted directory administrators.
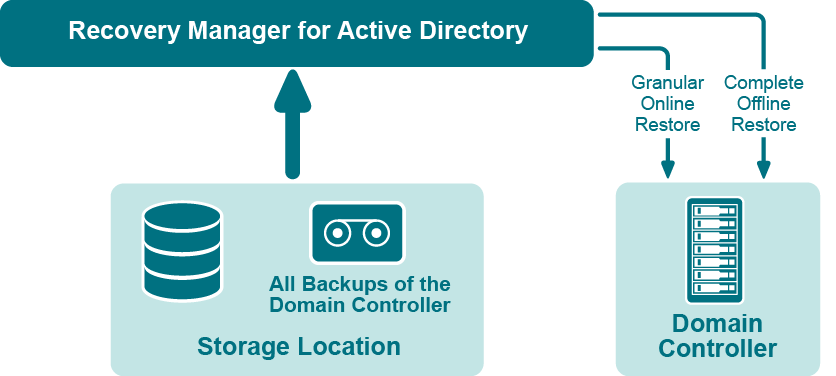
If certain objects are inadvertently deleted or modified in Active Directory, they can be restored from a backup of domain controller’s Active Directory® components, without restarting the domain controller or affecting other objects. If the Active Directory® database on a particular domain controller has been corrupted, the entire database can be restored from a Active Directory® backup created for that domain controller. All the restore operations are administered remotely.
Recovery Manager for Active Directory offers the following restore methods:
Granular online restore. Allows you to select Active Directory® objects from a backup, and then restore them to Active Directory®. This method allows for the recovery of individual Active Directory® objects, and selected attribute values in Active Directory® objects, with the least amount of administrative effort.
Complete offline restore. Restarts the target domain controller in Directory Services Restore mode, restores the Active Directory® database from the selected backup, and then restarts the domain controller in normal operational mode. This method enables the recovery of the entire Active Directory® database on a domain controller, and is most useful when recovering from database corruption.
Recovery Manager for Active Directory supports granular online restore from BMR backups.