Known complications between Foglight and Antivirus or Anti-malware products
It is recommended that the services / processes be disabled on the server running a FMS repository
- Sophos HitmanPro (part of the Sophos Endpoint Protection application)
- Crowdstrike
- Cylance
Identifying the presence of Anti-Virus or Anti-malware software running on the server from Windows Server Desktop.
Users may be able to use the following steps to review the Antivirus configuration on a Windows server.
- Identify the Antivirus being run on the server.
Most Windows Antivirus applications run as a Windows Service. Users can review the current running Windows Services from the Windows Control Panel to check for an actively running Antivirus such as "Microsoft Antimalware Service" used by Windows System Center 2012 Endpoint Protection.
Foglight Agent Manager support bundles also lists services running on the FglAM server are listed in the support bundle \systeminfo\runningservices.log or \system\Windows-system-info.txt files. Running services are indicated in the STATE field. - Find the paths where Agent Managers are running
Check the properties of the Windows Service to locate the installation folder for the FglAM for the "Agent Manager" or "Foglight Agent Manager" services. There may be multiple services running on a server.
With a FglAM support bundle, this value can be found in the first FglAM log (001) of a series and then looking for the “-Dquest.state.dir” value in the log file.
Or this Powershell query would pull the locations for all FglAMs installed in Windows Services
Get-WmiObject win32_service | ?{$_.PathName -like '*fglAM.exe*'} | select Name, DisplayName, State, PathName - Confirm the location for the FMS embedded database data file directory
These are typically located in
MySQL: $FGLHOME\mysql\data
Postgress: $FGLHOME\state\postgresql-data - Review the exclusions for the Antivirus software.
Many running Antivirus application services place an icon in the Windows taskbar. By right clicking this icon, the Antivirus settings and exclusions may be visible.
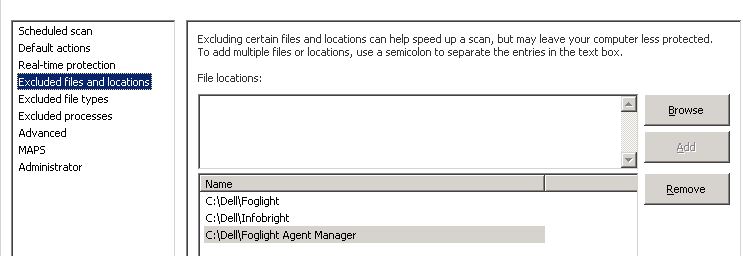
For Windows System Center Endpoint Protection, the following two Powershell queries can be used to retrieve the exclusions
Get-ItemProperty 'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Microsoft Antimalware\Exclusions\Paths' | select *
Get-ItemProperty 'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Microsoft Antimalware\Exclusions\Paths' | select *
You can also manually check for antivirus software on desktops (Windows 7, Windows 10) using this wmi query.
(From DOS) wmic /NAMESPACE:\\root\SecurityCenter2 PATH AntiVirusProduct Get displayname /Format:List
Windows desktops have these SecurityCenter2 WMI objects, but the namespace doesn’t exist on servers
(from PowerShell) Get-WmiObject -Namespace "root\SecurityCenter2" -Query "SELECT * FROM AntiVirusProduct"
