Secure Storage is enabled and configured for each Computer Collection separately. The Secure Storage backup can be enabled for both local and remote storage. When a backup is run for a Computer Collection with Secure Storage enabled, a copy of the backup is saved to the Secure Storage server.
Prerequisites
You must have completed the following steps before you can copy backups to your Secure Storage server.
Secure Storage servers must be created and hardened.
Computer Collections must be created.
The backup type, either Standard (Active Directory®) or Full (Bare Metal Recovery), must be set for the Computer Collection.
| NOTE |
Both Active Directory® and Bare Metal Recovery backups can be copied to a Secure Storage server. |
To enable a Secure Storage server for a Computer Collection
In the Recovery Manager for Active Directory console, expand the Computer Collections node.
Right-click the Computer Collection and select Properties.
On the Secondary Storage tab, select the Enable a Secure Storage server check box.
Select the radio button below Enable a Secure Storage server to choose the primary storage location for the backup file to be copied from. Select Copy backup from local storage location to the selected Secure Storage server to push the backup file from the local storage location.
If using both local and remote storage options for primary storage, the recommendation is to configure your Secure Storage server to communicate with the primary storage location closest for optimal network performance.
Under Copy backup from local storage location to the selected Secure Storage server, select the dropdown box and select a Secure Storage host.
| NOTE |
For both Secure Storage and Cloud Storage you may have to provide access credentials to be able to read from the primary storage location. If both types of primary storage are configured, Cloud Storage will default to copying from local storage. |
For the An account to read data from remote storage location: click on Select Account… button and add an account to read the backup data. It will be the same account that is used to access the Secure Storage server.
For the An account to read data from local storage location: click on Select Account… button and add the account to read the local storage backup data. It will be the same account (probably account used for RMAD) that is used to store the back data locally.
Click Apply then click OK.
To create backups and copy them to the Secure Storage server
In the Recovery Manager for Active Directory console, expand the Computer Collections node.
Right-click the Computer Collection and select Create Backup.
After the backup file is created and saved to primary storage locations, the backup will be pushed to the configured Secure Storage server.
| TIP |
You can schedule backup creation on the Schedule tab on the Computer Collections Properties window. |
To perform an integrity check
When a backup is created, a checksum is calculated for the backup file and saved in the backup file when the backup is registered. An integrity check recalculates the checksum and compares it to the checksum stored in the backup file.
In the Recovery Manager for Active Directory console, click on Secure Storage and expand the server node(s).
Click the Secure Storage server that contains the backup you want to perform the integrity check on.
In the Backups on the Secure Storage Server pane, click the backup to check, right click and select Check Integrity.
The following statuses can be displayed after running the integrity check:
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| Passed | The newly calculated checksum value matches the previously calculated checksum stored in the backup file. |
| Unknown | The integrity check was not performed. |
| Running | The integrity check is in progress. |
| Failed | The backup is not accessible (wrong credentials) or may have been moved from the path. |
| No Checksum | The previously calculated checksum could not be read. This could be due to the backup being created by a previous version of the product. The backup also may have been damaged in such a way that the checksum was also affected. |
| Corrupted | The newly calculated checksum value does not match the previously calculated checksum stored in the backup file. |
You can copy backups stored on the Secure Storage server to another location.
In the Recovery Manager for Active Directory console, click on Secure Storage and expand the server node(s).
Select the Secure Storage server that you want to copy backups from.
In the Backups on the Secure Storage Server pane, right-click the backup you want to copy and select Copy to.
In the Network path to copy the backup to field, type the network path to which you want to copy the backup.
In the User name and Password fields, type credentials that have write permissions for the network path.
Click OK.
The backup is copied to the provided network path and can now be registered for use within a recovery project.
If you create backups on a daily basis as recommended, you should configure a backup retention policy to maintain the backups created. It is recommended to maintain at least 2 weeks (14 days) of backups including backups on your Secure Storage server. This approach will provide you with a sufficient number of backups to recover from an Active Directory® failure that remained undetected for some time.
| note |
The default number of days to retain backups is 0 days. Ensure you configure the backup retention policy after adding a new Secure Storage server. |
To configure backup retention policy directly on the Secure Storage server
During the installation of the Secure Storage agent on the Secure Storage server, a PowerShell® module was installed and is located in the agent installation folder.
On the Secure Storage server, run Windows PowerShell. The module will automatically be imported.
To configure backup retention policy, run the cmdlet Set-RMADStorageServerRetentionPolicy. For further details on Set-RMADStorageServerRetentionPolicy see the Management Shell Guide supplied with this release of the product.
To get the current backup retention policy on the Secure Storage server
During the installation of the Secure Storage agent on the Secure Storage server, a PowerShell® module was installed and is located in the agent installation folder.
On the Secure Storage server, run the PowerShell console. The module will automatically be imported.
To configure backup retention policy, run the cmdlet Get-RMADStorageServerRetentionPolicy. For further details on Get-RMADStorageServerRetentionPolicy see the Management Shell Guide supplied with this release of the product.
After the Secure Storage server has been hardened some of the following such as, all incoming TCP ports are blocked by IPSec policies, ICMP traffic is blocked and only one TCP agent port is left open (48001) for communication with Recovery Manager for Active Directory, there may be a need to add an exception to these items to perform maintenance For example, opening a port to allow for Microsoft system updates.
| Warning |
Keeping exceptions in place for an extended period of time is not recommended. Secure Storage server exceptions should be removed as soon as possible after the need for the exception has finished. |
If an exception has been applied to a Secure Storage server the Security Status will read Secured with exceptions as seen below.
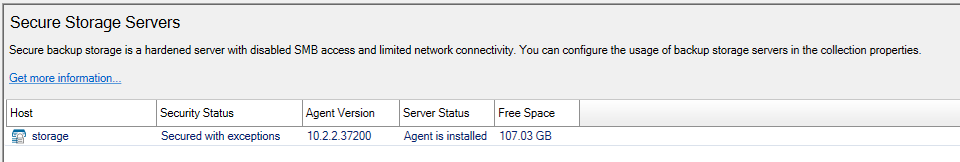
To configure an exception on the Secure Storage server for ICMP or ping
During the installation of the Secure Storage agent on the Secure Storage server, a PowerShell® module was installed and is located in the agent installation folder.
On the Secure Storage server, run Windows PowerShell. The module will automatically be imported.
To configure an exception for ICMP so that you can ping the Secure Storage server, run the cmdlet Add-RMADStorageServerException -Name "ping" -SourceAddress Any -DestinationAddress Me -Protocol Icmp. For further details on Add-RMADStorageServerException see the Management Shell Guide supplied with this release of the product.
To get the exceptions on the Secure Storage server
During the installation of the Secure Storage agent on the Secure Storage server, a PowerShell® module was installed and is located in the agent installation folder.
On the Secure Storage server, run the PowerShell console. The module will automatically be imported.
To list the exceptions for a Secure Storage server, run the cmdlet Get-RMADStorageServerException. For further details on Get-RMADStorageServerException see the Management Shell Guide supplied with this release of the product.
To remove the exceptions on the Secure Storage server
During the installation of the Secure Storage agent on the Secure Storage server, a PowerShell® module was installed and is located in the agent installation folder.
On the Secure Storage server, run the PowerShell console. The module will automatically be imported.
To remove an exception for ICMP, run the cmdlet Remove-RMADStorageServerException -Name "ping". For further details on Remove-RMADStorageServerException" see the Management Shell Guide supplied with this release of the product.
Recovery Manager for Active Directory integration with On Demand Recovery enables the restoration and undelete of on-premises objects that are synchronized with Azure Active Directory.
The Hybrid Connector Windows service establishes a secure connection to the On Demand Recovery online service enabling simultaneous restoration of both on-premises and online objects.
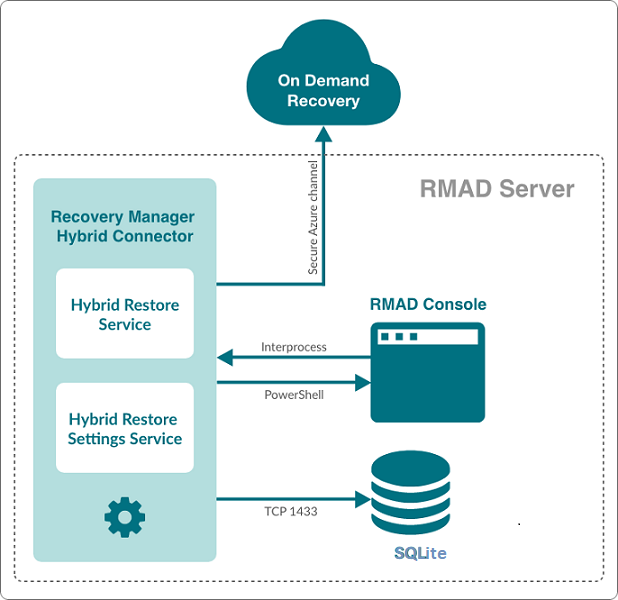
The TLSv1.2 protocol is enforced for the Hybrid Connection Service when communicating with On Demand Recovery.
On-premises groups
Microsoft 365® licenses (assignedLicenses property for cloud users) and cloud group membership
Deleted on-premises users and groups
Service principals' appRoleAssignments to on-premises users
appRoleAssignments to non-Microsoft 365® groups (used for SSO and App Roles)
Directory roles: Global administrator, Exchange administrator, Compliance administrator
Other cloud-only properties: such as Block sign in, Authentication contact information, Minors and Consent
Multifactor authentication (MFA) settings if a customer uses cloud MFA
Azure® application custom attributes (schema extension attributes)
Conditional access policies
Inactive mailboxes of permanently deleted users; the Federated Domain scenario is also supported.
To restore on-premises objects, On Demand Recovery uses attribute values from the RMAD backup that is closest in time but older than the cloud backup unpacked in the On Demand Recovery user interface. If the closest on-premises backup is 24 hours older than the cloud backup, you will receive the warning message.
By default, the search of the closest in time on-premises backup is performed among the backups that were unpacked in RMAD. You can use the Use unpack and encrypted backups for restore operations option on Hybrid Recovery settings of RMAD – in this case, the on-premises backup will be unpacked automatically during the restore operation.
On Demand Recovery shows only on-premises attributes synchronized with the cloud and cloud-only attributes for the selected object when you click Browse in the Restore Objects dialog. On-premises only attributes are not included in this list. To restore on-premises only attributes, you must select the Restore all attributes option in the Restore Objects dialog.
After the hybrid restore operation, On Demand Recovery forces Azure AD Connect synchronization to push on-premises changes to the cloud and wait until it completes the synchronization. Restore events can be used to track steps of Azure AD Connect synchronization, such as export and import.
To restore 'member' or 'memberOf' attributes for an object, restore the group from the Unpacked Objects view. Restoring of group memberships from the Differences report is not supported in hybrid environments.
Hybrid restore from the Differences report uses attribute values from the on-premises backup. These values may be different from the corresponding values shown in the Differences report.
On Demand Recovery supports one hybrid connection per On Demand organization. If you need to manage multiple hybrid tenants, create a separate On Demand organization for each Hybrid Azure AD tenant.
On Demand Recovery restores Back Link attributes: 'memberOf' (the back link for the 'member' attribute) and 'directReports' (the back link for the 'manager' attribute). These attributes can be selected along with all other attributes when you click Browse in the Restore Objects dialog.
Separate Microsoft Azure Relay service is used for each hybrid connection (one per On Demand organization). On Demand Recovery creates WCF Relay per On Demand organization. No changes to On-Premises Firewall settings are required.
On Demand Recovery users can restore objects from all on-premises domains and forests that are synchronized with the Azure AD tenant. Also, in Recovery Manager, you need to add domain controllers for every domain that will be restored and specify the account under which the restore operation will be performed.
Depending on which kind of restore operation (agent-based or agentless) you are going to perform in a hybrid configuration, the account under which you want the selected Recovery Manager for Active Directory instance to recover data in the domain must meet the corresponding requirements. For details about account permissions for agent-based and agentless restore, see Permissions required to use Recovery Manager for Active Directory.
To push an Azure® synchronization, the specified account must be a member of the ADSyncOperators group on the Azure® Active Directory® synchronization server. This account must also be able to run remote PowerShell commands against the server.
If hybrid integration is configured on the Web Portal it must be disabled prior to configuring hybrid integration from the Recovery Manager for AD (RMAD) console. Failure to do so may result in a failed online restoration.
Follow the steps below to fully disable hybrid integration on the Web Portal.
Logon to Web Portal
Select the “Configuration” tab at the top
Expand the “Portal Settings” expander
Click on the “Configure On Demand” button
Remove the checkmark from the “Enable integration” checkbox
Click “OK” to save and close the dialog
Open the Windows “Services” application
Find the Windows service “Quest Recovery Manager Portal” from the list
Right click on the service and select “Stop”
Once the service has been stopped it can then be re-enabled if desired
To continue using the Web Portal with newer versions of the RMAD console some configuration changes must be made.
For instructions on how to make the necessary configuration changes follow the steps below.
Navigate to the installation directory of the Web Portal (the default installation location is C:\Program Files (x86)\Quest\Recovery Manager Portal)
Open the file EnterprisePortalSettings.xml
Inside the GeneralSettings element find the property VersionValidationMode. If this property is not present one will have to be created
Change the value of the VersionValidationMode to None
Below is a sample of what the configuration should look like once the changes have been made.
<GeneralSettings>
<add key="VersionValidationMode" value="None" />
Other configuration values…
</GeneralSettings>
| NOTE |
Recovery Manager for Active Directory 10.3 no longer uses SQL Server® for Hybrid configuration. After upgrade to 10.3, it will be required to re-enter credentials for each domain listed under Discovered Domains. Previous versions of RMAD used SQL Server® and a database, RecoveryMgrHybridRestore, was created which contained the Hybrid information. This database can be deleted as it is no longer used. |
If Azure AD Connect (ADSync) is installed on a system or DC and not on the RMAD Console, PowerShell remoting must be enabled on the remote machine. If PowerShell remoting is not enabled, an Access Denied error will occur in the RMAD console when configuring Azure AD Connect settings:
Error is recorded in Portal log similar to the following:
From within the RMAD Console, select the Hybrid Recovery node from the tree on the left.
Select the Enable integration with On Demand Recovery checkbox to enable a secure connection to the online On Demand Recovery service.
Enter the On Demand Recovery Settings using the following procedure:
Enter in the Azure AD Connect host and its associated credentials under Azure AD Connector Settings. The values entered depends on where Azure AD Connect is installed.
NOTE: If Azure AD Connect is currently installed on the same server as the Recovery Manager for Active Directory console, then these fields can be left blank.
Azure AD connector Host: Enter in the host name or IP address of the system where Azure AD Connect is installed.
Username: Enter in the domain username for this server. This account should have the necessary permissions listed under the Required Permissions section.
Password: Enter in the domain password for this server.
Enter in the domain username, password and primary computer for each domain listed under Discovered Domains. The designated primary computer will be used for hybrid recovery operations.
The domains listed under Discovered Domains are pulled from backups; this means to fully populate this list at least one backup per domain is required.
After performing a backup, it may be necessary to manually refresh this list which can be done by clicking on the refresh button , 
Once all configuration has been entered click on the Save settings button located at the bottom of the screen