Analyzing Trends
For a single farm, Web application, or site collection, you can analyze trends over a specified time period in:
·activity
·site count, and/or
·storage.
To generate a Trends analysis:
1Select the object for which you want to analyze trends.
NOTE: You can only analyze trends for one object (farm, Web application, or site collection) at a time. If you multi-select, only the object on which you right-clicked will apply.
2Use the information in the following table to determine the appropriate action to take.
|
If you want to analyze trends in ... |
Choose ... |
|
activity |
Activity > Trend Analysis for Activity. |
|
site count |
Content > Trend Analysis for Site Count. |
|
storage |
Storage > Trend Analysis for Storage. |
Specify the following parameters for your analysis:
a)Enter or select a Start Date and End Date for your analysis.
The date range you select determines the time intervals captured in the analysis, as described in the following table.
|
If the time period you specified is ... |
Then the Trend Analysis will be reported ... |
|
up to 60 days |
by Day |
|
between 61 and 364 days |
by Week |
|
365 days or greater |
by Month. |
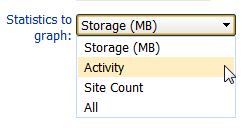
b)If you want to change the Statistics to Graph, select a different value from the drop-down.
c)If you want your graph to include a line that smooths out short-term fluctuations, check the Include moving Average box.
The default value for Moving average period (days) is 7, which represents the number of days within a given week. This value is useful for many business users who can expect less activity, for example, on the weekend. You can, however, change this value to measure moving average for a different time period. For example, if you generally experience week-to-week fluctuations over the course of a month, you may choose to set the Moving average period to 31.
Now you can:
·run the operation immediately (by clicking the [Run Now] button)
OR
·schedule the operation to run at a later time or on a recurring basis.
OR
·save the operation as XML Instructions that can be run at a later time.
Trend Analysis results consist of two graphs:
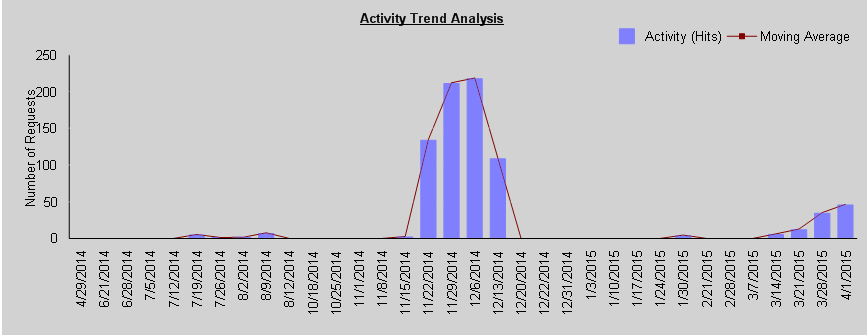
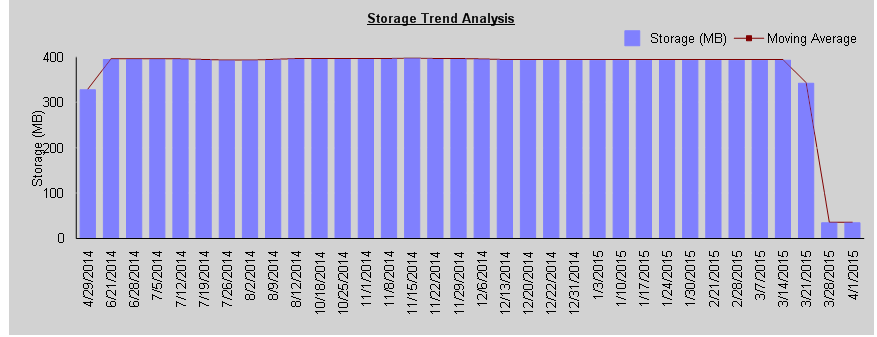
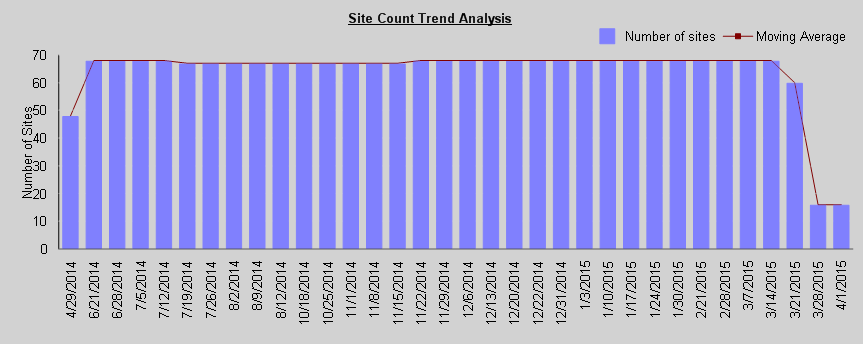
·The Trend Analysis bar graph includes the statistics for the selected criterion. (Note that if you selected ALL from the Statistics to graph drop-down, a separate graph will be included for each). Below are examples of Trend Analyses by Day reports (including a 7-day moving average) for Activity, Storage, and Site Count over the same 28-day time period.
Activity Trend Analysis
Storage Trend Analysis
Site Count Trend Analysis
·The second graph is a line graph that shows statistics for all three options (activity, storage, and site count) in terms of a percentage over the course of the selected time period. Note that the maximum value (100%) represents the most storage used, greatest level of activity, and largest site count over the selected time period.
Auditing Activities and Changes in Your SharePoint Environment
SharePoint captures activities and changes to the environment via the following mechanisms:
·the Audit Log, which focuses on activities performed by SharePoint users.
·the Change Log, which focuses on changes made to the SharePoint environment.
ControlPoint provides functionality that enables you to view contents of audit logs and change logs, which is not currently available in SharePoint.
Events Captured in SharePoint Logs
The following tables identify the log(s) where different types of events are recorded and the event codes used to identify them.
NOTE: Be aware that some events may not appear immediately in analysis results, as it can take several minutes for them to be recorded in the SharePoint log.
Add/Delete Site Collections, Sites, Libraries and Lists
|
Event |
Where Recorded (ControlPoint Event Type) |
|---|---|
|
·Site collection added ·Site added ·Library or list added |
Change Log (Add) NOTE: It may take several minutes for an added site to appear in the Change Log. |
|
·Site deleted ·Library or list deleted |
·Audit Log (Delete/Delete Child) NOTE: A Delete event is reported from the perspective of the object itself. A Delete Child event is reported from the perspective of the object's parent. ·Change Log (Delete) |
Add/Delete Document and List Items
|
Event |
Where Recorded (ControlPoint Event Type) |
|---|---|
|
Document or list item added |
·Audit Log (Update) ·Change Log (Add) |
|
Document or list item deleted |
·Audit Log (Delete/Delete Child) NOTE: A Delete event is reported from the perspective of the object itself. A Delete Child event is reported within the scope of the object's parent. ·Change Log (Delete) |
|
Document or list item restored |
·Audit Log (Undelete) ·Change Log (Restore) |
Other Actions on Document and List Items
|
Event |
Where Recorded (ControlPoint Event Type) |
|---|---|
|
·Document opened/downloaded ·List item viewed ·List item properties viewed |
Audit Log (View) |
|
·Document or list item edited ·Document or list item properties edited |
·Audit Log (Update) ·Change Log (Update) |
|
Item checked in/checked out |
·Audit Log (Check In/Check Out) ·Change Log (Update) |
|
Items moved to another location in the site |
Audit Log (Move) Change Log (Move Away/Move Into) |
|
Items copied to another location in the site (using the Send To menu entry) |
Audit Log (Update) |
|
Item accessed as part of a workflow |
Audit Log (Workflow) |
Add/Delete/Change Users and Permissions
|
Event |
Where Recorded (ControlPoint Event Type) (SharePoint Event Code) |
|---|---|
|
Site security inheritance broken
|
·Audit Log (Turn Off Inheritance from Parent) (SecRoleBindBreakInherit) ·Change Log (Add Assignment) (AssignmentAdd) |
|
Site security inheritance restored |
·Audit Log (Turn On Inheritance from Parent) (SecRoleBindInherit) ·Change Log (Delete Assignment) (Assignment) |
|
Permission level inheritance restored |
Change Log (Delete Assignment) (Assignment) |
|
Site permission level created |
·Audit Log (Create Permissions) (SecRoleDefCreate) ·Change Log (Add Role)(RoleUpdate) |
|
Site permission level deleted |
·Audit Log (Remove Permissions) (SecRoleDefDelete) ·Change Log (Delete Role) (RoleUpdate) |
|
Site Permission level changed |
·Audit Log (Modify Permissions) (SecGroupCreate) ·Change Log (Update Role) (RoleUpdate) |
|
User or SharePoint group permission changed |
·Audit Log (Change Permissions) (SecRoleBindUpdate) ·Change Log (Add Assignment and/or Delete Assignment) (AssignmentAdd and/or Assignment) |
|
SharePoint group created |
·Audit Log (Create Group) (SecGroupCreate) ·Change Log (Add) |
|
SharePoint group deleted |
·Audit Log (Delete Group) (SecGroupDelete) ·Change Log (Delete) |
|
Member added to SharePoint group |
·Audit Log (Add Member to Group) (SecGroupMemberAdd) ·Change Log (Add Member) (MemberAdd) |
|
Member deleted from SharePoint group |
·Audit Log (Delete Member from Group) (SecGroupemberDelete) ·Change Log ( Delete Member) (MemberDelete) |
Add Content Types and Columns
|
Action |
Where Recorded (ControlPoint Event Type) (SharePoint Event Code) |
|---|---|
|
Content Type added |
Audit Log (Change Profile) (ProfileChange) |
|
Column added |
Audit Log (Change Schema) (SchemaChange) |
SharePoint Search Activity
|
Event |
Where Recorded (ControlPoint Event Type) |
|---|---|
|
SharePoint search performed |
Audit Log (Search) |
Audit Settings
|
Event |
Where Recorded (ControlPoint Event Type) (SharePoint Event Code) |
|---|---|
|
Audit settings changed |
Audit Log (Change Mask) (AuditMaskChange) |
Analyzing Audit Log Contents
The ControlPoint Audit Log analysis extends SharePoint's built-in audit logging by letting you easily view entries written to the audit log. You can focus your analysis on specific event types, and even limit the scope to include only certain objects (sites, lists, documents, etc.).
Audit logging must be enabled for each site collection whose events you want to log. You can enable audit logging for multiple site collections at a time via the ControlPoint Manage Audit Settings action or Set Site Collection Properties action.
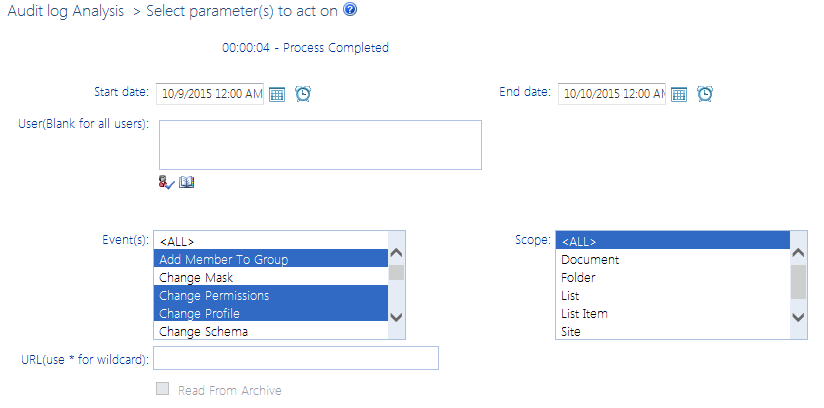
To generate an Audit Log analysis:
1Select the object(s) for which you want to view audited events.
NOTES:
§If the scope of your analysis includes site collections that have been deleted, audit events associated with that site collection will no longer exist.
§As with all ControlPoint analyses, if you initiated the analysis from the farm, Web application, or site collection level, all child items will be included by default. If you initiated the analysis at the site level, only information for that site (not its subsites) will be included. You can, however, use the Change Selection option to further refine your scope.
2Choose Audit and Alerts > Audit Log.
3Specify one or more of the following parameters for your analysis:
§select both a Start and End date (

NOTE: The time period for which you can generate an audit log analysis depends on how many days audit data is retained. The ControlPoint default is 0 (meaning that audit data is never deleted), but the ControlPoint Application Administrator can specify a different value via ControlPoint Configuration Settings.
§select the User(s) whose actions you want to audit (or leave blank for all users)
§enter a relative URL (note that you can enter a url down to the item level; you can also use an asterisk (*) at the beginning and end of a url as wildcards)
EXAMPLES
§sites/al*
§sites/alpha/shared documents/xcrSummaryReport.pdf
§select one or more Event types from the list box. Refer to the topic Events Captured in SharePoint Log.
CAUTION: Although you have the option of viewing ALL events, if you select this option your result set may be extremely large. One reason is that SharePoint records some events (such as a View) as a series of several events. Also, some event types (such as Update) may encompass a wide variety of events.