Apart from numerous factors, poor index maintenance can be a reason for decreased SQL Server performance. If a database contains tables with numerous entries, that get updated frequently, it is most likely that high index fragmentation will occur. For smaller indexes, high fragmentation does not necessarily degrade the performance of the queries that are run on a table. But for the larger tables, with indexes that consist of 1000 pages and more, fragmentation could cause noticeable performance issues. Luckily, performing index maintenance tasks on a regular basis can eliminate the risk of degrading performance significantly. The most effective ways for treating index fragmentation are reorganize and rebuild index operations.
For smaller databases, index maintenance tasks can be run manually, when the need arises. Detailed instructions for running reorganize and rebuild jobs manually can be found in the article: Why, when and how to rebuild and reorganize SQL Server indexes. But most larger and high traffic databases require index maintenance on a regular basis: weekly, or even daily. For these use cases, it is wise to configure a policy that would run automatically, on a schedule set by the DBA.
This article shows three solutions for creating fully functional SQL Server defragmentation policy:
Before we apply any of the listed solutions, it is necessary to run index analysis first, in order to detect highly fragmented indexes. Running a reorganize or rebuild job on each database, schema or table index might sound like the easiest solution, but is not advised, since it can be a quite time consuming and resource intensive task. The best way to check index fragmentation in SQL Server is to use the built-in function sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats. This function returns size and fragmentation information for all indexes on a server, all indexes in a database, all indexes in a table, or just a single index, depending on provided parameters. Querying the raw function with basic parameters should yield all necessary information for the analysis, but the results will be quite unorganized. Therefore, we use the modified query:
--Script 1: Detecting index fragmentation SELECT dbschemas.[name] AS 'Schema', dbtables.[name] AS 'Table', dbindexes.[name] AS 'Index', indexstats.avg_fragmentation_in_percent AS 'Frag (%)', indexstats.page_count AS 'Page count' FROM sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats (DB_ID(), NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL) AS indexstats INNER JOIN sys.tables dbtables ON dbtables.[object_id] = indexstats.[object_id] INNER JOIN sys.schemas dbschemas ON dbtables.[schema_id] = dbschemas.[schema_id] INNER JOIN sys.indexes AS dbindexes ON dbindexes.[object_id] = indexstats.[object_id] AND indexstats.index_id = dbindexes.index_id WHERE indexstats.database_id = DB_ID() ORDER BY indexstats.avg_fragmentation_in_percent DESC
Running the query on AdventureWorks2014 database yields the following results:
Schema, table, name, fragmentation percentage and page count is displayed for each index in the database. Results are sorted by fragmentation percentage descending, so we could easily isolate indexes with highest fragmentation.
Depending on the fragmentation percentage value, fragmentation may be recognized as:
As soon as analysis is completed, we can write the defragmentation script.
To write a custom script, decide which indexes to include in it, depending on the results from the previous query. Generally, indexes with fragmentation levels between 10% and 30% need to be reorganized, while those with higher fragmentation need to be rebuilt. Another important factor when choosing which indexes to include in a script is index size. Small indexes can be included in the script, but defragmenting them does not affect server performance significantly. In general, indexes smaller than 1000 pages are rarely included in defragmentation jobs.
To reorganize all indexes in a table or just specific index, use the following statements:
--Script 2: Reorganize script --2.1 Reorganize single index ALTER INDEX Index_name ON Table_name REORGANIZE ; --2.2 Reorganize all indexes in the table ALTER INDEX ALL ON Table_name REORGANIZE ;
Rebuild script has the same syntax, but uses REBUILD statement instead:
--Script 3: Rebuild script --2.1 Rebuild single index ALTER INDEX Index_name ON Table_name REBUILD ; --2.2 Rebuild all indexes in the table ALTER INDEX ALL ON Table_name REBUILD ;
Writing reorganize and rebuild statements for each index, especially for the large databases can be a tiresome job. Therefore, we decided to use a dynamic script that automatically checks for the index fragmentation and index page size, and applies reorganize or rebuild operation depending on the results.
To use the script effectively, it is necessary to set a few threshold variables first:
-- Script 4: Automatically analyze and defragment indexes -- Set variables -- ********************************************************************************************* SET NOCOUNT ON DECLARE @reorg_frag_thresh float SET @reorg_frag_thresh = 10.0 DECLARE @rebuild_frag_thresh float SET @rebuild_frag_thresh = 30.0 DECLARE @fill_factor tinyint SET @fill_factor = 0 DECLARE @report_only bit SET @report_only = 0 DECLARE @page_count_thresh smallint SET @page_count_thresh = 1 -- ********************************************************************************************* DECLARE @objectid int DECLARE @indexid int DECLARE @partitioncount bigint DECLARE @schemaname nvarchar(130) DECLARE @objectname nvarchar(130) DECLARE @indexname nvarchar(130) DECLARE @partitionnum bigint DECLARE @partitions bigint DECLARE @frag float DECLARE @page_count int DECLARE @command nvarchar(4000) DECLARE @intentions nvarchar(4000) DECLARE @table_var TABLE( objectid int, indexid int, partitionnum int, frag float, page_count int ) INSERT INTO @table_var SELECT [object_id] AS objectid, [index_id] AS indexid, [partition_number] AS partitionnum, [avg_fragmentation_in_percent] AS frag, [page_count] AS page_count FROM sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats (DB_ID(), NULL, NULL , NULL, 'LIMITED') WHERE [avg_fragmentation_in_percent] > @reorg_frag_thresh AND page_count > @page_count_thresh AND index_id > 0 DECLARE partitions CURSOR FOR SELECT * FROM @table_var OPEN partitions WHILE (1=1) BEGIN FETCH NEXT FROM partitions INTO @objectid, @indexid, @partitionnum, @frag, @page_count IF @@FETCH_STATUS < 0 BREAK SELECT @objectname = QUOTENAME(o.[name]), @schemaname = QUOTENAME(s.[name]) FROM sys.objects AS o WITH (NOLOCK) JOIN sys.schemas AS s WITH (NOLOCK) ON s.[schema_id] = o.[schema_id] WHERE o.[object_id] = @objectid SELECT @indexname = QUOTENAME([name]) FROM sys.indexes WITH (NOLOCK) WHERE [object_id] = @objectid AND [index_id] = @indexid SELECT @partitioncount = count (*) FROM sys.partitions WITH (NOLOCK) WHERE [object_id] = @objectid AND [index_id] = @indexid SET @intentions = @schemaname + N'.' + @objectname + N'.' + @indexname + N':' + CHAR(13) + CHAR(10) SET @intentions = REPLACE(SPACE(LEN(@intentions)), ' ', '=') + CHAR(13) + CHAR(10) + @intentions SET @intentions = @intentions + N' FRAGMENTATION: ' + CAST(@frag AS nvarchar) + N'%' + CHAR(13) + CHAR(10) + N' PAGE COUNT: ' + CAST(@page_count AS nvarchar) + CHAR(13) + CHAR(10) IF @frag < @rebuild_frag_thresh BEGIN SET @intentions = @intentions + N' OPERATION: REORGANIZE' + CHAR(13) + CHAR(10) SET @command = N'ALTER INDEX ' + @indexname + N' ON ' + @schemaname + N'.' + @objectname + N' REORGANIZE; ' + N' UPDATE STATISTICS ' + @schemaname + N'.' + @objectname + N' ' + @indexname + ';' END IF @frag >= @rebuild_frag_thresh BEGIN SET @intentions = @intentions + N' OPERATION: REBUILD' + CHAR(13) + CHAR(10) SET @command = N'ALTER INDEX ' + @indexname + N' ON ' + @schemaname + N'.' + @objectname + N' REBUILD' END IF @partitioncount > 1 BEGIN SET @intentions = @intentions + N' PARTITION: ' + CAST(@partitionnum AS nvarchar(10)) + CHAR(13) + CHAR(10) SET @command = @command + N' PARTITION=' + CAST(@partitionnum AS nvarchar(10)) END IF @frag >= @rebuild_frag_thresh AND @fill_factor > 0 AND @fill_factor < 100 BEGIN SET @intentions = @intentions + N' FILL FACTOR: ' + CAST(@fill_factor AS nvarchar) + CHAR(13) + CHAR(10) SET @command = @command + N' WITH (FILLFACTOR = ' + CAST(@fill_factor AS nvarchar) + ')' END IF @report_only = 0 BEGIN SET @intentions = @intentions + N' EXECUTING: ' + @command PRINT @intentions EXEC (@command) END ELSE BEGIN PRINT @intentions END PRINT @command END CLOSE partitions DEALLOCATE partitions GO
Before starting with the job configuration, make sure that SQL Server Agent is installed and running. To do this, open the SQL Server Management Studio, and find SQL Server Agent at the bottom of the Object Explorer. Right click on the agent, and click on the Start button in the context menu. In case that agent is running already, skip this step.
To create SQL Server agent that will defragment specified indexes automatically, perform the following steps:
Expand SQL Server Agent in Object explorer, right click on Jobs, and select New Job…:
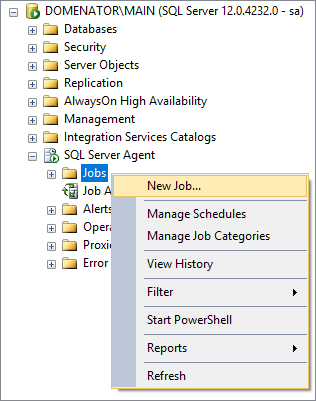
In General tab, specify the name and description for the job. Make sure to thick the Enabled checkbox. Proceed to the Steps tab:
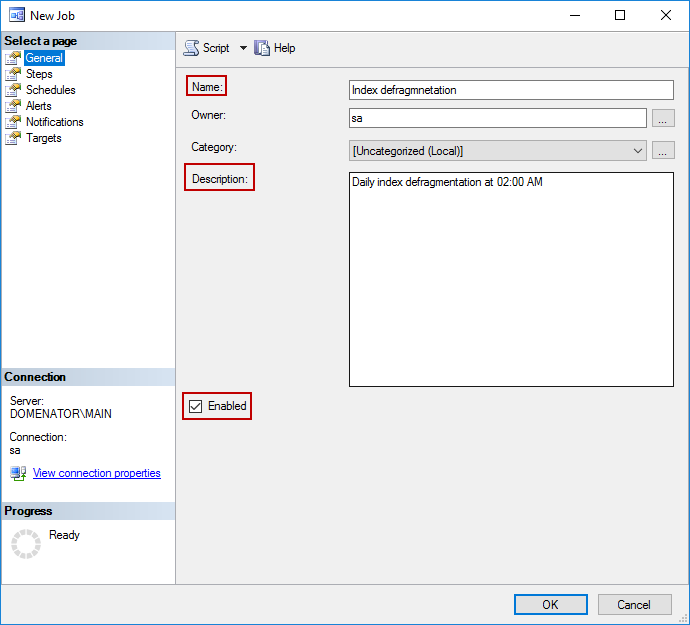
Clicking on New… button in Steps tab opens the form for the first job step configuration. Provide any name for the step, and leave all other values as default. In the command window, paste the script created in previous chapter, and click OK:
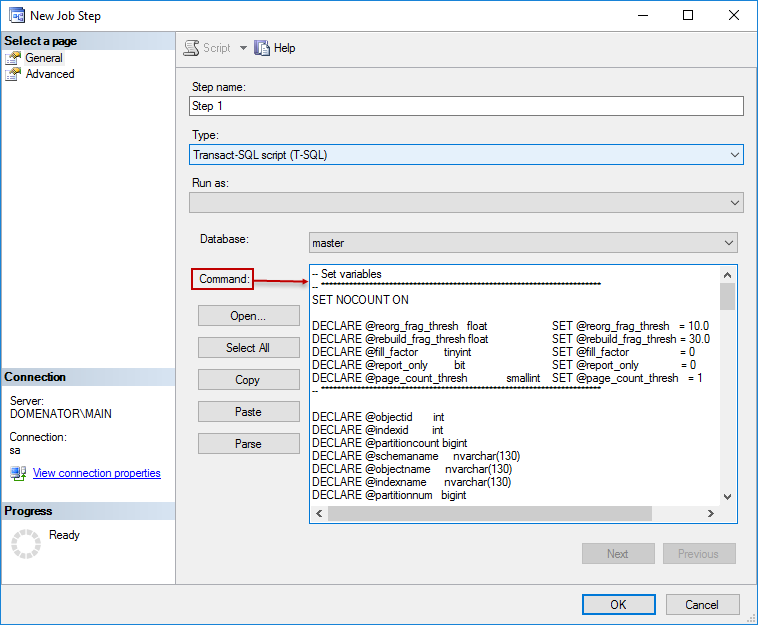
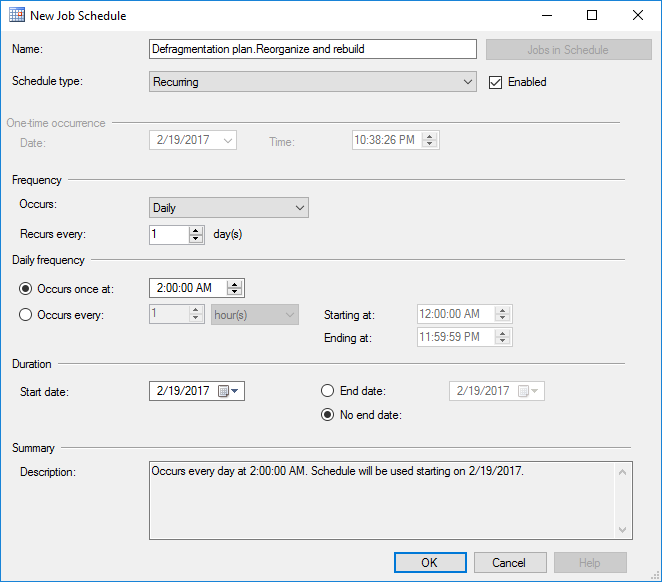
In Schedules tab, in New job window click New button to create the schedule for the job. Set the schedule type, frequency and daily frequency. Since REBUILD statements lock the tables during the defragmentation process, it is best to set the schedule to time when servers experience the least amount of traffic. In this example, schedule is set to run each day at 2:00 AM. Click OK to save the schedule:
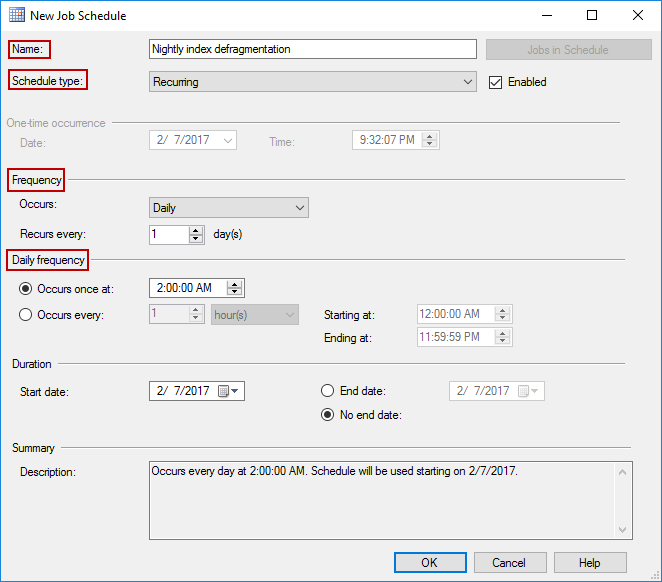
If needed, set Alerts and Notifications in respective tabs. In Targets tab, specify the targets for the job. To be able to target multiple servers, it is necessary to either create Central Management Server and Server groups or Multiserver environment. Click OK to finish job configuration:
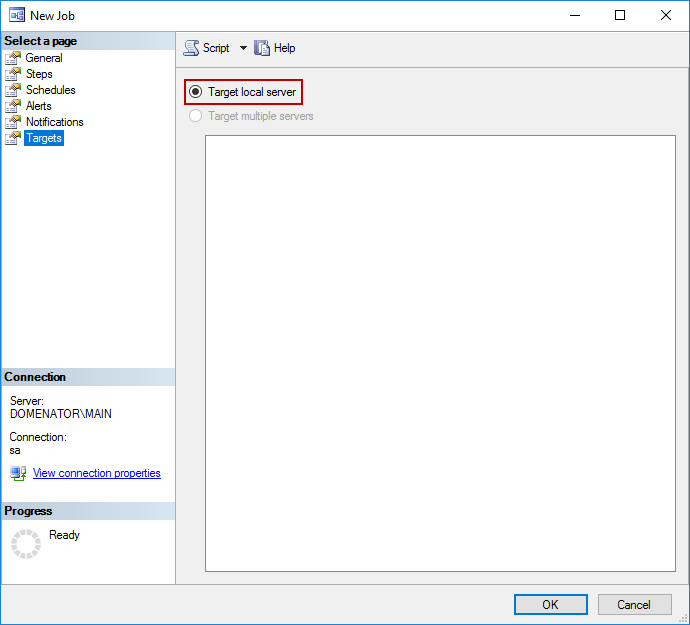
To run the selected job immediately, expand SQL Server Agent and Jobs in Object Explorer, right click on created job, and select Start Job at Step. Since our job has only one step, it will start executing automatically:
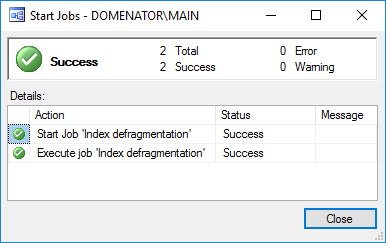
To create and run defragmentation policies with maintenance plans, it is necessary to perform the following steps in SQL Server management studio:
Expand the Management node in Object Explorer, right click on Maintenance Plans, and select New Maintenance Plan… from the context menu. Specify the name for the maintenance plan and click OK:
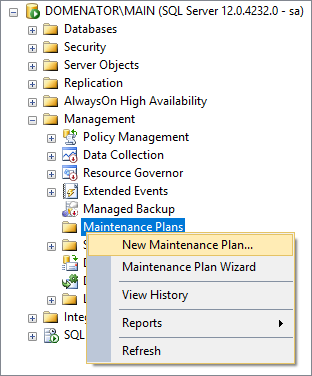
Double click on Subplan_1:
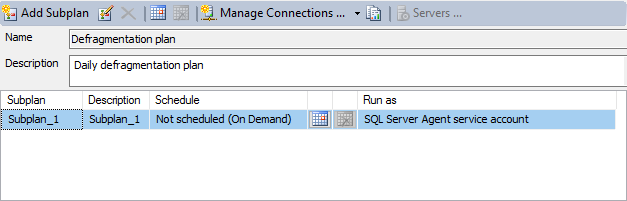
In Subplan Properties, set the name and description for the subplan, and click on schedule icon:
Set the schedule for the subplan. When completed, click OK in both New Job Schedule and Subplan Properties windows:
Drag and drop Rebuild Index Task and Reorganize Index Task from the Toolbox to the clear area in Defragmentation plan design. If there is no Too