Opening Management Shell
You can open the Management Shell by using either of the following procedures. Each procedure loads the Recovery Manager for Active Directory Management Shell snap-in into Windows PowerShell. If you do not load the Recovery Manager for Active Directory Management Shell snap-in before you run a command (cmdlet) provided by that snap-in, you will receive an error.
| Note |
Recovery Manager for Active Directory Management Shell console must be started with elevated privileges. Otherwise, you will get warning messages when you execute the snap-in cmdlets. |
To open the Management Shell
-
Start Windows PowerShell.
You can do so by running the powershell command at a command prompt (Cmd.exe).
-
At the Windows PowerShell prompt, enter the following command:
Add-PSSnapin Quest.RecoveryManager.AD.*
Alternatively, you can complete the following steps related to your version of Windows:
For Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 or 2008 R2
-
Click Start.
-
Point to All Programs | Quest | Recovery Manager for Active Directory.
-
Click Management Shell.
For later versions of Windows
On the Start screen, click the Management Shell tile.
Upon the shell start, the console may present you with a message stating that a certain file published by Quest is not trusted on your system. This security message indicates that the certificate the file is digitally signed with is not trusted on your computer, so the console requires you to enable trust for the certificate issuer before the file can be run. Press either R (Run once) or A (Always run). To prevent this message from appearing in the future, it is advisable to choose the second option (A).
Getting Help
The Recovery Manager for Active Directory Management Shell uses the Windows PowerShell help cmdlets to assist you in finding the appropriate information to accomplish your task. The following table provides some examples of how to use the Get-Help and Get-Command cmdlets to access the help information that is available for each cmdlet in the Recovery Manager for Active Directory Management Shell.
Get-Help
When you use Get-Help without any parameters, you are presented with basic instructions on how to use the help system in Windows PowerShell, including Help for the Recovery Manager for Active Directory Management Shell.
Get-Help
When you use Get-Help with the name of a cmdlet as an argument, you are presented with the help information for that cmdlet. For example, to retrieve the help information for the Get-RMADCollection cmdlet, use the following command:
Get-Help Get-RMADCollection
Get-Command
Get-Command without any parameters lists all the cmdlets that are available to the shell. You can use the Get-Command cmdlet with the Format-List or Format- Table cmdlet to provide a more readable display. For example, use Get-Command | Format-List to display the output in a list format. To display a list of all the Recovery Manager for Active Directory Management Shell cmdlets that are available to the shell, use the following syntax:
Get-Command *RMAD*
Get-Command
When you use Get-Command with the name of a cmdlet as an argument, you are presented with information about the parameters and other components of that cmdlet. The <Cmdlet> entry allows for wildcard character expansion. For example, to retrieve information about the cmdlets with the names ending in Member, you can use the following command:
Get-Command *Member
Creating virtual test environments
About Active Directory Virtual Lab
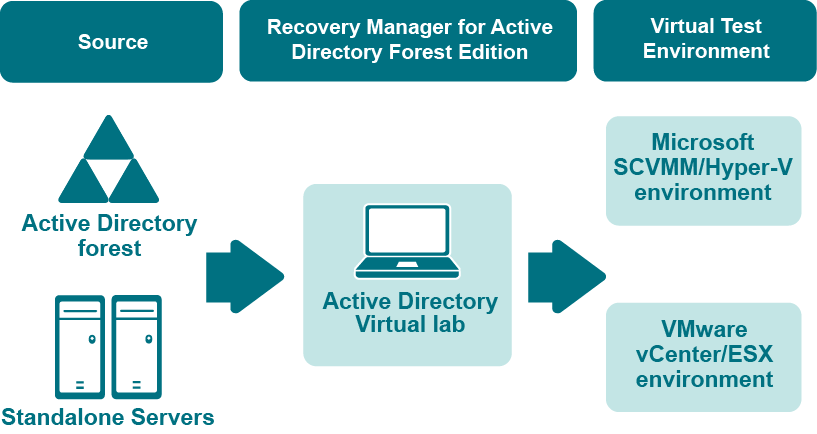
The Active Directory Virtual Lab is a component of Recovery Manager for Active Directory that helps you create virtual test environments from an Active Directory forest. You can use the created test environments to design and evaluate Active Directory disaster recovery scenarios, test planned Active Directory changes before deploying them to production, train your staff to perform Active Directory-related tasks, and more.
When creating virtual machines from the source computers, the Active Directory Virtual Lab uses third-party virtualization software, such as Microsoft System Center Virtual Machine Manager (SCVMM), VMware ESX, or VMware vCenter. For a full list of supported virtualization software, see the System Requirements section in the Recovery Manager for Active Directory Release Notes.
You can create virtual machines that maintain all the data available on the source computers, including Active Directory, installed programs, and files. To manage the created virtual test environment, you need to use the native tools provided by the virtualization software with which the Active Directory Virtual Lab created the virtual machines in the test environment.
To create a virtual test environment from an Active Directory forest, you first need to select the source computers (domain controllers or standalone servers) you want to include in the test environment, configure settings to create a virtual machine from each source computer, and then have the Active Directory Virtual Lab create the test environment for you.
For instructions on creating a virtual test environment, see How to create a virtual test environment.