Logging in
|
a |
In the Foglight login page, in the User box, type your Foglight user name. |
|
b |
In the Password box, type your Foglight password. |
|
c |
Click Login. |
|
• |
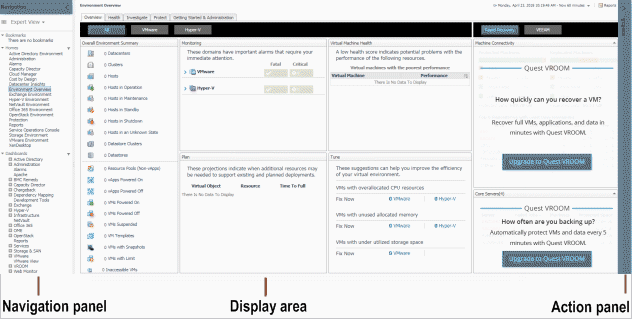
If your Management Server has a valid license, the Welcome to Foglight or the Environment Overview page appears in the browser interface. |
|
• |
If your user account includes the Administration role, in the Unlicensed Server View, click Install a License. In the Manage Licenses dashboard that appears, install the license for the Management Server. For more information, see Install licenses. |
|
• |
The Management Server supports integration with external LDAP directories. In a Kerberos-based environment, such as Microsoft® Active Directory®, most web browsers can authenticate users against the web server using their current credentials.
When this feature is configured, if you log in to a machine running a Windows® OS and then log in to the browser interface, the Management Server uses your Windows account credentials to authenticate you as a Management Server user.
Complete the following configuration steps to enable the Windows single sign-on (SSO) feature:
If you were using the VSJ SSO that was provided in earlier versions of Foglight, you must also migrate your settings to the Windows OS-based SSO. For more information, see Migrate to Windows SSO from VSJ SSO.
Microsoft® Active Directory® provides a directory service supporting the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), and a Kerberos KDC (key distribution center) to authenticate users. It allows organizations to share and manage information about users and network resources. When properly configured, Active Directory® provides an SSO environment that can be integrated with the standard Windows® OS desktop login.
|
TIP: When setting up the Kerberos Service Principal Name (SPN), use the following instructions to create mappings between the user account and SPNs, and to create a keytab file to configure in krb5‑auth.config. For example: ktpass -princ HTTP/<fmshost.example.com>@REALM -mapuser "<domain>\<user>" -pass <password> -out <keytabFilePath> And: Use setspn to set up the mapping for just the host name. For example: setspn -A HTTP/<fmshost> <user> |
|
NOTE: Duplicate SPNs cause Kerberos authentication to return an NTLM token and fallback to Form authentication. To search for duplicate SPNs: setspn -X -F If you locate duplicate SPNs for “HTTP/<fmshost>”, you can remove them with the following command: setspn -d HTTP/<fmshost> <user> |
Foglight provides SSO for the Management Server using Active Directory® as its identity store. It includes an enterprise-wide method of identification and authorization that can be administered in a consistent and transparent manner. This method allows users to access only those Management Server components for which they are authorized.
Enabling the Windows® SSO feature in Foglight requires the configuration of the following components:
|
The Active Directory® service principal. | |
|
Include the Active Directory® Domain name in the user principal name. | |
|
By default, the server gets the LDAP URL from krb5.config (see the Krb5ConfigFilePath property). This property can be used to override that value. The domain name must be set as lowercase ASCII. | |
|
AdditionalContextParameters = { | |
|
UserQueryFilter = "(&(objectClass=user)(sAMAccountName={0}))"; NOTE: If this property is not set, the default setting is: UserQueryFilter ="(&(objectClass=user)(sAMAccountName={0}))" | |
|
For example, to import direct groups: GroupQueryFilter = "(&(objectclass=group)(member={0}))"; For example, to import all nested groups: GroupQueryFilter = "(&(objectclass=group)(member:1.2.840.113556.1.4.1941:={0}))"; |
|
NOTE: The first KDC in krb5.conf will be used as the LDAP server for the related domain by default. If that is not appropriate you should configure LDAP URLs for each of their domains relevant to Foglight SSO in the LDAPURLOverides element in krb5-auth.config. |
|
IMPORTANT: Only Microsoft® Internet Explorer®, Google Chrome™, and Mozilla® Firefox® browsers can be configured to support SPNEGO authentication currently. |
|
3 |
|
4 |
Scroll down to the Security section. Select the option: Enable Integrated Windows Authentication (requires restart). |
|
5 |
|
• |
|
7 |
Select Local Intranet > Custom Level. |
|
8 |
Select the Security Settings > User Authentication option for Automatic logon only in Internet Zone option. |
|
1 |
From the Start menu, open the Control Panel. |
|
2 |
Select Internet Options. |
|
3 |
Select the Security tab. |
|
4 |
Click Local Intranet > Sites > Advanced. |
|
5 |
|
6 |
Click OK to close all the dialog boxes. |
|
3 |
In the address bar of a blank tab, type about:config. |
|
5 |
In the Filter field, type: negotiate. Locate the entry network.negotiate‑auth.trusted‑uris. This entry is used to configure the sites that are permitted to engage in SPNEGO authentication with Firefox. |
|
6 |
Double click network.negotiate‑auth.trusted‑uris. |
|
8 |
Click OK to close the dialog box, and restart Firefox to enable the new configuration. |
|
1 |
Make a backup of the vsj.properties file before you upgrade Foglight. You can find this file in the following location: <foglight_home>/server/default/deploy-foglight/console.war/WEB-INF/vsj.properties |
|
3 |
|
4 |
Edit the krb5-auth.config file to set the properties described in the following table. |
|
5 |
After you configure Windows® SSO, log in to your Active Directory® domain, start your web browser, and navigate to the Foglight browser interface. You are no longer required to provide your user name and password on the login page. The Management Server now uses your Kerberos credentials to log you in to the Foglight browser interface and grant you permissions associated with your Active Directory® account. This configuration allows you to bypass the common login page.
If you want to log in to the browser interface using an internal Foglight user account instead of your Windows account (for example, foglight/foglight), you have two options.
|
• |
If you are already in the browser interface, click Sign Out to navigate to the login page. Now you can enter the desired user name and password. |
|
• |
Start your web browser and navigate to: http://<host>:<port>/console/?nowinsso where host and port are the name of the machine on which the Management Server is running and the browser interface port number. |
Manage Licenses
|
1 |
|
2 |
Click Install. |
|
3 |
|
5 |
|
6 |
After a few moments, the Install License dialog box closes, and the Manage Licenses dashboard refreshes, showing the newly installed license in the list. |
|
1 |
|
2 |
Click Install Subscription License. |
|
3 |
In the Install Subscription License dialog box, input the Subscription License Number and click Install License. |
|
4 |
After a few moments, the Install License dialog box closes, and the Manage Licenses dashboard refreshes, showing the newly installed license in the list. |
|
1 |
|
4 |
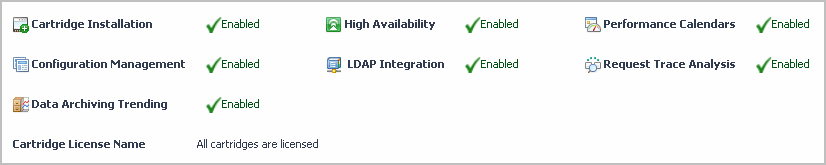
Find out which capabilities each individual license provides. In the list of installed licenses, observe the Capabilities column. This column shows a set of icons, each representing a licensed capability. |
Users can export a license usage report by clicking the Export License Usage button.
|
1 |
|
2 |
Deleting a license disables the features defined in the license.
|
1 |
|
3 |
Click Delete. |
|
4 |
Email Configuration
Use the Edit button on the Email Configuration dashboard to edit email settings.
|
1 |
|
3 |
|
5 |
Static values only. Specify the parameter value as instructed in the dwell and click Save. The Email Configuration dashboard refreshes, showing the newly configured value in the Value column. |
|
6 |
Dynamic values only. Use the registry editor to specify the email settings that are likely to change over time, orthat need to be scoped to particular object instances. |
|
a |
In the dwell, click Use the advanced registry variable editor for routing based on schedules or specific monitored objects. |
|
1 |
|
TIP: The Mail Server (Name or IP) and Email Sender Address parameters are mandatory for a successful email configuration. Your mail server setup may require you to set additional parameters, such as the user name and password of the default sender, among others. |
|
3 |
In the Email Server Configuration view, click Test Configuration. The Test Configuration dialog box opens. |
|
5 |
Check your email. Your mailbox contains a new email message with the subject Test Email from Foglight. |
|
6 |
Observe the sender’s email address. This is the value of the Email Sender Address parameter. |
|
7 |
Users and Security
The Users tab lists all Foglight users, including:
|
• |
the default foglight account |
For every user, the list shows the following:
|
• |
Internal. Internal users include the users that are created after the installation. When you create an internal user in Foglight, you assign a user name and password to that user. |
|
• |
Built In. Built-in users include the users that come with Foglight. One default account is included with Foglight. Unless you specify a different user name at installation time, that user name is foglight. This account has full access to all of Foglight features. |
|
• |
External. After Foglight validates external users, they are mapped from one of the LDAP-compatible directory services that Foglight supports (Active Directory, Oracle Directory Server Enterprise Edition, and OpenLDAP). When an external directory service is configured in Foglight, a user account is added to the list of existing users the first time an external user logs in to the browser interface. For more information about configuring Foglight to use an external directory service, see Configuring directory services. |
The Users tab includes controls for managing user settings, creating new users, deleting users, forcing password changes, unlocking a user accounts, and a search tool. Clicking a user’s role or group entry allows you to quickly edit user permissions.
To access this tab, on the navigation panel, click Dashboards > Administration > Users & Security. From there, to start managing user access, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles and ensure that the Users tab is open in the display area.
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard, under User Look Up, type a part of the user name for the user that you want to find. |
|
3 |
Click Look up. The Select a user dialog box opens, listing the users whose name matches the specified pattern. |
|
4 |
In the Select a user dialog box, select the row containing the user entry that you want to look up and click View Detail. |
The Users tab includes a wizard that allows you to create new users and grant them access permissions. The wizard is invoked using the New User button on the Users tab. Using this flow you can create one or more users with the same set of permissions.
Alternatively, use the fglcmd security:createuser command to create a user. For more information, see the Command-Line Reference Guide.
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
a |
|
b |
To specify additional user names, click Add more names, and type them into the list. |
|
c |
|
5 |
Select one or more groups that you want this user to belong to, followed by clicking Next. Adding a user to a group grants that user access to all of the roles that are associated with the group. |
|
6 |
Type the password for the user account you are about to create in each of the Password and Confirm Password boxes and click Next. |
|
7 |
|
a |
In the New User dialog box, review the list of dashboards in the Name column, paying special attention to the allowed roles. The list can be sorted alphabetically by module or allowed role, and includes a search tool. |
|
c |
Optional — Select the row containing the default time range for the data appearing on the home page. For example, to have the home page display the data collected in the last eight hours, select Last 8 Hours in the Default Time Range column. |
|
d |
Specify the refresh interval for the selected dashboard in seconds. For example, typing 600 causes the dashboard data display to refresh every ten minutes. |
|
8 |
Click Finish. |
|
9 |
Close the Make User Progress message box and observe the Users tab. The newly created user entry appears in the list. |
Use the Remove Users button on the Users tab to remove user accounts from Foglight. You can only delete those users that are added after the installation, or users imported into Foglight from an external directory. Their types appear as Internal and External, respectively, on the Users tab. The type of the default user account included with Foglight appears as Built-In. The Built-In account, or the account used to log in to Foglight, cannot be removed.
Deleting an external user from Foglight does not remove that account from the external directory.
Alternatively, you can delete internal or external users using the security:deleteuser command that comes with the fglcmd interface. For more information, see the Command-Line Reference Guide.
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
3 |
On the Users tab, select a user account that you want to delete. |
|
4 |
|
5 |
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
3 |
On the Users tab, in the row containing the user account that you want to edit, click the Name column and choose Copy from the shortcut menu that appears. |
|
a |
|
b |
To specify additional user names, click Add more names, type them into the list that appears, then click Add. |
|
c |
|
6 |
Type the password for the user account you are about to create in each of the Password and Confirm Password boxes. |
|
7 |
|
a |
In the New User dialog box, review the list of dashboards in the Name column, paying special attention to the allowed roles. You can sort the list alphabetically by module or allowed role, or use the search tool. |
|
c |
Optional — Select the row containing the default time range for the data appearing on the home page. For example, to have the home page display the data collected in the last eight hours, select Last 8 Hours in the Default Time Range column. |
|
d |
Specify the refresh interval for the selected dashboard in seconds. For example, typing 600 causes the dashboard data display to refresh every 10 minutes. |
|
8 |
Click Finish. |
|
9 |
Close the Make User Progress message box and observe the Users tab. The newly copied user entry appears in the list. |
On the Users tab, the Groups column shows the names of groups that are associated with each account, or the number of groups, if that number is higher than five. The Roles column contains the names of the roles that are granted to each group, or the number of roles, if a group takes on six or more roles.
Hovering over these columns shows a list of the groups and roles assigned to the user entry.
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
3 |
On the Users tab, in the row containing the user account that you want to edit, click the Groups column. |
|
5 |
Click Save. A message box opens, indicating the progress. |
|
6 |
Observe the Groups column on the Users tab. Hovering over this column shows the list of current groups, taking into account the latest changes. |
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
3 |
On the Users tab, in the row containing the user account that you want to edit, click the Roles column. |
|
5 |
Click Save. The dialog box closes and a message box opens, indicating the progress. |
|
6 |
Observe the Roles column on the Users tab. Hovering over this column shows the list of current roles, taking into account the latest changes. |
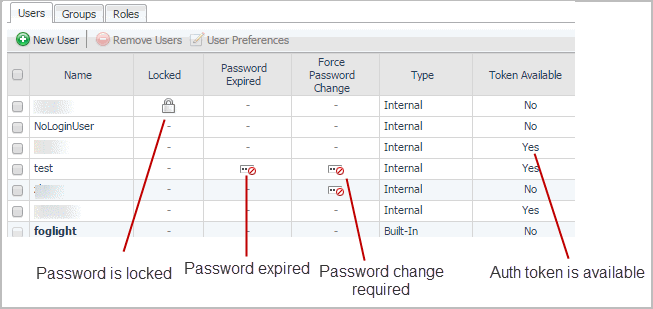
The restrictions include the number of unsuccessful attempts after which an account is locked, or the number of days after which a password expires. The Locked column on the Users tab indicates if an account is locked, while Password Expired shows which user accounts have an expired password. Force Password Change identifies the user accounts that, upon a successful login, are asked to change their passwords. Additionally, Token Available indicates if the Auth Token is available for an account. This setting is recommended during the user creation process, to protect user credentials.
For more information about password settings, see Configuring Password settings.
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
3 |
On the Users tab, in the row containing a built-in or internal user account whose password you want to change, click the Name column. |
|
4 |
|
5 |
|
• |
If you want the user to change the password upon the next login attempt, select Change Password at the next logon. |
|
• |
If you want to reset the Auth Token, select Set auth token. |
|
6 |
Click Change. |
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
3 |
On the Users tab, in the row containing a built-in or internal user account whose password you want to change, click the Name column. |
|
4 |
|
5 |
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
3 |
On the Users tab, in the row containing a built-in or internal user account whose password you want to unlock, click the Locked column. |
|
4 |
|
5 |
|
3 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
4 |
On the Users tab, select the user whose password you set to never expire. |
|
TIP: To set a specific expiry date, run the command: fglcmd.bat -cmd security:passwordexpiry -set <date> -u <user_name> |
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
3 |
On the Users tab, click the user account whose password you want to set. |
|
5 |
Click Expiration Policy. |
|
6 |
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
3 |
On the Users tab, click the user account which Auth Token you want to reset, then click Set Auth Token from the shortcut menu. |
|
4 |
Click Set. |
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
3 |
On the Users tab, click the user account which Auth Token you want to reset, then click Delete Auth Token from the shortcut menu. |
|
4 |
Click Delete. |
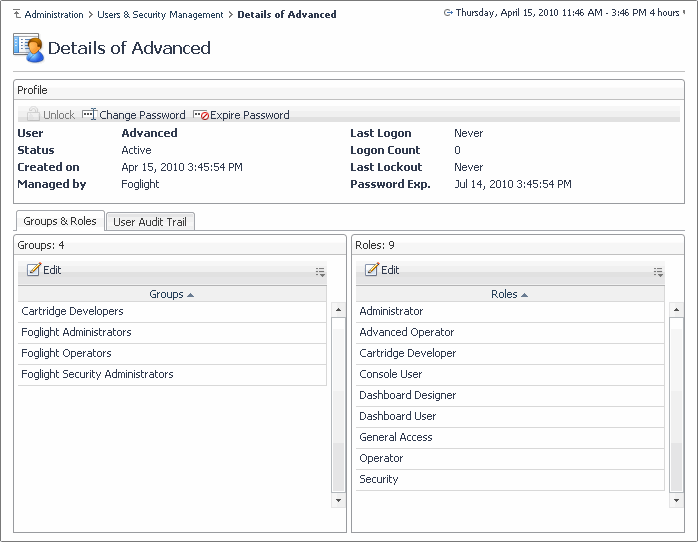
The Details of User View shows current user profile. It also allows you to edit individual settings, such as password changes, groups and roles associated with the user, and the user audit trail. Drill down to this view by clicking the Name column on the Users tab, and choosing View from the shortcut menu that appears.
You can also edit user information using a wizard flow. This flow is limited to internal and built-in users only. It is similar to the one for creating new users. Start this flow by clicking the Name column on the Users tab, and choosing Edit from the shortcut menu.
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
3 |
On the Users tab, locate the row containing a built-in or internal user account whose details you want to view. In that row, click the Name column and choose View from the shortcut menu that opens. |
|
• |
Profile shows the basic user details, such as the user name, status, logon statistics, and other. Clicking Unlock, Change Password, or Force PasswordChange allows you to perform these operations, as required. |
|
• |
Groups & Roles tab lists the groups and roles associated with the user account. Clicking Edit in the Groups or Roles view allows you to edit the user’s groups or roles. |
|
• |
User Audit Trail tab lists the audited operations related to the user’s login attempts. |
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
3 |
On the Users tab, in the row containing the built-in or internal user account whose details you want to edit, click the Name column. |
|
4 |
In the shortcut menu, click Edit. The Editing user dialog box opens. Any groups associated with the user account appear pre-selected in the flow. |
|
5 |
Click Next. The Editing user dialog box refreshes and the groups associated with the user account appear selected. |
|
6 |
If required, add or remove one or more groups, followed by clicking Next. Adding a user to a group grants access to all of the roles that are associated with that group. |
|
7 |
Optional — Edit the password for the user account you are editing in each of the Password and Confirm Password boxes. |
|
8 |
|
a |
In the Editing user dialog box, review the list of dashboards in the Name column, paying special attention to the allowed roles. The list can be sorted alphabetically by module or allowed role, and includes a search tool. |
|
c |
Select the row containing the default time range for the data appearing on the home page, and click Next. For example, to have the home page display the data collected in the last eight hours, select Last 8 Hours in the Default Time Range column. |
|
d |
Specify the refresh interval for the selected dashboard in seconds, and click Finish. For example, typing 300 causes the dashboard data display to refresh every five minutes. |
|
9 |
|
10 |
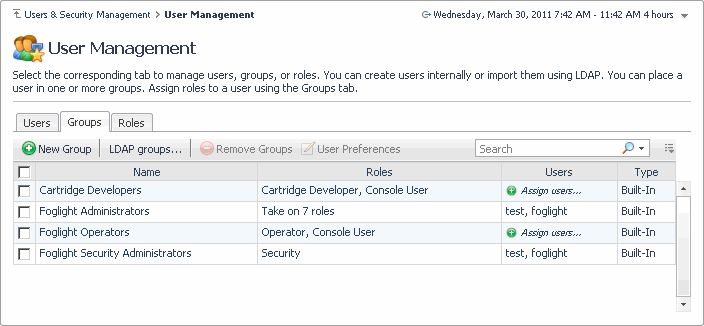
The Groups tab lists all Foglight users. This includes the default groups included with Foglight and any groups that you create after the installation. For every group, the list shows its name, the roles and users associated with that group, and the group type. There are three types of groups in Foglight:
|
• |
Internal. Includes the groups that are created after the installation. |
|
• |
Built-In. Includes the built-in groups that come with Foglight: |
|
• |
Cartridge Developers. Allows the users to modify core dashboards and system modules. |
|
• |
Foglight Administrators. Grants access to administration-level dashboards, except for the Users & Security dashboard. |
|
• |
Foglight Operators. Allows the users to have access to core and cartridge dashboards. |
|
• |
Foglight Security Administrators. Provides access to the Users & Security dashboard. |
|
IMPORTANT: Built-in groups can not be deleted. |
|
• |
External. The groups that are mapped from an LDAP-compatible directory service that Foglight supports as part of the process of mapping external users. When an external directory service is configured in Foglight, you can display selected external groups on the Groups tab. For more information about configuring Foglight to use an external directory service, see Configuring directory services. |
To access this tab, on the navigation panel, choose Dashboards > Administration > Users & Security. From there, to start managing user access, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles and open the Groups tab.
The Groups tab includes a wizard that allows you to create new groups and associate them with roles and users. The wizard is invoked using the New Group button on the Groups tab. Using this flow you can create one or more groups.
Alternatively, you can create groups using the security:createuser fglcmd. For more information, see the Command-Line Reference Guide.
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
3 |
Select the Groups tab. |
|
4 |
|
a |
In the Name box, type the group name. |
|
b |
|
c |
Optional — In the Description box, type the group description. |
|
d |
Click Next. |
|
6 |
Select one or more users that you want to add to the group. Click Next. Adding a user to a group grants that user access to all of the roles that you are associating with the group. |
|
7 |
Select one or more roles that you want to associate with the group. Click Finish. Adding a role to a group grants the members of that group access to all of the roles that you are associating with that group. |
LDAP groups are any user groups that are mapped from an LDAP-compatible directory service supported by Foglight, when external directory services are configured. By default, external groups do not appear on the Groups tab of the Users & Security Management dashboard. You can enable them for visibility, when required. Any groups that appear on this tab also appear in other flows.
When you integrate Foglight with an external directory service, any user that is granted the Security Administration role (regardless of whether their account type is internal, built-in, or external), can import LDAP groups. To import one or more LDAP groups into Foglight, you must log in with an internal Foglight account (for example, foglight/foglight) to import and configure LDAP groups.
For more information about configuring Foglight to use an external directory service, see Configuring directory services.
|
1 |
Log in to the browser interface using an internal Foglight account (for example, foglight/foglight). |
|
2 |
|
3 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
4 |
Open the Groups tab. |
|
5 |
|
6 |
|
7 |
In the Import External Groups dialog box, find one or more groups that you want to import. |
|
a |
Optional — Limit the number of search results. In the Import External Groups dialog box, click Results Limit and select an appropriate value. |
|
b |
Enter a text string as a filter. For example, to find the groups whose names start with Office.Services, in the Group Name box, type Office.Services, and click Update Group List. |
|
8 |
Select the groups that you want to import using the check boxes in the left-most column and click Import Groups to import them into Foglight. |
|
9 |
Close the Import Successful message box and observe the updated LDAP Group Visibility Settings dialog box. |
|
10 |
In the LDAP Group Visibility Settings dialog box, select the groups that you want to import and click Save. |
|
11 |
From here, you can grant appropriate Foglight roles to the imported groups. For more information, see Associate users with groups and roles .
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
• |
If you want to edit user preferences for one or more users, on the Users tab, select those users, and click User Preferences. |
|
• |
If you want to edit user preferences for one or more groups, open the Groups tab, select those groups, and click User Preferences. |
|
4 |
In the Edit User Preferences dialog box, review the list of dashboards in the Name column, paying special attention to the allowed roles. The list can be sorted alphabetically by module or allowed role, and includes a search tool. |
|
5 |
|
6 |
Select the row containing the default time range for the data appearing on the home page, and click Next. For example, to have the home page display the data collected in the last eight hours, select Last 8 Hours in the Default Time Range column. |
|
7 |
Specify the refresh interval for the selected dashboard in seconds, and click Finish. For example, typing 600 causes the dashboard data display to refresh every ten minutes. |
Use the Remove Groups button on the Groups tab to remove groups from Foglight. You can only delete those groups that are added after the installation, or groups from en external directory that are selected for visibility on the Groups tab. Their types appear as Internal and External, respectively, on the Groups tab. The type of the default groups included with Foglight appears as Built-In. Built-In groups cannot be removed. Removing an external group has no effect on the external directory in which it is defined.
Alternatively, you can delete internal or external groups using the security:deleteuser fglcmd command. For more information, see the Command-Line Reference Guide.
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
3 |
Open the Groups tab. |
|
4 |
On the Groups tab, select the group that you want to delete. |
|
5 |
Click Remove Groups. |
|
6 |
On the Groups tab, the Role Names column shows the roles granted to each group, or the number of roles, if that number is higher than five. The User Names column contains the names of the users that belong to each group, or the number of users, if a group contains six or more users.
Hovering over these columns shows a list of the groups and roles associated with the group entry.
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
3 |
Open the Groups tab. |
|
4 |
On the Groups tab, in the row containing the group entry that you want to edit, click the Role Names column. |
|
6 |
Click Save. The dialog box closes and a message box opens, indicating the progress. |
|
7 |
Observe the Roles Names column. Hovering over this column shows the list of current roles, taking into account the latest changes. |
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
3 |
Open the Groups tab. |
|
4 |
On the Groups tab, in the row containing an internal or built-in group entry that you want to edit, click the User Names column. |
|
6 |
Click Save. A message box opens, indicating the progress. |
|
7 |
Observe the User Names column. Hovering over this column shows the list of current users, taking into account the latest changes. |
You can edit group details using a wizard. This workflow is very similar to the one used creating new groups. Start it by clicking the Name column on the Groups tab.
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
3 |
Open the Groups tab. |
|
4 |
On the Groups tab, in the row containing the user account whose details you want to edit, click the Name column. |
|
5 |
Click Next. |
|
6 |
Internal and built-in groups only: If required, add or remove one or more groups, then click Next. Adding a user to a group grants access to all of the roles that are associated with that group. |
|
7 |
If required, add or remove one or more roles, then click Finish. Granting a role to a group grants all members of that group access to the role. |
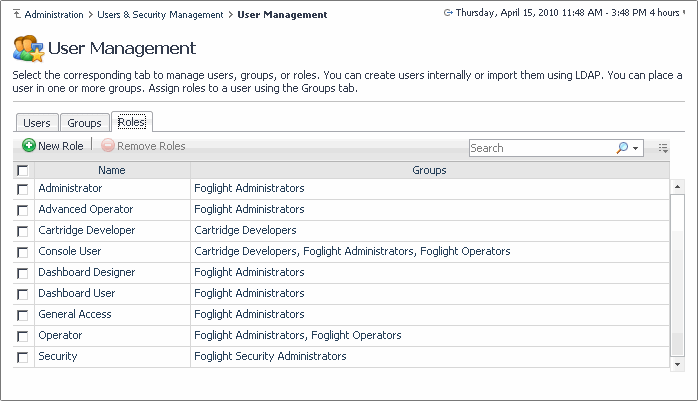
There are two types of roles in Foglight:
|
• |
Built-In. They dictate what actions users can perform. That is, when a role is assigned to a group, it enables the members of that group to use specific features or components for which access is controlled. |
|
IMPORTANT: The Built-In roles cannot be deleted. |
|
• |
Administrator. This role enables a user to access the Administration Module, the Web Console (web.xml), hidden Administration URLs, and the JMX-Console. An Administrator can manipulate agents, rules, derived metrics, registry variables, cartridges, types, and scripts. Users with this role also have access to all available report templates. Other users can use only those report templates whose roles match their user roles. The only limitation for Administrators is that they cannot access or edit the Users and Security dashboard, or access the Dashboard Development dashboard. |
|
• |
Advanced Operator. This role builds on the Operator role by adding the ability to access build-oriented dashboards such as the Service Builder and the Reports page, where users can add, manage, and manipulate scheduled reports. Users with this role can only access the report templates with advanced operator roles. |
|
• |
Cartridge Developer. This role extends the Dashboard Designer role by allowing the user to modify core dashboards and system modules. It also grants access to the Dashboard Development dashboard. |
|
• |
Console User. This role enables a user to access the Web Console (web.xml) only. It is the base level locked-down read-only role. Users assigned this role will not have access to core dashboards. |
|
• |
Core Reports. This role is assigned to all report templates included with the Management Server. This role is required by vFoglight to limit access to the reports provided by Core. |
|
• |
Dashboard Designer. This role builds on the Dashboard User role by adding the ability to access all dashboard tools such as Definitions and Data Sources. This role is for users who design dashboards using these advanced dashboard tools. |
|
• |
Dashboard User. This role is similar to the Console User role, but with additional access to any additional dashboards associated with the user. This role also includes permission to create new dashboards, new reports, and to configure the dashboard environment. |
|
• |
General Access. This role is for pre-5.2 cartridges installed on a version 5.2 or later Management Server. The role will be added to the appropriate views so that dashboards from the cartridge will appear in the Foglight interface. |
|
• |
Operator. This is the base level role for monitoring in Foglight. Users assigned this role have access to the core dashboard set such as Hosts, Alarms, Services, and Reports, with the ability to create new dashboards. Users with this role can only access the report templates with operator-level roles. This is the recommended default for new users. |
|
• |
Report Manager. This role allows users to generate and schedule the reports to which they have role access. It is different from the Operator role in that the users granted the Operator role can generate reports but not schedule them. The Report Manager role does not allow the user to create report templates with either the Definitions editor or custom report builder. For complete information about the Definitions editor, see the Web Component Guide. For details about the custom report builder feature, see “Creating a Report based on the Current Dashboard” in the Foglight User Help. |
|
• |
Security. This role provides access to the Users & Security dashboard. |
|
• |
Support. Users with this role have access to the Manage Support Bundles dashboard and the report artifacts necessary to generate the Diagnostic report contained in the support bundle. |
|
• |
Internal. Users with the Security role can create Internal roles. |
To access this tab, on the navigation panel, choose Dashboards > Administration > Users & Security. From there, to start managing user access, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles and open the Roles tab.
The Roles tab includes a wizard that allows you to create new roles and associate them with groups. The wizard is invoked using the New Role button on the Roles tab. Using this flow you can create one or more roles.
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
3 |
Select the Roles tab. |
|
a |
In the Name box, type the role name. |
|
b |
To create multiple groups, click Add more names, and type them into the list that appears, followed by clicking Add. |
|
c |
Optional — In the Description box, type the role description. |
|
d |
Click Next. |
|
6 |
Select one or more groups to which you want to grant the role you are about to create, followed by clicking Finish. Granting a role to group grants that role to all of the users that are the members of that group. |
Use the Remove Roles button on the Roles tab to remove roles from Foglight. You can only delete internal roles that are added after the installation.
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
3 |
Open the Roles tab. |
|
4 |
On the Roles tab, select the internal role that you want to delete. |
|
5 |
|
6 |
Click Delete. |
Granting a role to a group grants the role access to all users that are the members of that group.
On the Roles tab, the Groups column shows the roles granted to each group, or the number of roles, if that number is higher than five.
Hovering over this column shows a list of the groups associated with the role entry.
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
3 |
Open the Roles tab. |
|
4 |
On the Roles tab, in the row containing the role entry that you want to edit, click the Groups column. |
|
6 |
Click Save. The dialog box closes and a message box opens, indicating the progress. |
|
7 |
Observe the Groups column. Hovering over this column shows the list of current groups, taking into account the latest changes. |
You can edit role details using a wizard flow. This flow is very similar to the one used creating new roles. Start this flow by clicking the Name column on the Roles tab.
|
1 |
|
2 |
On the Users and Security Management dashboard that appears in the display area, click Manage Users, Groups, Roles. |
|
3 |
Open the Roles tab. |
|
4 |
On the Groups tab, in the row containing the user account whose details you want to edit, click the Name column. |
|
5 |
Click Next. |
|
6 |
If required, add or remove one or more groups, followed by clicking Finish. Associating a group with a role grants the group members access to that role. |
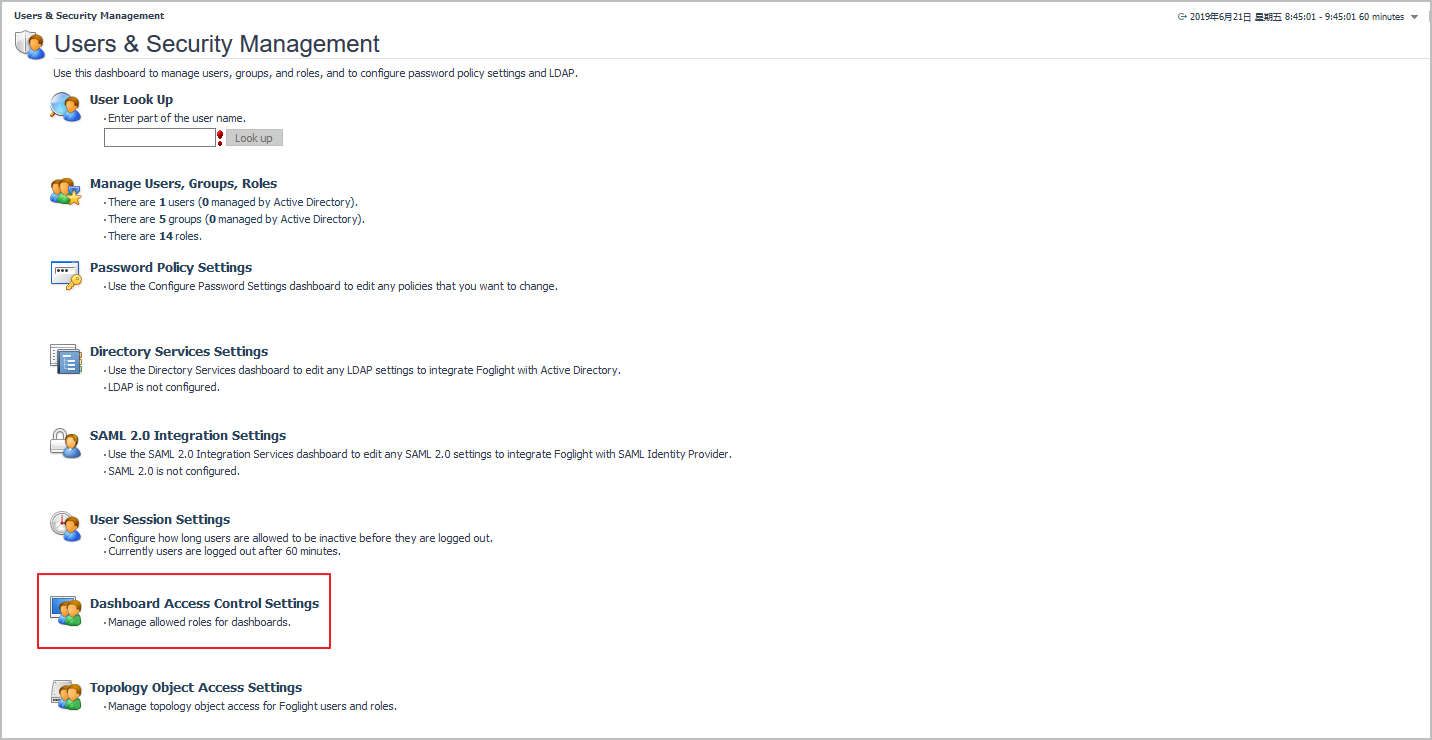
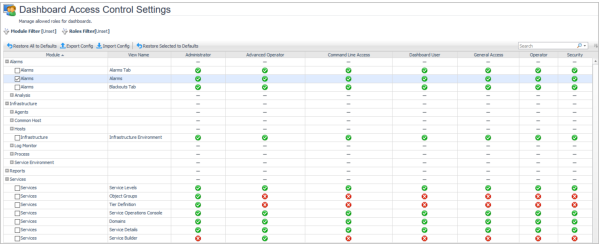
Foglight administrators can use the setting to control dashboard access for a specific role.
|
NOTE: This feature requires cartridge support. If a cartridge supports Dashboard Access Control Settings feature, the key dashboards which support access control will be displayed on the Dashboard Access Control Settings view. |
To get access to Dashboard Access Control Settings, click Dashboards > Administration > Users & Security in the Navigation panel.
The Dashboard Access Control Settings include the following fields:
|
NOTE: The For example, the Hosts view on Infrastructure cartridge can be accessed by any roles from other cartridge, but not all roles can see the Hosts view on the menu. |
|
• |
|
• |
|
• |
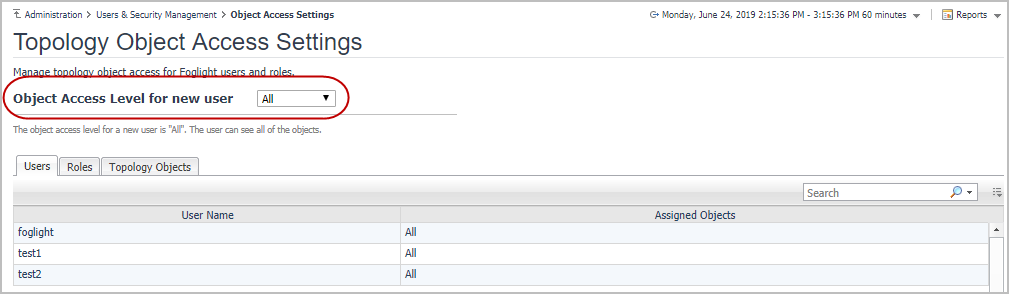
There are three access levels, All, Customized, and None. By default, all the existed users and newly created users are set to All level. The administrators can change the access level either from the object access level drop-down list for newly created users, or from the cell action in assigned objects column on Users tab for specific users.
|
• |
All: It indicates the users can see all of the objects. |
|
• |
None: It indicates that the users can see none of the objects. |
|
• |
Customized: It indicates that the users can see the objects which has been assigned to the users or the roles the user belong to. |
|
NOTE: The drop-down list can only set access level for the newly created users. To set access level for existed users, click the relevant Assigned Objects column on the Users tab, then click the pop-up action menu. |
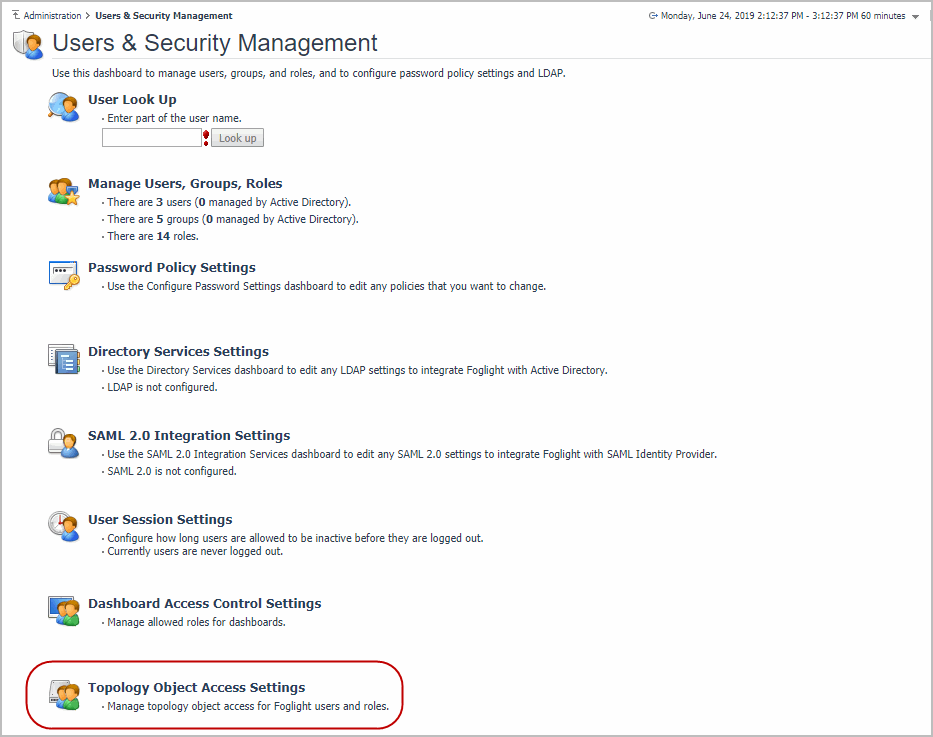
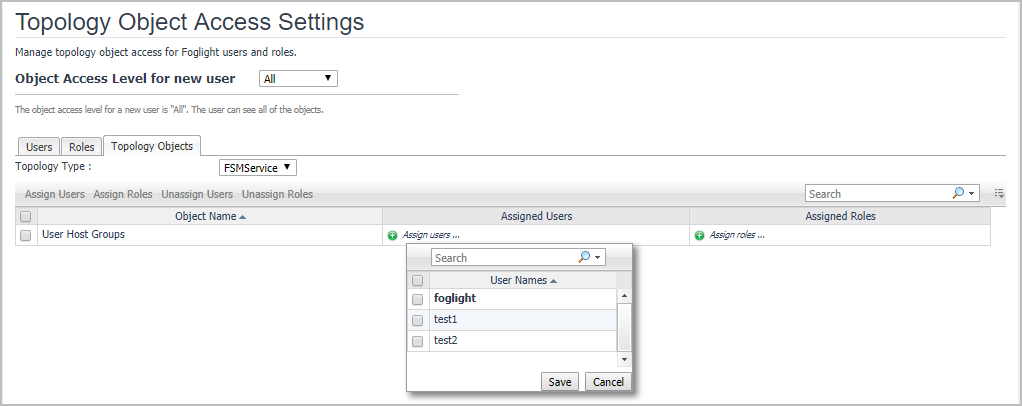
To get access to Topology Object Access Settings, click Dashboards > Administration > Users & Security in the Navigation panel.
The administrators can assign objects to user or role by using the Users, Roles, or Topology Objects tabs. A user can see clearly which objects are assigned through the Users tab.
The Users tab is the main tab to configure the object access. The Assigned Objects column shows the current access level for the user. If the level is Customized, then it will display the numbers of the objects assigned to the user. By clicking the Assigned Objects column of each user, you can change the object access level. The options include, All, None, and Manage.
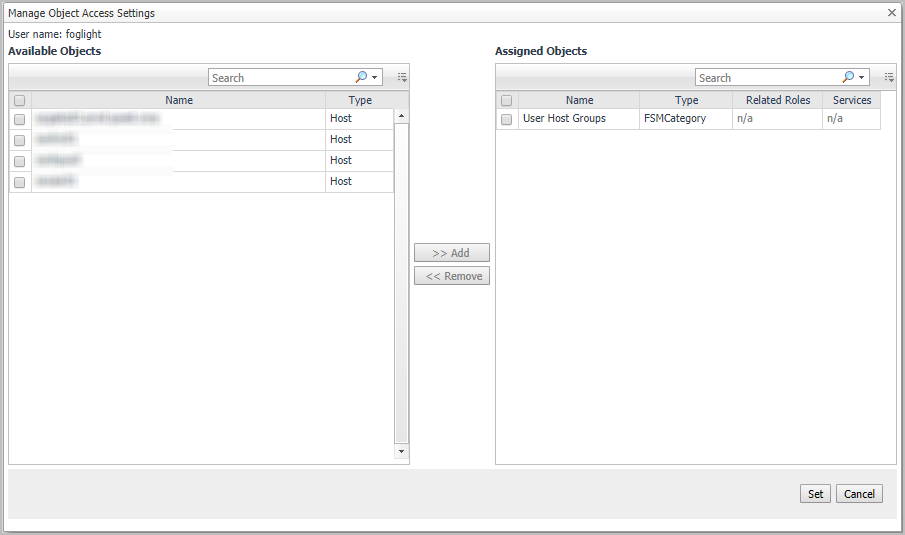
By clicking Manage, a Manage Object Access Settings dialog-box opens. In the Available Objects fields, it shows the objects that can be assigned to the user. In the Assigned Objects fields, it shows the objects that have been assigned to the user and the roles or services the assigned object belongs to. By checking check-box, you can add Available Objects to the user, or remove the Assigned Objects from the user.
|
NOTE: For the objects belong to a role or a service, you cannot remove the assigned objects from the user through the Users tab. For a role related object, remove the objects through Roles tab, while for a service related objects, remove the service via Service > Service Builder dashboard. |
After finishing configuration, click Set to apply the change. The Set button is also used to change the level from All or None to Customized.
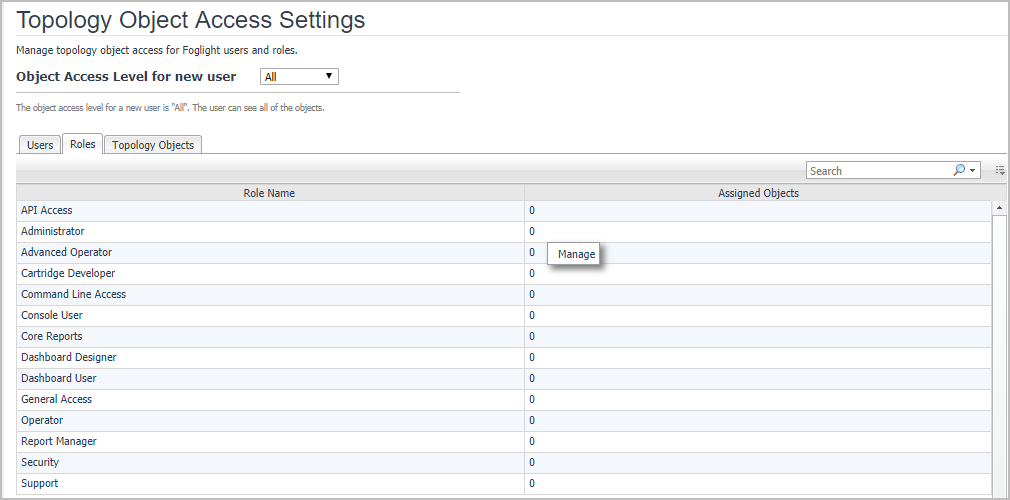
The Roles tab lists the assigned objects numbers to a certain role. By clicking the number of the Assigned Object and Manage, a Manage Object Access Settings dialog-box opens. By checking check-box, you can add Available Objects to the role, or remove the Assigned Objects from the role. After finishing configuration, click Set to apply the change.
The Topology Objects tab shows the objects assignment for each object. The supported Topology Type is determined by the cartridge you installed. By default, there is only one type, FSMService.
|
• |
Check the Object Name you want to assign, click the buttons Assign Users, Assign Roles, Unassign Users, or Unassign Roles to make desired changes. |