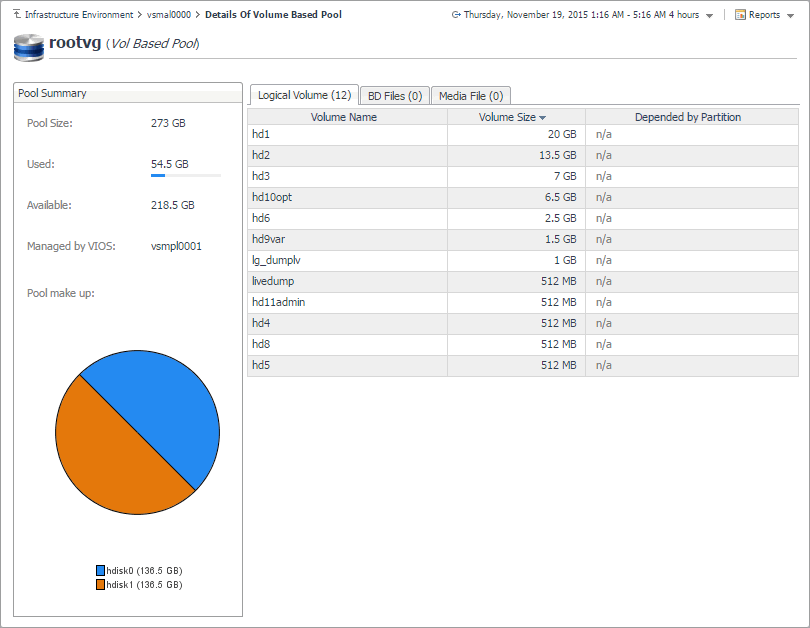
Investigating volume-based storage pools
PowerVM® managed servers and PowerVM virtual I/O servers typically rely on volume-based shared storage pools to efficiently use system resources and increase their overall utilization. When you explore the managed server and PowerVM VIOS Storage Breakdown views, you can drill down on a volume-based storage pool to see the logical volumes that belong to it, the PowerVM partition associated with them, their size, and other details, in the Details Of Volume Based Pool view. This view also displays general information about the selected disk pool, such as its size, the managing VIOS, and identifies the hard disks on which the containing logical disk partitions. Use this view to find out the sizes of individual volumes and their association with PowerVM partitions, when needed.
To navigate to this view, in the Selected Service PowerVM view, select a managed server or a PowerVM VIOS, and click Explore. Open the Storage tab, and in the Volume Based Pool Entitled view, click the title bar of the volume-based pool that you want to investigate.
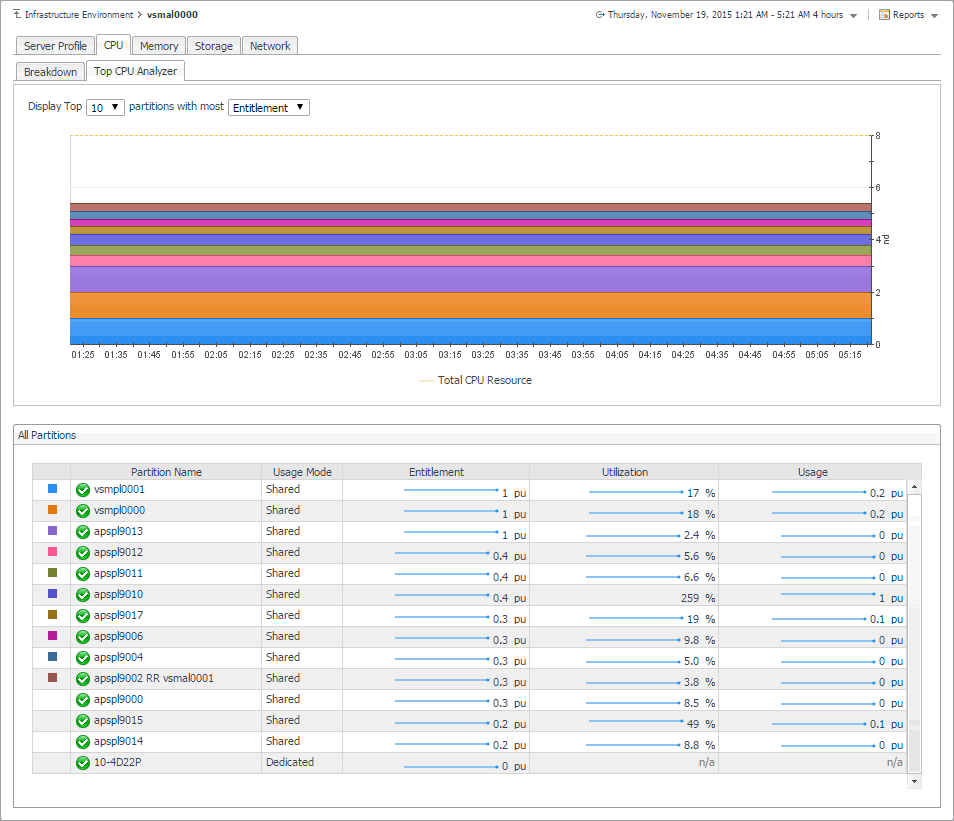
Exploring top resource analyzers
The Top Analyzer views appearing on the individual tabs of the managed server details view and PowerVM VIOS details view identify the partitions with the highest resource entitlement, utilization, and usage, and the physical adapters with the highest network throughput. Use them it to find out if any of the logical partitions running on the selected managed server or associated with the selected PowerVM VIOS show the signs of processor, memory, or disk space exhaustion or poor utilization, or unusually high network activity. This can help you maintain the stability of your system and ensure optimum resource usage.
To navigate to this tab, in the Selected Service PowerVM view, select a managed server or a VIOS, and click Explore. Open the CPU (managed servers only), Memory (managed servers only), Storage, or Network tab, and open the Top CPU Analyzer (managed servers only), Top Memory Analyzer (managed servers only), Top Storage Analyzer, or Top Network Analyzer tab.
|
Display Top n partitions with most… |
||
|
When Entitlement is selected, the Total CPU Resource areas in the graph represent the number of processing units allocated to the PowerVM partitions that are associated with the managed server. When Utilization is selected, the areas in the graph represent the percentage of the managed server processor resources allocated to the partitions that are associated with the server and in use over the selected time range. When Usage is selected, the areas in the graph represent the number of processing units allocated to the partitions associated with the managed server that are in use over the selected time range. | ||
|
When Entitlement is selected, the Total Memory Resource areas in the graph represent the amount of memory resources allocated to the PowerVM partitions that are associated with the managed server. When Utilization is selected, the areas in the graph represent the percentage of the managed server memory resources allocated to the partitions associated with the server that are in use over the selected time range. When Usage is selected, the areas in the graph represent the amount of memory resources allocated to the partitions associated with the managed server that are in use over the selected time range. | ||
|
When Usage is selected, the areas in the graph represent the disk space allocated to the partitions associated with the managed server or PowerVM VIOS, that are in use over the selected time range. | ||
|
Top CPU Analyzer and Top Memory Analyzer only. Indicates if the processor or memory resources allocated to the PowerVM partition are participated in shared processor or memory pools (Shared), or are dedicated specifically to that partition (Dedicated). | ||
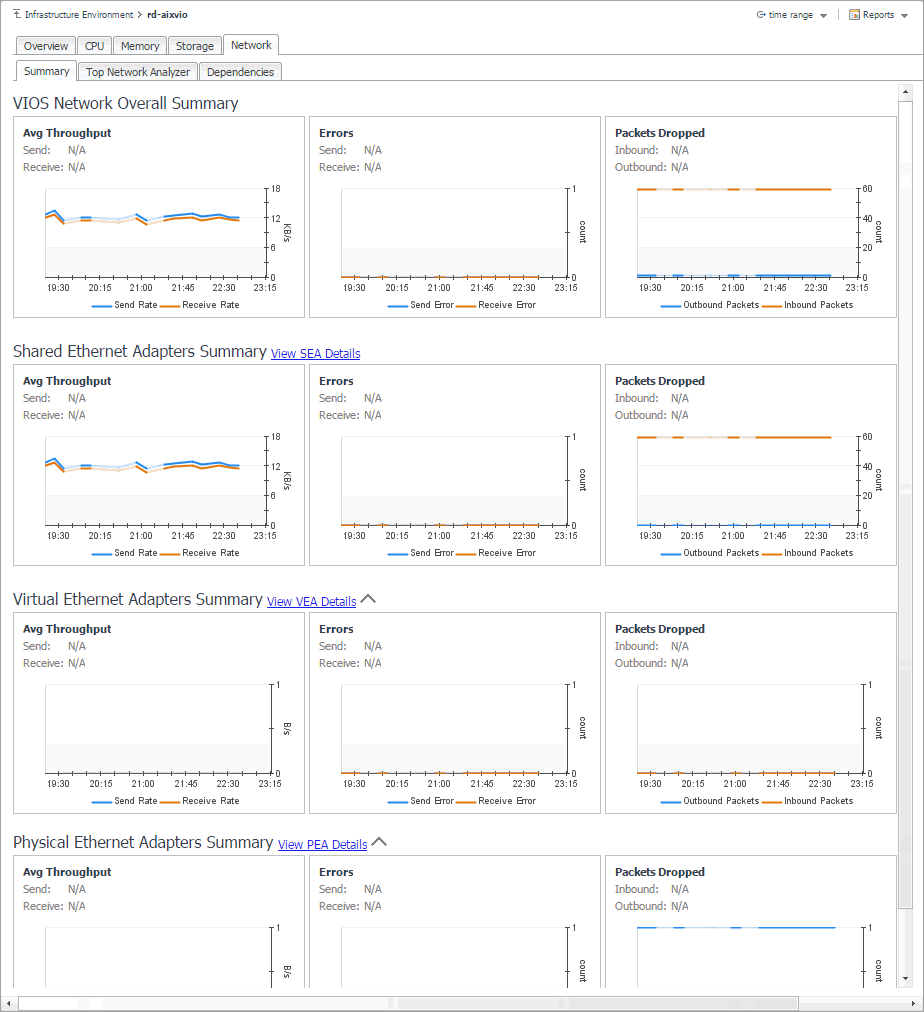
Exploring PowerVM VIOS network summaries
The Summary tab on the Network tab of the PowerVM VIOS detail view provides information all network adapters associated with the selected PowerVM® VIOS, shared ethernet adapters, virtual ethernet adapters, and physical ethernet adapters. Use it to find out if any specific collection of adapters exhibits low throughput, high levels of dropped packets or errors, to maintain the stability of your system and ensure optimum network throughput levels.
To navigate to this tab, in the Selected Service PowerVM view, select a PowerVM VIOS, and click Explore. Open the Network tab, and open the Summary tab.
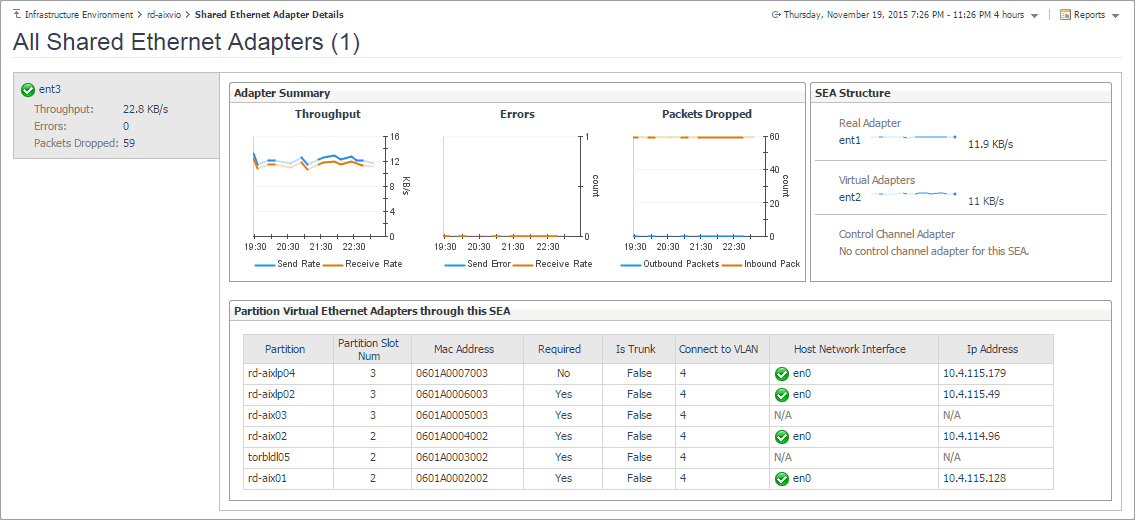
Drilling down on shared network adapters
The Shared Ethernet Adapter Details view provides information about all shared network adapters associated with the selected PowerVM® VIOS. A shared network adapter enables multiple PowerVM partitions to share one adapter, to optimize the overall use of physical resources. Use it to find out if the adapters exhibits low throughput, high levels of dropped packets or errors, to maintain the stability of your system and ensure optimum network throughput levels. You can also use this view to review the PowerVM partitions that use these adapters, and to review their settings.
To navigate to this view, in the Selected Service PowerVM, select a PowerVM VIOS, and click Explore. Open the Network tab, click Summary, and in the Shared Ethernet Adapters Summary area, click View SEA Details.
|
Indicates whether the I/O slot or virtual I/O adapter is required for the partition. Valid values:
| |||||||
| |||||||
|
The physical network adapter associated with the PowerVM partition. | |||||||