Permissions requirements
In general, requirements relating to permissions can be split into two categories:
·Accounts / Permissions needed for running the Core
·Accounts / Permissions needed for running the modules
Each of those can use independent permissions. In fact, if required, each module can use independent permissions from each other module. And that account can be different from the one running the Core.
Installing the Core typically requires a plain domain service account with Local Admin permissions on the machine and the dbcreator role on SQL. Installing Modules requires a plain domain service account with Local Admin permissions (for the install only) and then different permissions, depending on the role of the module.
·Core: Local Admin
·Module: Local Admin
·SQL: DBCreator
·Staging: Full rights for Module users
Sources/targets:
·Enterprise Vault: EV Service Account
·Exchange / Office 365: Domain service account with Local Admin rights (to run the module)
·Exchange: Multiple accounts with Application Impersonation will be added to our Credential Editor
·Office 365: 5 Office 365 service accounts will be added to our Credential Editor. All 5 accounts need Application Impersonation rights and 1 needs a custom admin role.
Minimum permissions for migrations to Office 365
|
|
NOTE: Basic authentication has been deprecated from Archive Shuttle 11.0. For authentication under modern authentication (OAuth) in Archive Shuttle, go to the Archive Shuttle Planning Guide. |
In some organizations using a user with Global Admin rights is not desirable. This topic describes an alternative approach.
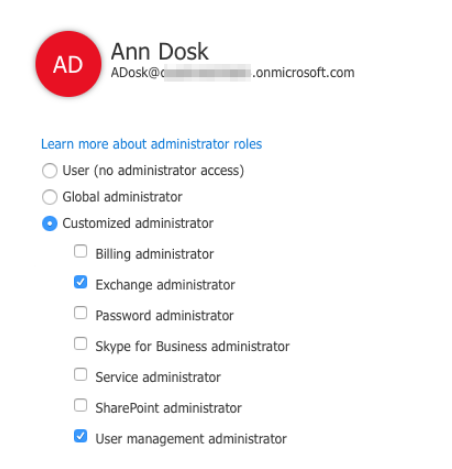
For Archive Shuttle, a user can be giving a customized administrator role, containing:
·Exchange Administrator
·User Management Administration
This is shown in the screenshot below:
With those options enabled, the required permissions will be available. When entering this user information into the Credential Editor, the check box should be enabled next to Global Administrator.
|
|
NOTE: The global administrator account needs to be able to authenticate using basic authentication. |
Additional requirements for imports to Exchange
|
|
NOTE: This section is for ingesting data into Exchange 2010 SP 2 or later. |
Additional Permissions (Exchange 2010 SP 2 or later)
The Archive Shuttle Exchange Import module ingests data in to Exchange mailboxes or Personal Archives using MAPI. However, certain messages may fail to ingest using this mechanism even after a number of retries. By default the module will fall back to use Exchange Web Services (EWS) when this situation arises.
In order to support this failback, the service account that is being used to ingest the data must be granted an additional role within Exchange.
An example of the PowerShell command that can be used to grant this extra permission is shown below:
[PS] C:\>New-ManagementRoleAssignment -Name:VaultAdminImpersonization -Role:ApplicationImpersonation -User: ADomain\TheUser
Additional Permissions (Exchange 2010 SP1 or earlier)
Ingestion to versions of Exchange 2010 SP 1 or earlier can be done by using EWS only. This means that the ingest provider order, on the System Configuration page, should be updated to show just EWS.
In order to support this feature, the service account that is being used to ingest the data must be granted an additional role within Exchange.An example of the PowerShell command that can be used to grant this extra permission is shown below:
[PS] C:\>New-ManagementRoleAssignment -Name:VaultAdminImpersonization -Role:ApplicationImpersonation -User: ADomain\TheUser
Recommended Bitness
It is recommended to use 64 bit modules when ingesting data into Microsoft Exchange. In many environments an ingest bridgehead server is used to perform the ingest, and whilst the machine (physical or virtual) may have 16 Gb or more RAM, out of memory errors may be observed from time to time if the regular, 32 bit modules are used.
To use the 64 bit modules it will be necessary to install 64 bit Outlook, and then the 64 bit modules. These modules will utilize RAM beyond the normal 2 Gb Windows process limit allow for faster and more reliable migrations to take place.