SQL Optimizer for Oracle® automates the SQL optimization process and maximizes the performance of your SQL statements. SQL Optimizer for Oracle® analyzes, rewrites, and evaluates SQL statements located within database objects, files, or collections of SQL statements from Oracle's System Global Area (SGA). Once SQL Optimizer identifies problematic SQL statements, it optimizes the SQL and provides replacement code that includes the optimized statement.
SQL Optimizer also provides a complete index optimization and plan change analysis solution. It provides index recommendations for multiple SQL statements or a SQL workload, simulates index impact analysis, and generates SQL execution plan alternatives.
SQL Optimizer consists of the following modules:
Optimize SQL includes a SQL Rewrite mode and a Plan Control mode.
| SQL Rewrite Mode | Description |
| Optimize SQL Statements |
Uses SQL Optimizer's Artificial Intelligence engine to execute SQL syntax rules and apply Oracle optimization hints to create semantically equivalent SQL statement alternatives. In addition, you can create user-defined alternatives to test with your database environment. |
| Test Run SQL Alternatives |
Test run SQL statement alternatives to view execution statistics. This provides execution times that allow you to identify the best SQL statement for your database environment. |
| Generate Index Alternatives |
Analyzes SQL statement syntax and database structure to provide index alternatives that improve performance. SQL Optimizer uses virtual indexes to generate alternatives without physically creating the indexes on your database. |
| Test for Scalability | Uses Benchmark Factory™ to simulate potential workload conditions to test SQL statement performance. |
| Incorporate Best Practices | Incorporates common best practices techniques to improve database performance. |
| Plan Control Mode | Description |
| Generate Execution Plan Alternatives | Generates execution plan alternatives for your SQL statements without changing the original source code. |
| Deploy Baselines |
Creates baselines from the execution plan alternatives and deploys these baselines to ensure optimal database performance. |
Optimize Indexes analyzes a SQL workload or any group of SQL statements and determines the best index set for the workload or group of statements.
Batch Optimize submits files, database objects, or SQL text for batch processing. Batch Optimize scans and extracts the SQL statements, optimizes the statements, and tests the alternatives to find the best performing SQL statements for your database environment.
Scan SQL identifies problematic SQL statements in your source code and database objects without execution. Scan SQL then analyzes the problematic SQL statements and categorizes them according to performance levels.
Inspect SGA analyzes SQL statements from Oracle's SGA. You can specify the criteria used to retrieve SQL statements and execution statistics to review SQL performance.
Use Analyze Impact to evaluate the impact on a SQL workload from database changes by tracking execution plan and Oracle cost changes for SQL statements. You can run an impact analysis to estimate the performance impacts from parameter changes and new indexing. You can also run a comparison of two different databases that run the same application.
Manage Plans organizes stored baselines and outlines used to improve SQL statement performance.
The SQL Optimization workflow ensures that your SQL statements perform optimally in your database environment.
| Procedure | Description |
|---|---|
| Identify Problematic SQL |
Batch Optimize SQL extracts embedded SQL statements from your database objects. After extracting the statements, it analyzes execution plan operations and identifies potential performance bottlenecks. Notes:
|
| Optimize SQL Statements |
Once Batch Optimize SQL identifies problematic SQL statements, it automatically optimizes these statements and generates alternatives with unique execution plans. Batch Optimize SQL generates the alternatives by analyzing SQL statement syntax and database structure. You can also use hints during the optimization process. Note: You can also use SQL Rewrite mode in Optimize SQL to optimize SQL statements extracted with Scan SQL. |
| Test Run SQL Alternatives |
After Batch Optimize SQL generates alternatives, it will automatically test run the alternatives and provide you with the best statement for your database environment. Note: Since Batch Optimize SQL automates the SQL optimization process, you are only provided with the best alternative statement it generates. You can send your statement to Optimize SQL to view all statement alternatives available. |
| Compare SQL Alternatives |
Batch Optimize SQL compares the SQL text and execution plans of your original SQL statement and the best alternative. Note: If you send your statement to Optimize SQL, you can compare your original SQL statement with any of the statement alternatives available. |
| Replace Problematic SQL Statements | Batch Optimize SQL creates a script that you can use to replace your original source code. |
| Generate Index Alternatives |
In addition to optimizing SQL statements, you can generate index alternatives for your statement in Optimize SQL. You can generate new indexes for a group of SQL statements or for a SQL workload using Optimize Indexes. |
| Generate Execution Plan Alternatives | You can use Plan Control mode in Optimize SQL to generate execution plan alternatives for your SQL statements without changing the original source code. Plan Control mode finds the best execution plan for your SQL statement and deploys it as a baseline. |
| Analyze Performance Changes | Analyze Impact evaluates what impact certain changes, such as indexing and parameter changes, will have on SQL statement performance. |
 |
What's New in |
This release of SQL Optimizer for Oracle® includes the following new features and enhancements.
SQL Optimizer for Oracle 9.3.3 is a minor release and includes resolved issues and the following enhancements.
For a complete list of enhancements and resolved issues in this release, see the SQL Optimizer for Oracle 9.3.3 Release Notes at: Quest Support - SQL Optimizer for Oracle Technical Documentation.
SQL Optimizer for Oracle 9.3.2 is a minor release and includes resolved issues and the following enhancement.
Support for Oracle 19c.
For a complete list of enhancements and resolved issues in this release, see the SQL Optimizer for Oracle 9.3.2 Release Notes at: Quest Support - SQL Optimizer for Oracle Technical Documentation.
SQL Optimizer for Oracle 9.3.1 is a minor release and includes resolved issues and the following enhancement.
Improved performance when identifying invalid SQL. This release includes an enhancement to the SQL parsing process which significantly reduces the time required to identify certain invalid SQL statements.
For a complete list of enhancements and resolved issues in this release, see the SQL Optimizer for Oracle 9.3.1 Release Notes at: Quest Support - SQL Optimizer for Oracle Technical Documentation.
SQL Optimizer for Oracle 9.3 is a minor release and includes resolved issues and the following enhancements.
For a complete list of enhancements and resolved issues in this release, see the SQL Optimizer for Oracle 9.3 Release Notes at: Quest Support - SQL Optimizer for Oracle Technical Documentation.
Test Run Different Bind Values
Performance Chart - Customize Colors. You can now modify the chart line color for each alternative displayed in the Performance Chart (Performance variation view) in the results page. This allows you to customize chart colors for better viewing.
Additional Enhancements
For a complete list of enhancements and resolved issues in this release, see the SQL Optimizer for Oracle 9.2.3 Release Notes at: Quest Support - SQL Optimizer for Oracle Technical Documentation
New Option to Ignore Record Count Mismatch. You can now instruct SQL Optimizer to ignore a record count mismatch between alternatives and the original SQL.
Custom Test Run Settings - SQL Termination Criteria. When using run time of the fastest SQL as the SQL termination time, you can now instruct SQL Optimizer to use the fastest run time in this test run only or to include the fastest run time from tested alternatives.
User Interface. A Chinese language version of the SQL Optimizer for Oracle application is not provided for this release. You can find a Chinese language version of the SQL Optimizer documentation (User Guide, Installation Guide, and Release Notes) at: https://support.quest.com/sql-optimizer-for-oracle/technical-documents.
This release of SQL Optimizer includes an exciting new enhancement to the Optimize SQL workflow. You can now interrupt the optimization process without losing the SQL alternatives and test run results generated thus far in your SQL Rewrite session. This is useful if you need to close SQL Optimizer or shut down your computer in the middle of a long-running optimization session. When it is convenient, reopen the saved session and resume running the optimization process, beginning from the point where it was interrupted.
Another important workflow enhancement enabled by this new feature is the ability to increase the intelligence level in the middle of an optimization process. If you find that the current intelligence level is not generating better or sufficient alternatives, you can stop the process, increase the level, and then resume the process. SQL Optimizer will use increased quotas and hints to find additional alternatives without losing the alternatives and results generated thus far.
Note: This new feature is available for SQL Rewrite sessions only. It is not available for Plan Control sessions at this time.
To stop the optimization process, click the Stop button in the SQL Details toolbar.
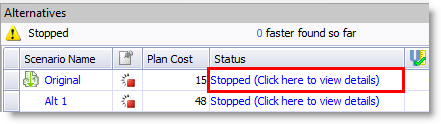
After the optimization process stops, alternatives that were in the process of executing now display a status of Stopped in the Alternatives pane.
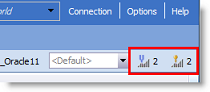
If you want to increase the intelligence level to find additional alternatives, click one of the Intelligence Level buttons in the upper-right portion of the SQL Rewrite window, increase the level, and then resume the process.
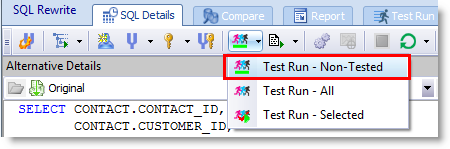
The Test Run button now includes a new command, Test Run - Non-Tested. Use this command to test run SQL alternatives that have never been tested. This is useful if you paused the optimization process during the test run phase.
Note: This new feature is available for SQL Rewrite sessions only. It is not available for Plan Control sessions at this time.
To test run untested alternatives, click the arrow beside the Test Run button and select Test Run - Non-Tested.
This release of SQL Optimizer provides a way to specify optimization settings for a single session without changing your default settings.
To change the Intelligence level for the current session (SQL Rewrite or Plan Control), click the Optimizer Intelligence Level button. Then select a predefined setting and intelligence level, or customize the settings. Your settings are applied to the current session only. The settings previously specified through Options | Optimize SQL | Optimizer or Options | Optimize SQL | Plan Control remain unchanged.
To change the Intelligence level for index generation for the current session (SQL Rewrite), click the Index Generation Intelligence Level button. Then select an intelligence level or customize the settings. Your settings are applied to the current session only. Any settings previously specified through Options | Optimize SQL | Index Generation remain unchanged.
Note: Settings specified through the Options dialog (for example Options | Optimize SQL | Optimizer) are now used as the default settings only and are applied to any new SQL Rewrite and Plan Control sessions you create. These default settings remain unchanged when you modify optimization settings at the session level.
This release includes multiple enhancements to the Test Run Different Bind Values feature.
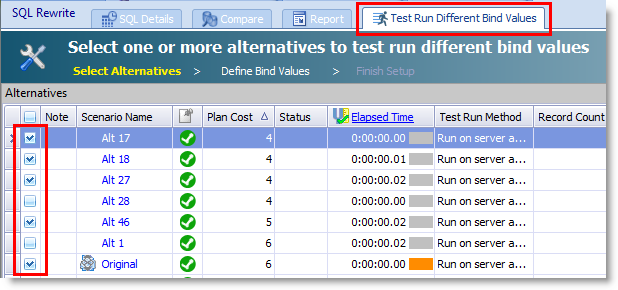
To use this feature, generate and test run SQL alternatives using the SQL Details tab in Optimize SQL. Then select the Test Run Different Bind Values tab where you can test run the best-performing SQL alternatives again, this time using a list of bind values you specify.
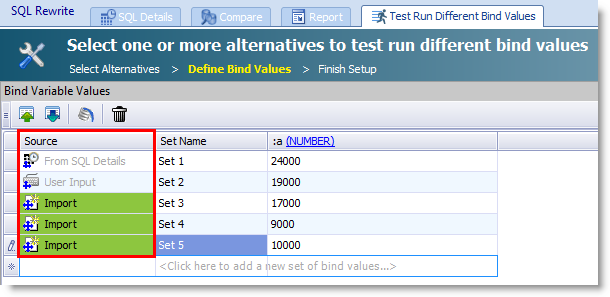
Bind value source. A new column in the Bind Values page identifies the source of the bind value. In addition, when you modify the list of bind values, new entries are highlighted green.
Auto Fill finds all available values from Oracle. When you click the Auto Fill button to retrieve bind values from Oracle, all available bind value sets captured by Oracle are now retrieved. In the previous release, only the latest set of bind values captured by Oracle was retrieved. The Bind Variables Values grid is automatically populated with any value sets found that are not currently listed in the grid.
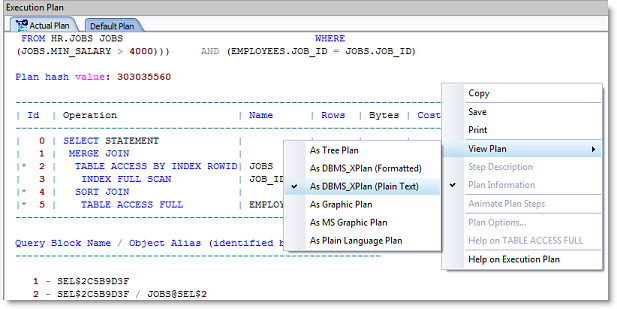
Display DBMS_XPLAN as plain text. You can now display execution plans using the DBMS_XPLAN in plain text format. This is the format returned from Oracle. To use this format, in the Execution Plan window right-click the plan and select View Plan | As DBMS_XPlan (Plain Text).
For a complete list of enhancements and resolved issues in this release, open the SQL Optimizer Release Notes from the Help menu (Help | Release Notes).

Remember, you can find blogs, videos, and forums at the SQL Optimizer for Oracle Community.
Date: Wednesday, May 6, 2020