Row chaining occurs when a row cannot physically fit into an Oracle block, and another block is required to store the remainder of the row.
Migration of an Oracle row occurs when a row is updated in an Oracle block and the amount of free space in the block is not enough to store all of the row's data. The row is migrated to another physical block in the table, but the indexes that refer to the row still indicate the block where the row used to be.
To open the Chains / Migrations page
Click I/O | Chains / Migrations.

Space Manager
If Space Manager is installed on your system, you can click the Space Manager icon at the top of the page to open that application. Tools | Space Manager
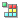
Fetch Rates Chart
Fetch Rates shows the rate of relevant row fetch operations.
Note that rows fetched by table can never chain and hence the rate of rows accessed via full table scan is not shown.
Segments With Chained Rows Grid
Segments with Chained Rows shows tables that are known to have chained or migrated rows.
Chained rows are noted when a table is analyzed using the ANALYZE command. Tables that have not been analyzed or have been analyzed via procedures in the DBMS_STATS package will not be displayed here, they will need to be analyzed with the ANALYZE command.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
|
Table Name |
The name of the table under investigation. |
|
Rows |
The number of rows in the table. |
|
Chained Rows |
The number of chained rows in the table. |
|
Pct Chained |
The percentage of rows in the table that are chained. |
|
PCTFREE |
The minimum percentage of a data block that is kept free to accommodate updates to rows that already exist in the block. |
Sessions Experiencing Continued Fetch Grid
Sessions Experiencing Continued Fetch shows sessions that have experienced Continued Fetch operations as they accessed rows. The current SQL statement is also shown.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
|
SID |
Session ID. |
|
Oracle User |
The Oracle account name for the session. |
|
Continued Fetches |
Fetches from chained or migrated rows. |
|
Logical Reads |
Logical database reads for the session. |
|
Physical Reads |
Physical database reads for the session. |
|
OS User |
The operating system user that established the session. |
|
Machine |
The machine hosting the database under investigation. |
|
Program |
The program causing the Continued Fetch operation. |
|
Status |
The status of the session — for example, ACTIVE or INACTIVE. |
|
Type |
The type of session — FOREGROUND or BACKGROUND. |
|
SQL |
The current SQL statement. |
|
Process ID |
Operating system process ID for the client program. |
|
Serial |
Serial number of the session. SIDs can be reused after the session disconnects, but the combination of SID and Serial number is always unique. |