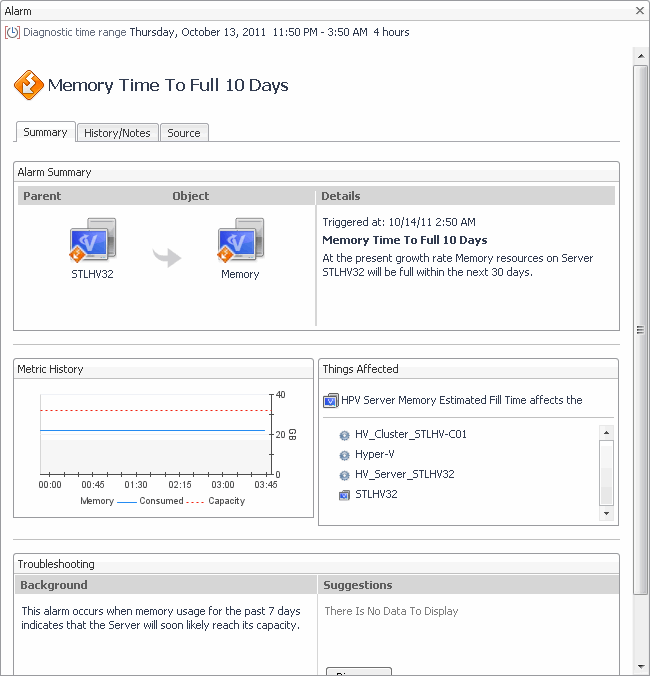
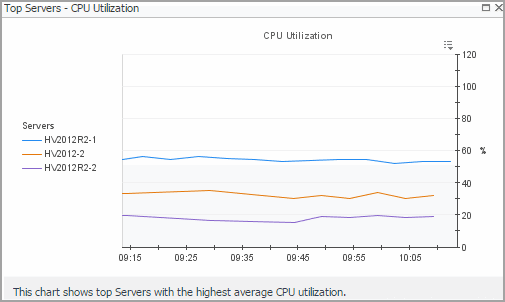
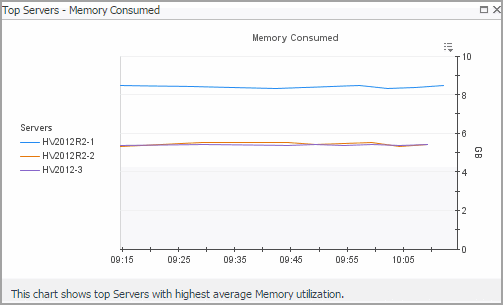
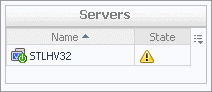
Servers view
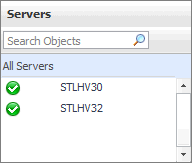
The Servers view is a tree view. It lists the servers that exist in your environment and shows their state.
This view appears in the Quick-View on the left when you select the Servers tile in the Virtual Environment view.
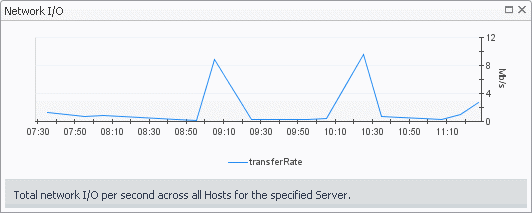
Selecting the All Servers node displays overall resource utilization for all servers in your integrated system, and the elements that consume the highest amount of system resources in the Summary - All Servers view on the right. Similarly, selecting a server node shows server-specific metrics in the Server Summary view.
Summary - All Servers view
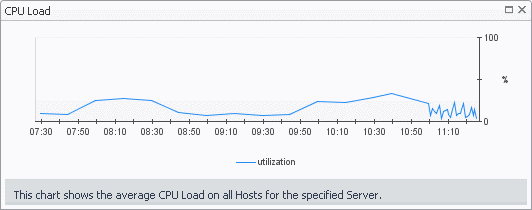
The Summary - All Servers view displays overall resource utilization information for a group of physical servers and shows the elements that consume the highest amount of system resources.
This view appears in the Quick-View on the left when you select All Servers in the Servers view.

This view is made up of the following embedded views:
Server Summary view
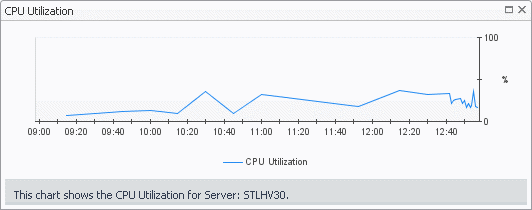
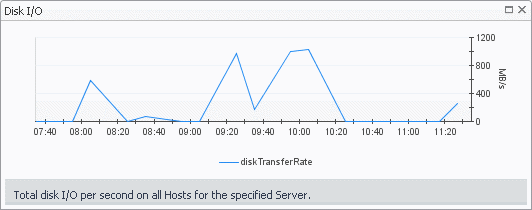
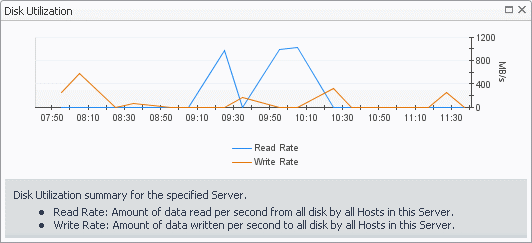
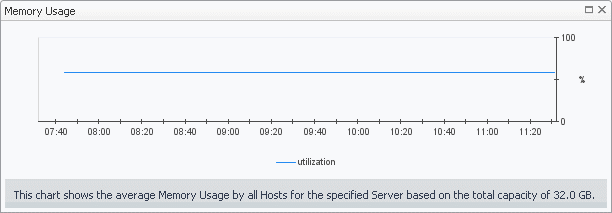
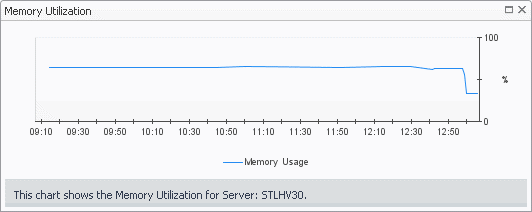
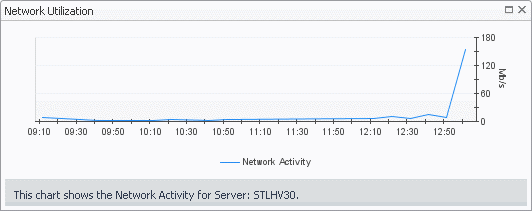
The Server Summary view shows the overall resource utilization and the amounts of system resource consumption for a physical server.
This view appears in the Quick-View on the left when you select a server in the Servers view.
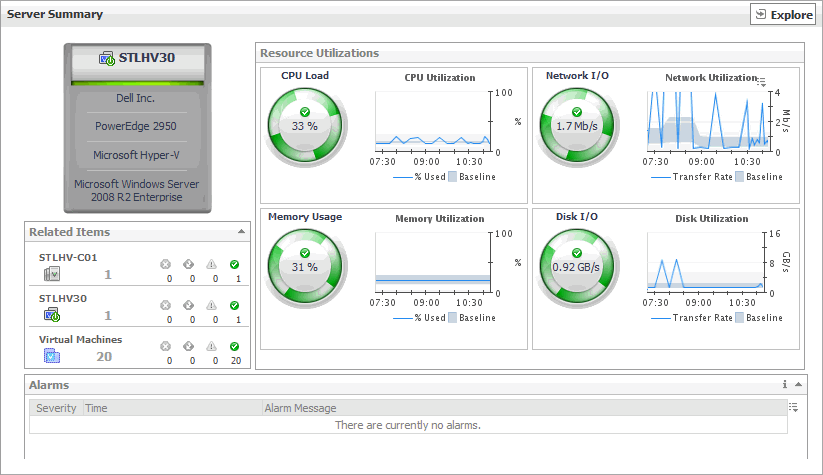
This view is made up of the following embedded views:
|
|
Shows the numbers and states of the cluster the selected server belongs to, the selected server, and the virtual machine running on the selected server. |
|
|
|
• |
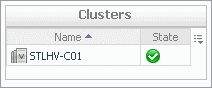
Cluster. The name of the cluster to which the selected server belongs, followed by the counts of all alarms associated with the cluster, broken down by the alarm state (Normal, Warning, Critical, Fatal). | |
|
|
|
• |
Server. The name of the selected server, followed by the counts of all alarms associated with that server, broken down by the alarm state (Normal, Warning, Critical, Fatal). | |
|
|
|
• |
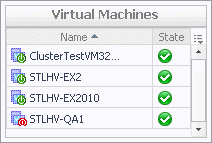
Virtual machines. The number of the virtual machines running on the selected server, followed by the counts of all alarms associated with those virtual machines, broken down by the alarm state (Normal, Warning, Critical, Fatal). | |
|
|
Drill down on: |
|
|
|
• |
Alarm count. Displays a dwell that shows the objects against which alarms are generated. |
|
|
|
|
• |
Cluster. Displays the Clusters dwell, showing the name and state of the cluster the selected server belongs to. |
|
|
|
|
• |
Server. Displays the Servers dwell, showing the name and state of the selected server. |
|
|
|
|
• |
Virtual Machines. Displays the Virtual Machines dwell, showing the names and states of the virtual machines that are running on the selected server. |
|
SOFS Server monitoring
A Scale-Out File Server (SOFS) server is a physical component required to begin building a virtual infrastructure. SOFS servers provide hypervisor-based architecture for controlling and managing resources for the virtual machines that run on it. Virtual machines running on an SOFS server share the server’s resources.
To review data collected about a specific SOFS server or all SOFS servers, make your selection in the Quick-View.