Connecting to an Excel file is easy. To create the connection, simply open the Excel file from the Create New Connection dialog 
To create an Excel connection
Click 
Select Excel from the Group list.
Complete the Create New Connection dialog. Review the following for additional information:
| General Tab | Description |
|
Category |
Select a category if you want to color code your connection. Tip: The color is applied in the Connection Manager and other connection dialogs. You can also create a new category for your connection. |
| Advanced Tab | Description |
|
Enable import mode |
Select this checkbox to set IMEX=1 in the connection string, which converts intermixed data to text. |
|
Show system tables |
Select to display worksheets as system tables. Toad uses the worksheet name suffixed with a dollar sign ($). |
|
Automatically create ranges |
Select this option if you want Toad to automatically create named ranges. Toad creates one named range in each worksheet (unless the Toad name, AutoRange_<worksheet name>, already exists). Note: Toad does not overwrite the user defined named ranges. The Toad-created named ranges and the user defined named ranges are both visible in the Object Explorer after connecting. Deselect this option if the Excel file contains user defined named ranges and you do not want Toad to create additional named ranges. Important: If you deselect this option, and your Excel file does not contain named ranges, Toad is unable to create tables from your data. The feature is selected by default. |
|
Hide named ranges |
Select the named ranges to hide. Note: Named ranges are not displayed until after a connection is created (in the Connections or Connection Properties dialog). In Excel 2007 files, named ranges are not displayed for active connections. |
|
Open in Excel |
Click to open the selected file in Excel. This is useful if you want to modify your file or define named ranges before connecting. |
Click Connect to connect immediately while saving the connection information. Optionally, click Save to save the connection without connecting.
Understand how Toad creates data tables from an Excel file
Toad uses Excel named ranges (regions) to define the data to include in a table. Therefore, any data that you want to display and easily query in Toad must be included in an Excel named range (region).
You can create named ranges using one of the following methods:
To create a named range in Excel
In the Excel file, select the data that you want to include in the table (including column headings). Then define a named range.
| » | In Excel 2003, select Insert | Name | Define. |
| » | In Excel 2007, right-click the data and select Name a Range. |
To allow Toad to automatically create named ranges
| » | When creating a new connection to the Excel file, in the New Connection dialog, select Automatically create ranges. Toad creates one named range for each worksheet and includes the contents of every formatted cell. |
Tip: For an Excel file with an existing connection, in the Navigation Manger, right-click the file and select Properties. On the Advanced tab, select Automatically create ranges. Toad creates the named ranges the next time you reconnect to this file.
To hide named ranges
You can hide an Excel file's named ranges so that they do not display as tables in the Object Explorer.
In the Navigation Manager, right-click an Excel file connection and select Properties.
Note: In Excel 2007 files, the connection must be inactive for the named ranges to display.
To view or modify connection properties
To view an Excel connection's properties, do one of the following:
 on the Connections toolbar to open the Connections dialog. Select the Excel file connection in the left pane to view the connection properties in the right pane.
on the Connections toolbar to open the Connections dialog. Select the Excel file connection in the left pane to view the connection properties in the right pane. | Consideration/Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
|
Excel 2016 64-bit or Office 365 64-bit |
To successfully create a connection to an Excel file using Excel 2016 64-bit, the Microsoft Access Database Engine is required and might not have been included in the Excel installation. In addition, the architecture (bitness) of the engine must match the bitness of Toad. Note: This requirement applies only to connections to Excel, not to the Toad functionality of importing/exporting to Excel. |
To troubleshoot Excel issues, see the following:

Tip: Connections are stored in the connections.xml file and can be found by clicking the Application Data Directory link in Help | About.
Toad allows you to connect to SharePoint via OData service to view and query SharePoint lists as tables. Toad supports SharePoint 2010 and 2013. You can also create a connection to SharePoint Online.
After creating a connection, see About SharePoint Data Sources for more information.
To create a SharePoint connection
 on the Connections toolbar (ALT+F+N).
on the Connections toolbar (ALT+F+N).
Enter the connection information in the Create New Connection dialog. Review the following for additional information:
| URL |
Enter the full URL address to the SharePoint OData service endpoint for the SharePoint site to which you want to connect. The URL address should have the following format: http://<servername>/_vti_bin/listdata.svc |
| Authentication |
Select the type of authentication to use for this connection. Toad offers two options:
The required login fields will be enabled or disabled according to the authentication type that is chosen. |
| Username |
For SharePoint—Enter your Windows user name to use when connecting to this SharePoint site. For SharePoint Online—Enter the user name to use when connecting to this instance of SharePoint Online. |
| Password |
Enter the password to use when connecting. Tip: After connecting, you can set a master password to further secure your connection in Tools | Options| Environment | Security. |
| SharePoint Online | Select this option if creating a connection to a SharePoint Online instance. |
| Category | (Optional) Select an existing category or create a new one. |
|
Note: In NoSQL and Business Intelligence connections, Toad automatically saves the password in the connections.xml file as obfuscated text, as well as in Toad. To add additional password security, use Toad's Master Password feature. | |
Tips:
To create this type of connection to SharePoint, Active Directory Universal with MFA needs to be selected from the Authentication field dropdown.
The next step is to enter a user name which has been configured for multi-factor authentication and click on Connect.
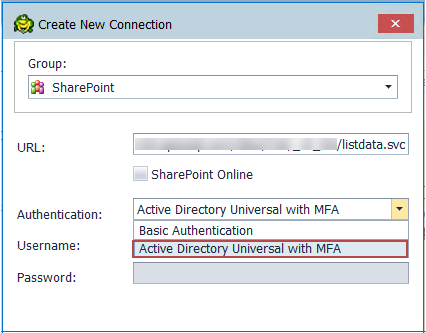
Toad Authentication Window will appear allowing you to select either Windows Authentication or AzureADTrust for the type of credentials which will be used for the connection.
The step that follows will enable you to select a user from the list or add another one by clicking on Use another account.
After that, you will be prompted to enter your credentials and depending on the type of authentication that the account has been configured with, you will undergo an additional authentication step, such as the one in the image below.
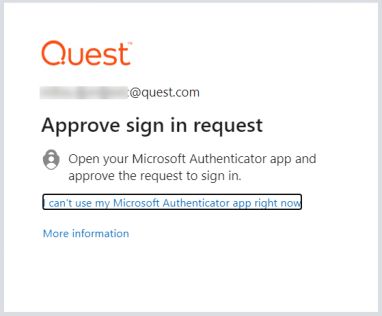
After completing the final authentication step, a successful connection to SharePoint will be made.
Setting a default SharePoint connection in Tools|Options|Environment is currently available only for Basic Authentication
Toad allows you to create connections to your Google Analytics data. A connection in Toad allows you to access the Google Analytics accounts and data that are available to you from your Google user account.
If you have multiple Google user accounts, you can create a separate Google Analytics connection in Toad for each account. For an explanation of Google accounts, see the following: https://developers.google.com/analytics/resources/concepts/gaConceptsAccounts
After creating a connection, see About Google Analytics Data Sources for more information about working with this data source.
When you create a Google Analytics connection in Toad, you log in to Google using your Google account. During the connection creation process, you also grant Toad access to the Google Analytics data accessible from that Google account.
Toad provides you with an interface to the Google log-in and authorization pages and displays these pages within the Create New Connection (and Connection Properties) dialog. The Google pages displayed are independent of Toad. The log-in process is the same as you normally encounter with your other Web-based Google log-in procedures. The only difference is that by creating a connection in Toad, you are giving Toad permission to access your Google Analytics data. This is accomplished when you click Accept in the Google authorization page.
To create a Google Analytics connection
 on the Connections toolbar (ALT+F+N).
on the Connections toolbar (ALT+F+N).
Enter the credentials (email address and password) for your Google account and click Sign in.
Note: If you have multiple Google accounts and have previously logged in to Google (or connected through Toad), the Google log-in page may display the last Google account used. To specify a different Google account for the new connection, use the Google links/menu to select another account.
In the Google authorization page that displays, click Accept to allow Toad access to your Google Analytics data. Toad then attempts to establish a connection to Google Analytics. If the connection is successful, the Create New Connection dialog closes.
If you encounter an error message when attempting to connect using your Google Analytics connection, Toad's authorization (access) to the Google account for that connection may have been lost. Use the following procedure to re-establish authorization for the connection.
You can also use this procedure to specify a different Google log-in account for a connection.
To Reauthorize
Notes:
Toad allows you to connect to a Hive data warehouse system. Apache Hive is one of the NoSQL data sources supported by Toad.
See also, About Apache Hive Data Sources.
To create a Hive connection
 on the Connections toolbar (ALT+F+N).
on the Connections toolbar (ALT+F+N).
Enter the connection information in the Create New Connection dialog. Review the following for additional information:
|
Server tab |
|
|
Host |
Enter the host name or IP address of the Hive data source. |
|
Port |
Enter the port number. |
|
Schema |
Enter a Hive schema to open upon connection. (HiveServer2 only) After connecting, you can select a different available schema in the Object Explorer. |
|
Server type |
Select the version of HiveServer the host uses, HiveServer1 or HiveServer2. |
|
Use SSL |
(HiveServer2 only) Select to use SSL to connect to Hive. |
|
HTTP mode |
(HiveServer2 only) Select to connect to HiveServer2 running in HTTP mode. Then enter the service endpoint. The default is cliservice. |
|
Session Initialization |
(HiveServer1 only) Enter any Hive session initialization commands. These commands will be executed once, at the start of each connection. |
|
Category |
(Optional) Select an existing category or create a new one. |
| Authentication tab (HiveServer1) | |
|
Connect with SSH |
Select to use SSH to connect to Hive. Then enter a user name and select an authentication method (key file or password). |
|
SSH user |
Enter the user name to log in when using SSH. |
|
SSH port |
Select the SSH port number. The default is 22. |
|
Authenticate with a key file |
Select if the host uses a key file to authenticate the SSH user field. Private key path—Enter the absolute path (including file name) to the private key file on the host (not the client). Pass phrase—Enter your passphrase. |
| Authenticate with a password |
Select if the host uses a password to authenticate the SSH user field. Password—Enter the password to log in using SSH. |
| Authentication tab (HiveServer2) | |
| Authentication |
Select an authentication method. To enter only a user name, select the Username and password method. |
| Username |
Enter the user name to use for this connection. If using Kerberos authentication, enter your user name in the following format: user@REALM or domain\user. |
| Hive host realm |
(Kerberos only) Enter the Kerberos realm of the HiveServer2 host. Note: If necessary, contact your IT department to obtain this information. Before you can successfully connect to Hive using Kerberos authentication, the Toad client computer must have a Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC) address entry for the Hive host realm. To define the KDC entry, use the following procedure. Open a Windows Command Prompt as Administrator and enter the following command: ksetup /addkdc <REALM> <KDC name> You only need to run this command once for the given realm. To confirm the setting, enter the following command: ksetup. This command should return both the name of the Hive host realm and the KDC name you specified. |
| Hive host FQDN |
(Kerberos only) Enter the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the HiveServer2 host. Note: If necessary, contact your IT department to obtain this information. |
| Service name | (Kerberos only) Enter the service name of the Hive server. The default is hive. |
|
Note: In NoSQL and Business Intelligence connections, Toad automatically saves the password in the connections.xml file as obfuscated text, as well as in Toad. To add additional password security, use Toad's Master Password feature. | |
Click Connect to connect immediately while saving the connection information. Optionally, click Save to save the connection without connecting.
Tips: