To implement role-based InTrust administration, do the following:
It is recommended that you create groups with descriptive names. For example, if you need to define an auditing administrator role, you should create a group called InTrust Auditing Admins or something similar, depending on the naming conventions in your environment.
Objects can inherit security permissions from their parents or have them assigned directly. You can specify security settings to a number of InTrust configuration objects using InTrust Manager snap-in. Setting permissions on these objects affects the objects' availability in the InTrust Manager snap-in and the InTrust operations, if the respective jobs or tasks are running under an account other than the InTrust Server account. Permissions control whether specific people can access objects in the snap-in and whether an account under which a certain job is running can access objects used by this job.
The following figure illustrates the inheritance of security permissions of InTrust configuration objects available in the InTrust Manager snap-in. Containers are shown as folders. The lock icon means that you can edit security settings of the marked object using the Security tab in its properties dialog box.
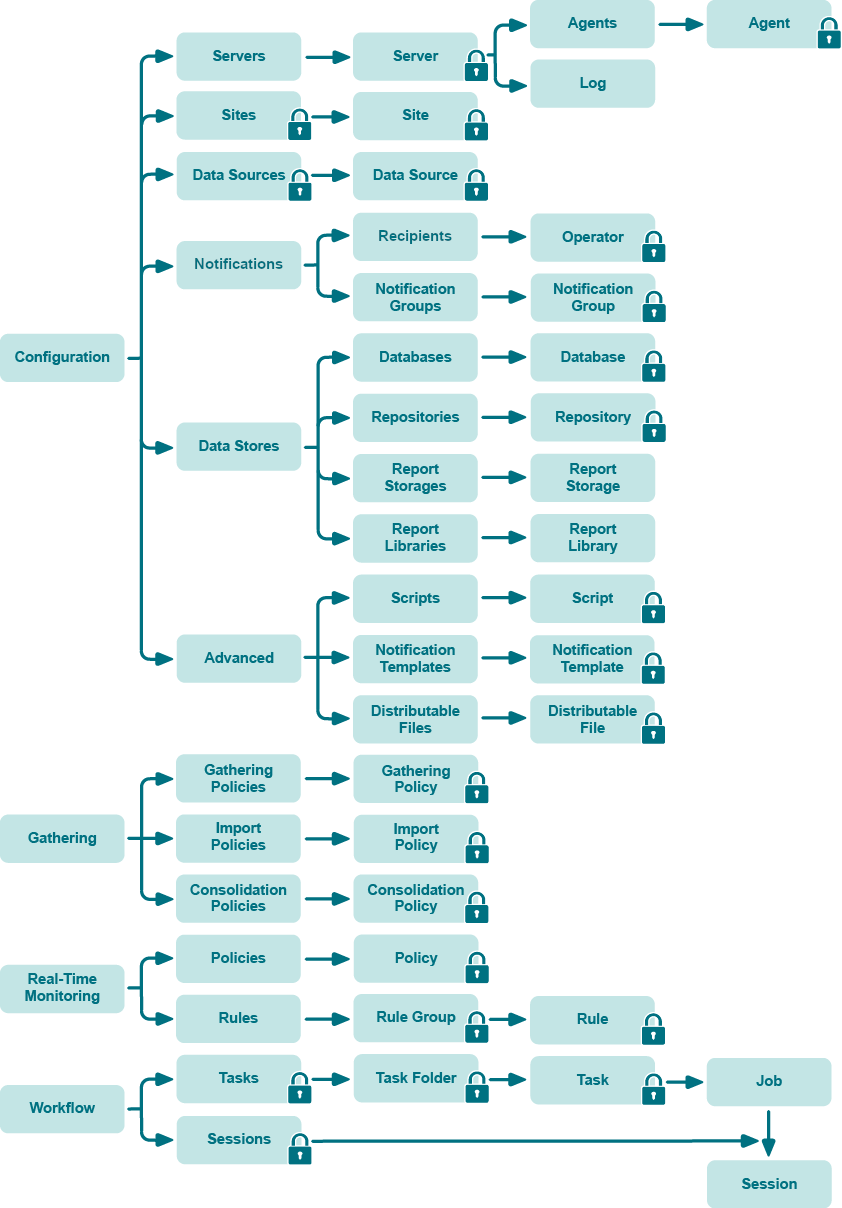
Consider the following examples:
To set object security
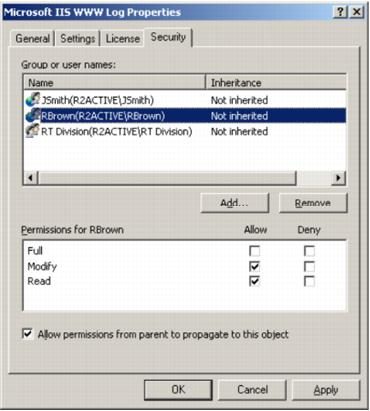
For convenience, InTrust offers a simplified security model with only three options: Full Control, Modify, and Read. The state of each of these options can be either Allow or Deny.
Internally, however, security is more granular and resembles the NTFS model. For example, extended privileges over InTrust objects are given to users who create those objects. This is analogous to users retaining the Creator Owner permission on an NTFS file or folder that they create—object creators can change their own permissions.
|
|
Note: Selecting the Allow permissions from parent to propagate to this object option means that object parent permissions will be inherited by the object. If you clear the option, the parent permissions will no longer be applied to this object. |
To enable or disable the InTrust role-based administration feature, use the adccfgsec.exe utility from the Resource Kit (located in the <InTrust_installation_folder>\Server\ADC\SupportTools folder on the InTrust Server computer). You can run this command-line utility with the following parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Use this parameter if you need to find out whether the role-based administration feature is currently enabled. One of the following values is returned:
| |
| Use this parameter to switch role-based administration on or off. | |
| Activates role-based administration. | |
| Deactivates role-based administration. |
|
|
IMPORTANT: After you have enabled or disabled role-based administration using adccfgsec.exe, you need to restart the following services on all InTrust servers in the organization:
This will make sure your configuration changes are fully applied. |
If you need to enable a group of users to use several configuration objects in their InTrust workflow, consider the following:
An administrator who creates an InTrust configuration object automatically gets the Full Control permission on that object. In addition, unrestricted access to the object is given to the accounts in the list of InTrust organization administrators. If you want another group of users to be able to manage an object, delete it, or associate it with other InTrust objects, you must grant them the desired permissions explicitly. Specifically, consider the following:
To authorize a group of users to read alerts from a certain InTrust site and a certain rule group, keep in mind the following:
You may want to enable a group of users to view and modify alert records generated by rules in a specific rule group in a specific InTrust site. Alert records are available to users only if their accounts have sufficient permissions. To do this, consider the following:
Suppose that Acme Corporation has its headquarters in London and branch offices in Mexico and Tokyo. The desired configuration is as follows:
To implement this scenario, consider the following: