Hyper-V server and virtual machine administration
A Hyper-V® environment typically includes a collection of clusters, server, and virtual machines. A cluster can have one or more servers associated with it, one or more virtual machines can run on each server. Each virtual machine is allocated a portion of the server’s resources, including disk, CPU, memory, and network resources. A virtual machine has its own machine name and IP address, and it runs a guest OS (for example, Microsoft® Windows® XP), along with other applications.
Additionally, Hyper-V implements the concepts of virtual machine snapshots and server workflows. A virtual machine snapshot is a virtual machine image that you can return to at any point in time. A workflow, on another hand, is a way to automate server tasks, and re-run them using a different set of parameters. For example, you can use an existing virtual machine creation task, change some of its resource allocation parameters, and run it again.
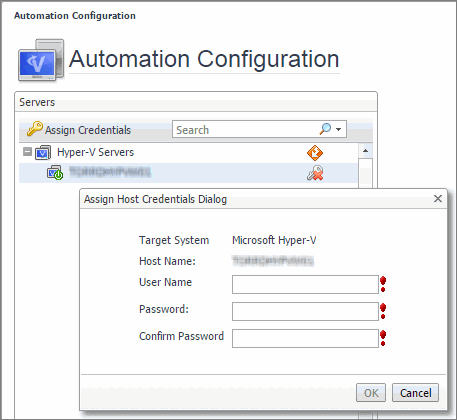
These actions require that you set up credentials for the virtual center on the Automation Configuration dashboard. To do that, on the navigation panel, under Dashboards, choose Hyper-V > Automation Configuration. On the Automation Configuration dashboard that appears, in the Servers view, select a Hyper-V server, click Assign Credentials, and provide host credentials in the Assign Host Credentials Dialog box. Failing to configure host credentials results prevents the automated tasks from being executed.
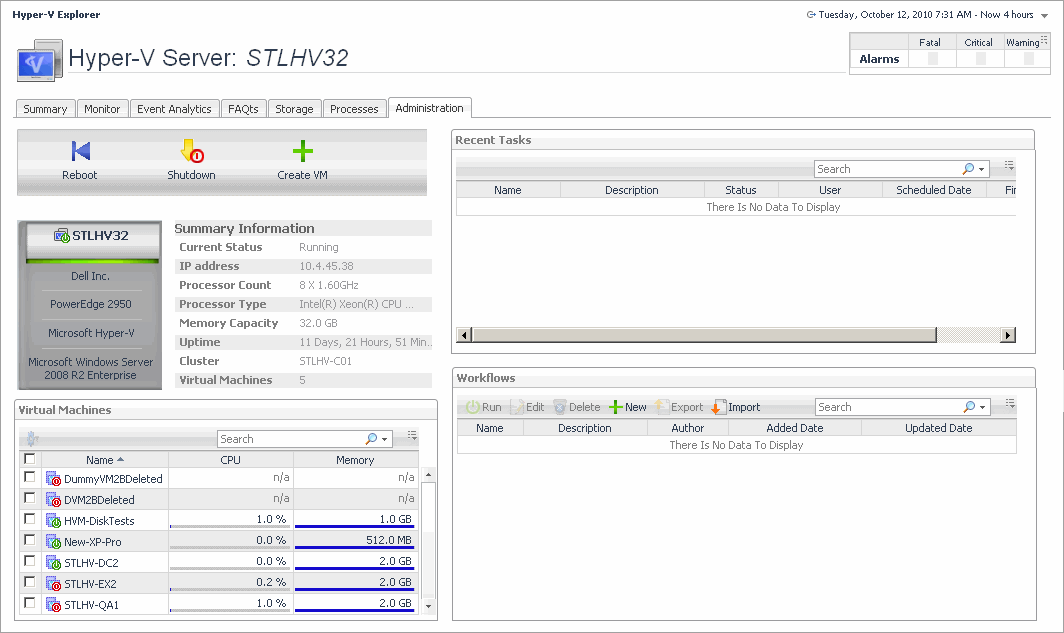
The Hyper-V Explorer’s Administration tab provides access to most of these administration tasks. Use it to shut down or reboot physical servers and virtual machines or create virtual machines and edit their resource allocation. This tab also provides quick access to creating and editing virtual machine snapshots and server workflows.
|
|
NOTE: The Hyper-V Explorer Administration tab is only available when the Virtual-HyperV-Admin-<version>.car and Virtual-HyperV-<version>.car are installed. This tab is accessible if your Foglight user account includes the Hyper-V Automation User role, when you are exploring individual servers and virtual machines. |
Accessing the Hyper-V Explorer Administration tab
The Hyper-V Explorer Administration tab provides quick access to common administrative tasks that include server shutdown, virtual machine creation, resource allocation, and others. The range of available tasks depends on whether you are exploring server or virtual machine objects. For example, when exploring server details, use this tab to access server-related workflows, such as rebooting or shutting down servers, or adding virtual machines. Similarly, when you select a virtual machine in the Hyper-V Explorer, use this tab to power off, shut down, save, pause, delete, clone, move, or edit resource allocation for the selected virtual machine. For more information about the administrative tasks, see Hyper-V server and virtual machine administration .
This tab also lists the related workflows and snapshots updated in real time, and allows you to edit and re-run them to simplify your daily administration load quickly and easily.
|
|
NOTE: The Hyper-V Explorer Administration tab is only available when the Virtual-HyperV-Admin-<version>.car and Virtual-HyperV-<version>.car are installed. This tab is accessible if your Foglight user account includes the Hyper-V Automation User role, when you are exploring individual servers and virtual machines. |
Hyper-V Explorer Administration tab
The Hyper-V Explorer Administration tab provides access to common administrative tasks. It also shows configuration details for a server or a virtual machine (depending on the selected object type), and some high-level information about the object’s resource consumption.
|
|
NOTE: The Hyper-V Explorer Administration tab is only available when the Virtual-HyperV-Admin and Virtual-HyperV cartridges are installed. It is accessible if your Foglight™ user account includes the Hyper-V Automation User role, while exploring individual servers and virtual machines. |
This tab appears in the Hyper-V Explorer when you select a Hyper-V server or a virtual machine on the Hyper-V Explorer Topology tab.

This tab is made up of the following embedded views:
Shutting down and rebooting Hyper-V servers
Use the Reboot and Shutdown buttons on the Hyper-V Administration tab to reboot and shut down servers, as required.

The Reboot Hyper-V Server dialog box appears.
|
3 |
In the Reboot Hyper-V Server dialog box, in the Reason box, type the reason for rebooting the server. |
|
5 |
In the Reboot Hyper-V Server dialog box, click OK. |
The Shutdown Hyper-V Server dialog box appears.
|
3 |
In the Shutdown Hyper-V Server dialog box, in the Reason box, type the reason for shutting down the server. |