The most common scenario for the use of EPW is during Active Directory migration from one domain to another within the same forest. User accounts are migrated with their Exchange-related properties intact.
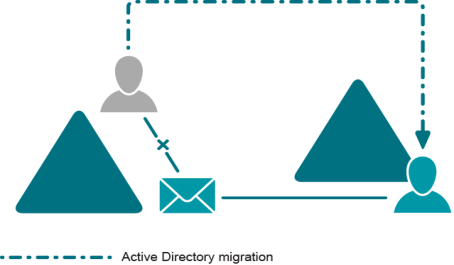
After the migration of user accounts is complete, the users in the target domain can still log in to their mailboxes, provided that the Reconnect Exchange mailbox option was used in the migration session. However, these users do not have any of the permissions that the source user accounts had (because the target users have different SIDs). In public folders, the permissions are also based on the old domain configuration.
Run EPW against the Exchange server after the migration to make sure that:
|
|
NOTE: You may need to use Active Directory Processing Wizard in the source domain after these steps. |
A popular scenario involving EPW is creation of an Exchange resource forest (ERF) topology instead of a single forest. In this variation of the scenario, user accounts move to another newly-created or existing Active Directory forest, and the target users are supposed to become the new owners of the mailboxes. The source forest remains as an ERF, and the source users are disabled.
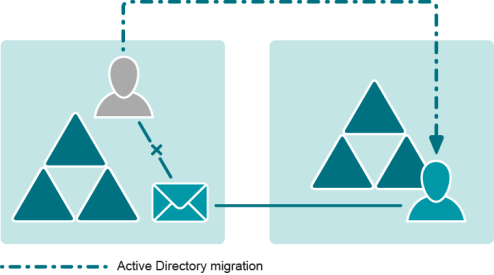
After the migration of user accounts is complete, the users in the target forest have no access to the mailboxes in the ERF. Run EPW against the Exchange server after the migration to make sure that:
|
|
NOTE:
|
A possible scenario is when users from one forest have mailboxes in another (ERF) forest and are moved to a third forest. The target users are supposed to become the new owners of the mailboxes in the ERF, and the old forest is supposed to be decommissioned.
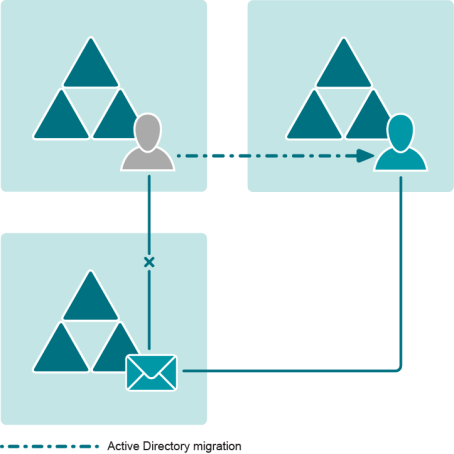
After the migration of user accounts is complete, the users in the target forest have no access to the mailboxes in the ERF. Run EPW against the Exchange server after the migration to make sure that:
|
|
NOTE: You may need to use Active Directory Processing Wizard in the Exchange resource forest after these steps. |