Mirroring Table
The Mirroring table displays the columns listed below.
The table below provides data about the columns that appear by default in the table. For a list of additional metrics, which are hidden by default, see Additional metrics in the Mirroring table .
The metrics listed below, which are also part of the Database Mirroring collection, do not appear by default in the Mirroring table. For details on these metrics, see the Database Mirroring Collection section in Foglight for SQL Server Reference Guide.
|
1 |
|
• |
Viewing the Role and Data Flow of the Selected Database
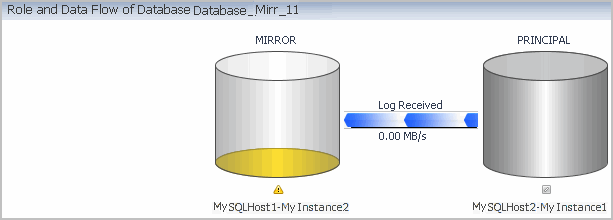
The Role and Data Flow of Database section displays the mirroring operation of the database selected in the Mirroring table and its mirroring partner. The monitored instance is always displayed on the left, and the data is shown as flowing in this instance’s direction, that is: Log Received if the database is Mirror, and Log Sent if the database is Principal.
|
• |
Click the link Investigate using the Partner’s Mirroring Page on the upper right side of the panel, above the table. |
If the partner is currently monitored, its mirroring page will now be displayed. For details, see Viewing the Partner’s Mirroring Page . Otherwise, an error message is displayed, notifying that the partner server is currently not monitored.
Viewing the Selected Database's Mirroring Performance History
The middle section of the Mirroring Performance History page includes the following panes:
|
• |
Principal Counters — this pane displays a chart of the following values, which can be selected from the list on the upper left: |
|
• |
|
• |
Mirror Counters — this pane displays a chart of the following values, which can be selected from the list on the upper left: |
Viewing the Partner's Mirroring Page
|
• |
Clicking the link Investigate using the Partner’s Mirroring Page on the upper right side of the table. |