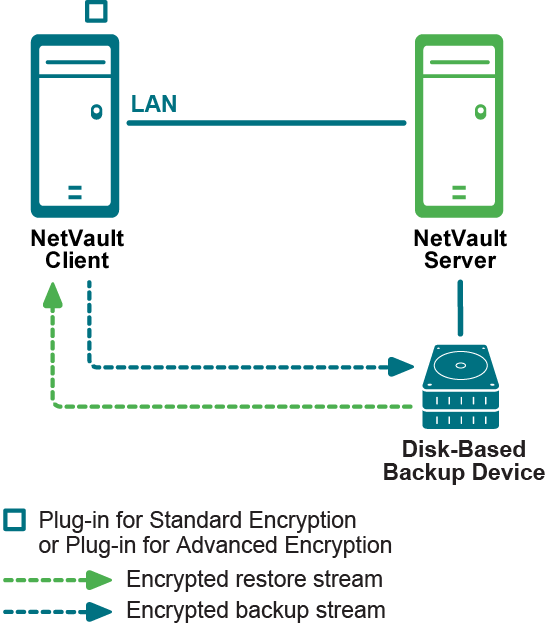
Using Plug-in for Encryption
About Plug-in for Encryption
NetVault offers four encryption options:
|
• |
CAST128: CAST-128 is a 12- or 16-round Feistel network with a 64-bit block size and a key size of between 40 to 128 bits, but only in 8-bit increments. |
|
• |
CAST256: CAST-256 uses the same elements as CAST-128, but it is adapted for a block size of 128 bits — twice the size of its 64-bit predecessor. Acceptable key sizes are 128, 160, 192, 224 and 256 bits. CAST-256 is composed of 48 rounds, sometimes described as 12 “quad-rounds”, arranged in a generalized Feistel network. |
|
• |
AES256: Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is an encryption standard adopted by the U.S. government. The standard consists of three block ciphers, AES-128, AES-192, and AES-256. Each AES cipher has a 128-bit block size, with key sizes of 128, 192 and 256 bits, respectively. When you select the AES256 option, the plug-in uses a FIPS compliant AES-256 encryption algorithm to encrypt backups. |
|
• |
AES256_OLD: Select this option for the plug-in to use the non FIPS compliant AES-256 encryption algorithm to encrypt backups, specifically when FIPS compliance is not a requirements for your backups and you prefer using the non FIPS compliant AES-256 algorithm to benefit backup speeds. |
|
NOTE: The CAST-128 and CAST-256 encryption algorithms do not comply with the requirements of the United States Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS). These algorithms are provided for the restoration of legacy data. The option AES256_OLD provides an AES-256 encryption algorithm that is non FIPS compliant. To instruct NetVault Plug-in for Encryption to use the FIPS compliant AES-256 algorithm, use the AES256 option. |
For a list of NetVault Plug-ins that are incompatible with the Plug‑in for Encryption, see the respective release notes.
Encryption strategy overview
When defining an encryption strategy, you must determine the following: