This article will provide an overview of automating the comparison and synchronization the data between a SQL script folder and a live SQL Server database
In the article on how to automatically compare and synchronize SQL Server database objects with a shared script folder, a “poor man’s source control repository” was explained. It was shown how to set up a SQL script folder on a shared network location, in order to “mimic” the work on a SQL source control repository, where all developers will commit their changes, without any cost concerns.
As for SQL Server database objects changes, the same goes for data changes as well. After setting up the shared SQL script folder that contains the complete database schema, e.g. all objects from a database, the next thing is to fill it out with data.
When any new data changes are made by a developer, a tool will be needed that could compare developer’s database vs. shared SQL script folder, and push those changes to a shared SQL script folder.
Also, the tool should be capable to filter data before and after the comparison process, to limit what will be compared and synchronized, and to review the differences upon comparison, in order to create comprehensive reports and output files with needed information about the process and changes. Furthermore, developers should be able to run the complete process unattended, by automating it, scheduling and run it on a click.
A third-party tool – ApexSQL Data Diff, will be presented in this article as a tool that can handle database data comparison and synchronization between a database and a SQL script folder. It can also compare and synchronize data between backups and source control projects. Also, the complete process can be automated via the CLI, along with creating reports and being scheduled to run at desired time unattended.
As explained in article for ApexSQL Diff on how to automatically compare and synchronize SQL Server database objects with a shared script folder, the installation topography is basically the same:
Before even working with data comparison and synchronization, database schema should be exported, in order to have the same database schema in a database and SQL script folder. Check out the article on exporting SQL data sources and how to set up the initial SQL script folder.
In order to setup the process, check out the following steps:
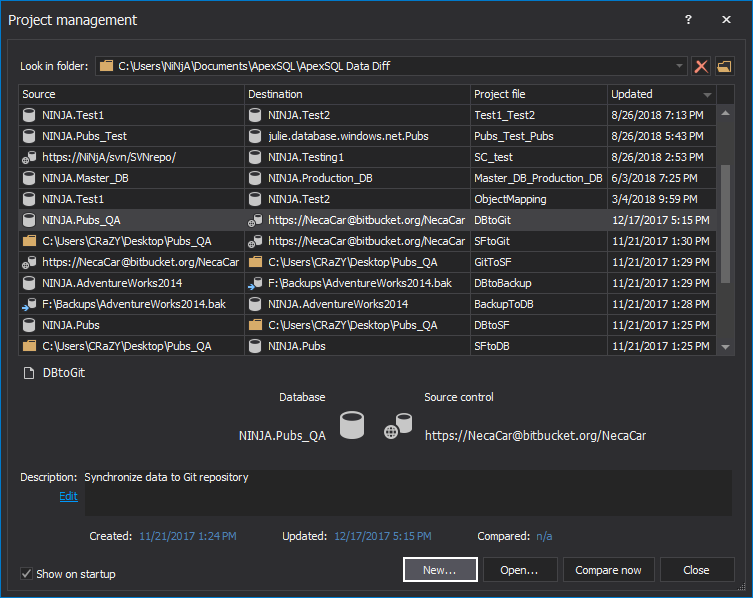
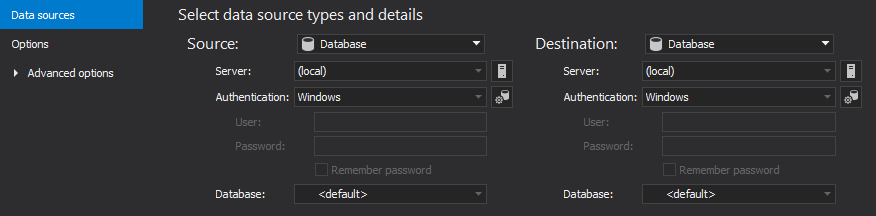
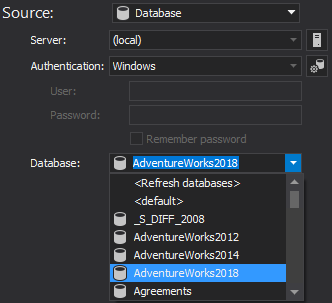
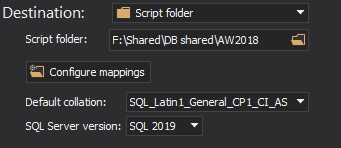
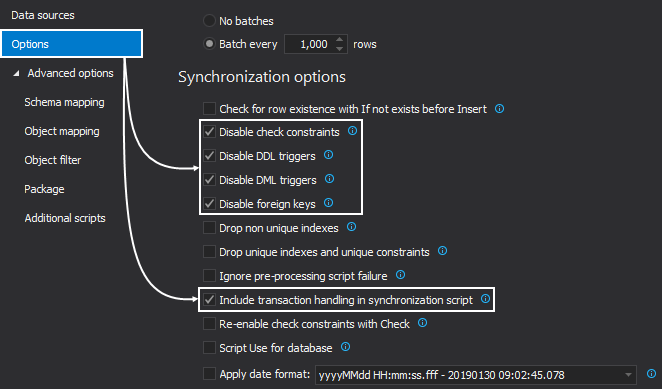
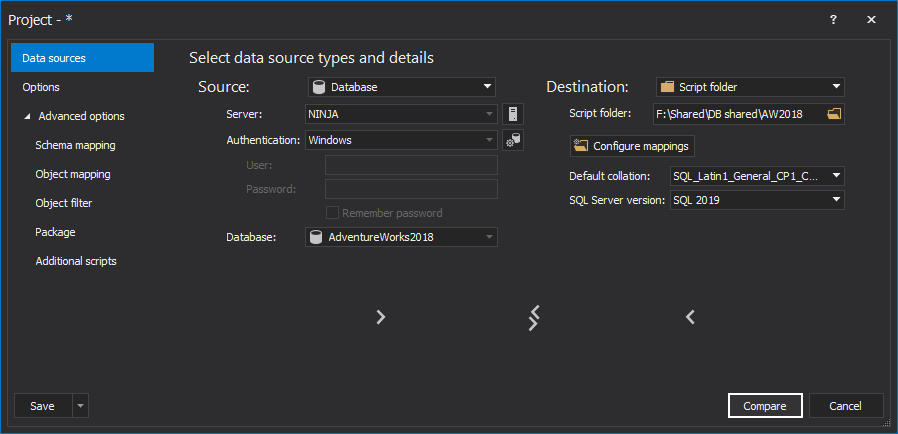
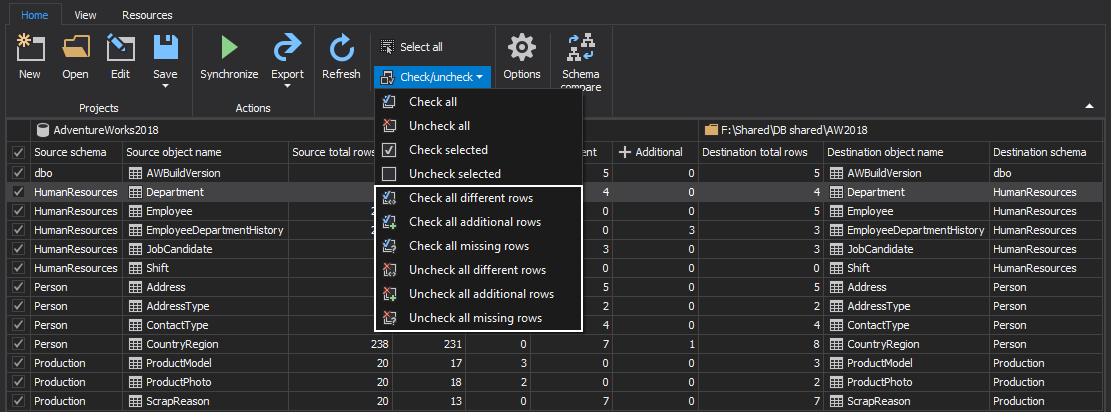
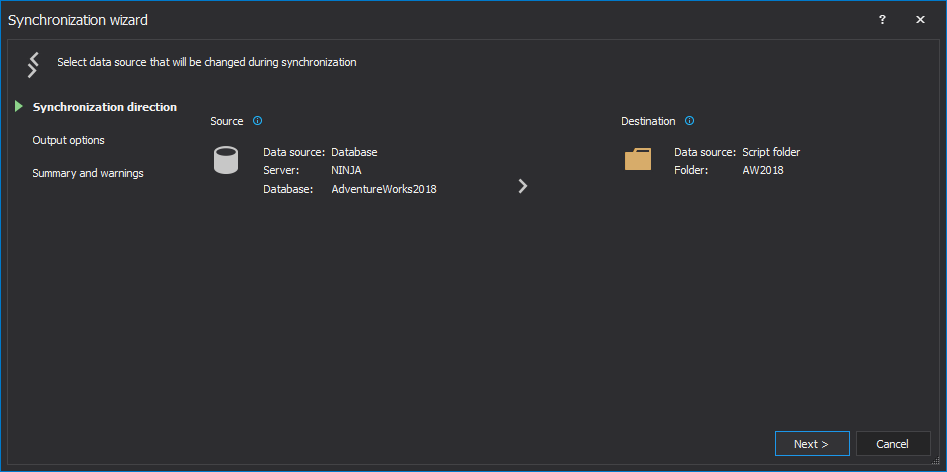
The saved project file can be used in the automation script for all developer databases, as the previously saved file with a list of all servers/databases will be used to override the source data source (developer database) from the saved project file.

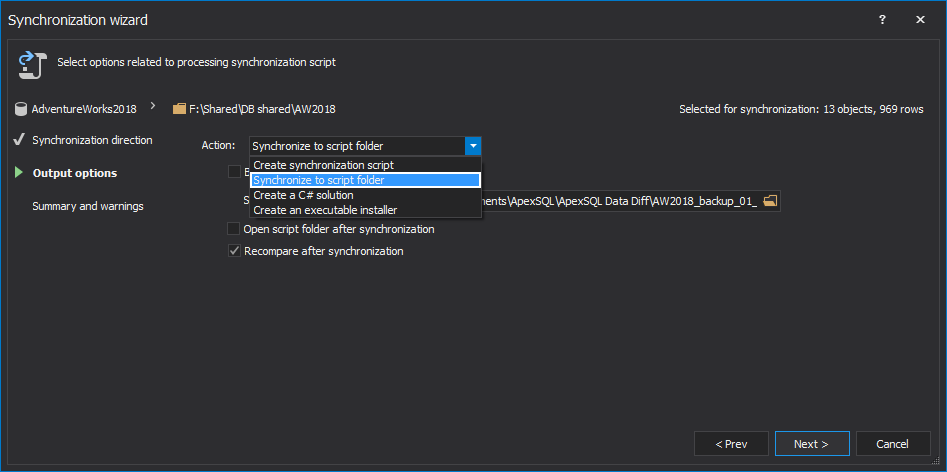
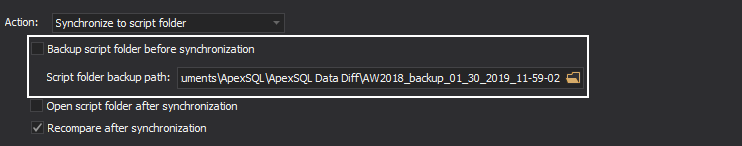
Also, it can be set to backup the SQL script folder (create a copy of it) before synchronization:
Let’s work on automating the complete process, as a shared SQL script folder is ready and there is a created project file with all project settings. Now, we can work on creating a PowerShell script that will iterate thru the saved file with developers’ servers/databases, create date/time stamped reports and outputs, and synchronize any detected data changes to a shared SQL script folder.
As mentioned in the beginning, Windows authentication will be used as the authentication type, however if SQL Server authentication is chosen, login password will be encrypted and saved to previously created project file.
Next, only the most important parts and the ones that can be edited, will be shown and explained. The complete PowerShell script can be downloaded from the link below and used for desired setup. Additionally, setting up the root folder, automatic folder creating, output storing and location setup, are explained in the Appendix A.
First, define ApexSQL Data Diff’s and servers/databases file locations:
#ApexSQL Data Diff and servers/databases file locations $dataDiffLocation = "ApexSQLDataDiff" $serverDatabasesLocation = "servers-databases.txt"
Next, let’s define date/time stamped variable, ApexSQL Data Diff’s execution parameters, and variable for return code:
#date/time stamp variable, ApexSQL Data Diff's parameters, and return code
variable: $dateTimeStamp = (Get-Date -Format "MMddyyyy_HHMMss") $dataDiffParams = "/s1:""$server"" /d1:""$database""
/pr:""ScriptFolderSync.axdd"" /rts:m d /ot:html /dhtmo:d co ro dr /on:
""$dataRepLocation\DataReport_$dateTimeStamp.html"" /out:""
$dataOutLocation\DataOutput_$dateTimeStamp.txt"" /sync /v /f" $returnCode = $LastExitCode
After setting up these, let’s define the function which will use the servers/databases file to go through it and to execute ApexSQL Data Diff’s parameters for each line in the file:
#function to go through each server/database and execute ApexSQL Data Diff's
parameters foreach($line in [System.IO.File]::ReadAllLines($serverDatabasesLocation)) { $server = ($line -split ",")[0] $database = ($line -split ",")[1] #call ApexSQL Data Diff to run the data comparison and synchronization
process (Invoke-Expression ("& `"" + $dataDiffLocation +"`" " +$dataDiffParams)) }
Furthermore, any possible outcome can be handled in different way. To learn more about handling different outcomes, check out the article on utilizing the “no differences detected” return code.
Additional improvement for this process would be to get e-mail notifications when a change is detected (one of developers performed successful synchronization) or when error occurs. In this way, each developer will get e-mail on detected change or error with corresponding report and output files, which can be further reviewed. To learn how to set it up, check out the article on how to setup an e-mail alert system for ApexSQL tools.
With e-mail system set, developers can get two potential e-mails with the following subjects:
Let’s see one of the potential error examples, if the second e-mail is received with an error. In this example, two same switches are added /ot:sql and /ot:html and the following is shown:
An error occurred during the application execution at: 01302019_122541. Return error code: 3 Error description: Switches /ot, /output_type cannot be used more than once
All return codes can be reviewed within the CLI help, or check out the article about General usage and the common Command Line Interface (CLI) switches for ApexSQL tools, where the complete list of return codes is explained.
In this particular example, when there is a need to have two types of outputs (SQL script and HTML report), the ApexSQL Diff Command Line Interface (CLI) switches article can be consulted, where it can be found that for the second output type number 2 should be added into the switch name, to look like this /ot2:html and in this way the error will be resolved.
After creating the complete PowerShell script with desired options, the process can be run unattended by setting up the schedule process. Learn more about scheduling from the article about ways of scheduling ApexSQL tools.
Since the whole system was set and there were some changes done by developers, created outputs can be reviewed on defined locations (check out Appendix A).
When needed, a developer can review changes that are done at specific time, since all HTML reports are date/time stamped, it can be easily found and opened for a review from the DataReports folder:
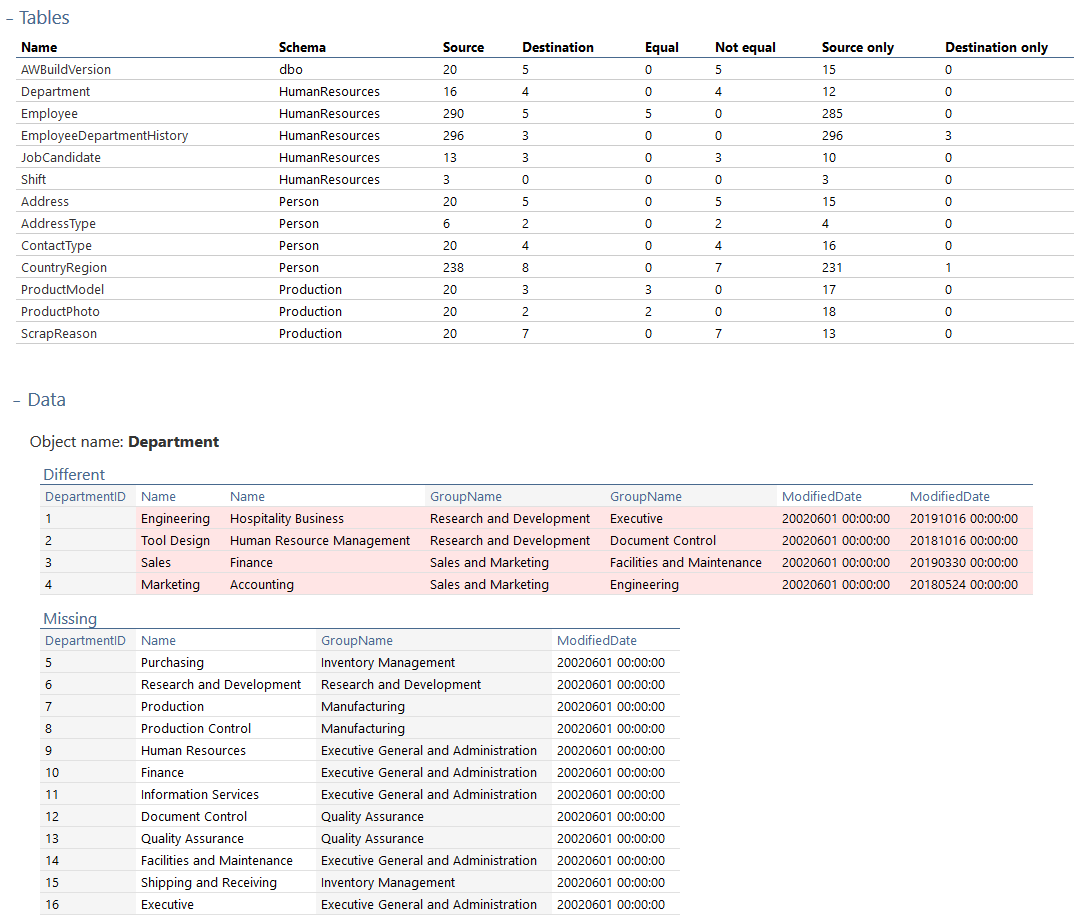
Once opened, comparison results can be reviewed and with a click on an object name and expanding the Data section, so that exact data difference can be reviewed for compared object and in that way, developer can see what exact data change was done for that particular object:
Also, if there is a need to review the complete execution output with all information about comparison and execution, go to the DataOutputs folder and locate a desired output file:
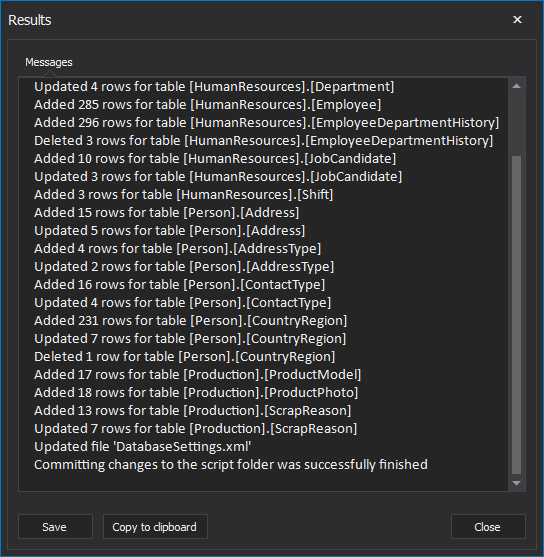
Once opened, it will show the complete process from start to the end, along with the final summary or error message:
Please download the script(s) associated with this article on our GitHub repository.
Please contact us for any problems or questions with the scripts.
A mentioned above, to automate this process further, let’s define a function that will check for folder existence and create necessary folders for reports and outputs:
#check existence and create DataReports and DataOutputs folders function CheckAndCreateFolder { param ( [string] $folderRoot, [switch] $dataReports, [switch] $dataOutputs ) $location = $folderRoot #set the location based on the used switch if ($dataReports -eq $true) { $location += "\DataReports" } if ($dataOutputs -eq $true) { $location += "\DataOutputs" } #create the folder if it doesn't exist and return its path if (-not (Test-Path $location)) { mkdir $location -Force:$true -Confirm:$false | Out-Null } return $location
Next, let’s define variable for the root folder location, along with HTML reports and output summaries locations:
#root folder $folderRoot = "\\host1\Shared SF\AutoSF"
| Quick tip: In this example, a shared network location of the root folder should be used, in order to allow all developers to review reports and outputs when needed |
#HTML reports location $dataRepLocation = CheckAndCreateFolder $rootFolder -DataReports #data output summaries location $dataOutLocation = CheckAndCreateFolder $rootFolder -DataOutputs