purge config
Use the purge config command to remove the data from all queues associated with a configuration without removing the queues themselves or deactivating the configuration. Avoiding a deactivation avoids the need for SharePlex to recalculate the configuration data. This saves time when the tables are large and numerous, enabling replication can start sooner.
Issue the purge config command on the source system to affect the source system and all target systems in the configured routes. Should any SharePlex process stop prior to or during the purge config activity, the command also stops working. When the process starts again, the command resumes working. Thus, purge config works even when the network is temporarily unavailable — the command remains in the queues until the connection is restored.
Cautions for using the purge config command
- Do not activate a configuration and then follow the activate config command with a purge config command. You might be purging more than just queued data, including the configuration information that controls replication, thus rendering the activation invalid.
- When there are multiple active configurations on the same source system, use the purge config command only if there are named export queues that separate the replication streams for each one. Without named export queues, SharePlex funnels all replicated data through one export queue, and a purge config command for one configuration deletes the data for all of them. To create named queues, see Chapter 5 of the SharePlex Administrator’s Guide.
Usage
| Supported sources: |
Oracle |
| Supported targets: |
All |
| Authorization level: |
Administrator (1) |
| Issued for: |
source system |
| Related commands: |
abort config, deactivate config |
Syntax
| purge config filename |
[ on host |
on host:portnumber |
on login/password@host |
on login/password@host:portnumber ] |
Syntax description
| filename |
The name of the configuration that you want to purge. Configuration names are case-sensitive.
Example:
sp_ctrl(sysA)> purge config sales |
Remote options
These options enable you to issue the command on a remote machine and to script commands that include a login name, password, port number, or combination of those items.
| on host |
Execute the command on a remote system (one other than the one where the current sp_ctrl session is running). You are prompted for login credentials for the remote system. If used, must be the last component of the command syntax.
Example: sp_ctrl(sysB)>status on SysA |
| on host:portnumber |
Execute the command on a remote system when a remote login and port number must be provided. If used, must be the last component of the command syntax.
Example: sp_ctrl(sysB)>status on SysA:8304 |
| on login/password@host |
Execute the command on a remote system when a remote login, password, and host name must be provided. If used, must be the last component of the command syntax.
Example: sp_ctrl(sysB)>status on john/spot5489@SysA |
| on login/password@host:portnumber |
Execute the command on a remote system when a remote login, password, host name, and port number must be provided. If used, must be the last component of the command syntax.
Example: sp_ctrl(sysB)>status on john/spot5489@SysA:8304 |
qstatus
Use the qstatus command to view statistics for the capture, post, and export queues on any system. It displays the number of messages in each queue, their age, and the current size of the queue. Typically, a message approximately corresponds to a SQL operation, but there can be multiple messages for one operation on a LONG or LOB column, and there could be just one record for numerous operations of an array insert. A message also can be an internal SharePlex operation.
When to use the qstatus command
Use the qstatus command to:
- Determine if there is data still waiting to be read by a replication process or posted to the target database.
- Estimate the speed at which SharePlex is processing by analyzing the rate at which messages accumulate.
- View the size of the queues to ensure that they do not exceed available disk space.
- Verify that all of the queues are empty when that is required for certain operational procedures or when you need to shut down replication for system maintenance, upgrades, and other administrative tasks.
- Determine if there is user activity on a target system that can cause data to go out of synchronization.
About the output
- The number of messages in a queue reflects the messages that have been read by the next SharePlex process, as well as those that have not been read. As part of its checkpoint recovery system SharePlex retains copies of messages that were sent to the next process. These messages are deleted when receipt by that process is acknowledged.
- The Backlog field indicates the number of messages yet to be read by the next SharePlex process.
- The Age field is the difference in time between when the oldest and newest messages in the queue were written to the queue.
- The presence of a Post queue on a system that also has capture and export queues indicates that this system is used both as a source system and as a target system.
- The Size field indicates the true size of a queue.
Usage
| Supported sources: |
Oracle |
| Supported targets: |
All |
| Authorization level: |
Viewer (3) |
| Issued for: |
source or target system |
| Related commands: |
lstatus, show |
Syntax
| qstatus |
[ on host |
on host:portnumber |
on login/password@host |
on login/password@host:portnumber ] |
Remote options
These options enable you to issue the command on a remote machine and to script commands that include a login name, password, port number, or combination of those items.
| on host |
Execute the command on a remote system (one other than the one where the current sp_ctrl session is running). You are prompted for login credentials for the remote system. If used, must be the last component of the command syntax.
Example: sp_ctrl(sysB)>status on SysA |
| on host:portnumber |
Execute the command on a remote system when a remote login and port number must be provided. If used, must be the last component of the command syntax.
Example: sp_ctrl(sysB)>status on SysA:8304 |
| on login/password@host |
Execute the command on a remote system when a remote login, password, and host name must be provided. If used, must be the last component of the command syntax.
Example: sp_ctrl(sysB)>status on john/spot5489@SysA |
| on login/password@host:portnumber |
Execute the command on a remote system when a remote login, password, host name, and port number must be provided. If used, must be the last component of the command syntax.
Example: sp_ctrl(sysB)>status on john/spot5489@SysA:8304 |
quit
Use the quit command to close the current session of sp_ctrl. Closing sp_ctrl does not shut down replication; all replication processes continue without interruption unless they have been stopped by a user. This command merely discontinues your session with sp_ctrl on that system. To run sp_ctrl again, change to the directory containing the SharePlex binaries and enter double-click the sp_ctrl shortcut.
There are no [on host] options for the quit command. It must be issued on the system where you want to stop running sp_ctrl. This command is the same as the exit command.
Usage
| Supported sources: |
Oracle |
| Supported targets: |
All |
| Authorization level: |
Viewer (3) |
| Issued for: |
source or target system |
| Related commands: |
exit |
Syntax
reconcile
Use the reconcile command as part of a procedure to synchronize (instantiate) source and target data with minimal interruption to the database users. The reconcile command coordinates the results of ongoing replication with a copy of the source data that is applied to the target system, such as that applied by a hot-backup or a native copy utility. The reconcile function compares the replicated changes in the post queue with the state of the target database after the recovery process. It differentiates between the transactions that were applied during recovery from those that have not yet been applied (still waiting in the post queue), and it only posts the non-duplicated changes so that both systems are synchronized.
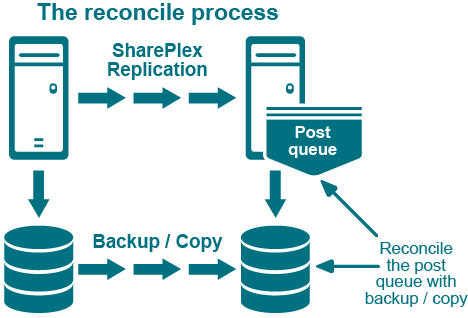
Although the reconcile command is designed for use in high-volume environments, it can be used in low-volume environments with an understanding that the reconcile process can, in some circumstances, seem to stall. This happens because the reconcile command depends on data continuing to arrive from the source system. If there is no replication activity on the source system after the hot backup or copy, the reconcile process waits until source activity resumes.
Considerations when using the reconcile command
The reconcile command should be used when following specific procedures for the initial synchronization of source and target data. It is not meant to be a standalone command. For initial synchronization procedures, see the SharePlex Administration Guide.
Usage
| Supported sources: |
Oracle |
| Supported targets: |
All |
| Authorization level: |
Administrator (1) |
| Issued for: |
target system |
| Related commands: |
flush |
Syntax
| reconcile queue queuename for datasource-datadest |
[seq sequence_number]
[scn scn_number]
[to flush] |
[ on host |
on host:portnumber |
on login/password@host |
on login/password@host:portnumber ] |
Syntax description
| queue |
queue is a required part of the command. |
| queuename |
The post queue on the target system that you want to reconcile. Valid values are:
- The name of the source system if using default queues
- The name of the queue if using named queues
When using named post queues, issue the reconcile command for each one. To determine the queue name, issue the qstatus command in sp_ctrl. Queue names are case-sensitive on all platforms. |
| for datasource-datadest |
- datasource is expressed as o.SID, where SID is the ORACLE_SID of the source instance.
- datadest is expressed as o.SID, where SID is the ORACLE_SID of the target instance.
Example:
sp_ctrl (sysB)> reconcile queue SysA for o.oraA-o.oraB |
| seq sequence_number |
(Oracle) Use this option when an Oracle hot backup is used to establish Oracle target data in the synchronization procedure. It directs SharePlex to reconcile to the end of the same log that Oracle uses for its recovery.
sequence_number is the sequence number of the log to which Oracle recovers.
The syntax must appear after the syntax for the basic command. Do not use this option with the to flush option.
Example:
sp_ctrl (sysB)> reconcile queue SysA for o.oraA-o.oraB seq 1234 |
| scn scn_number |
(Oracle) Use this option when an Oracle hot backup is used to establish Oracle target data in the synchronization procedure. It directs SharePlex to reconcile to a specific Oracle System Change Number (SCN).
scn_number is the SCN to which Oracle recovers.
The syntax must appear after the syntax for the basic command. Do not use this option with the to flush option.
Example:
sp_ctrl (sysB)> reconcile queue SysA for o.oraA-o.oraB scn 0123456789 |
| to flush |
Use this option to reconcile to a flush marker that is established with the flush command. Use it for synchronizing multiple Oracle databases in a peer-to-peer replication environment.
The syntax must appear after the syntax for the basic command. Do not use this option with the seq sequence_number option.
Example:
sp_ctrl (sysA)> reconcile queue SysA for o.oraA-o.oraB to flush |
Remote options
These options enable you to issue the command on a remote machine and to script commands that include a login name, password, port number, or combination of those items.
| on host |
Execute the command on a remote system (one other than the one where the current sp_ctrl session is running). You are prompted for login credentials for the remote system. If used, must be the last component of the command syntax.
Example: sp_ctrl(sysB)>status on SysA |
| on host:portnumber |
Execute the command on a remote system when a remote login and port number must be provided. If used, must be the last component of the command syntax.
Example: sp_ctrl(sysB)>status on SysA:8304 |
| on login/password@host |
Execute the command on a remote system when a remote login, password, and host name must be provided. If used, must be the last component of the command syntax.
Example: sp_ctrl(sysB)>status on john/spot5489@SysA |
| on login/password@host:portnumber |
Execute the command on a remote system when a remote login, password, host name, and port number must be provided. If used, must be the last component of the command syntax.
Example: sp_ctrl(sysB)>status on john/spot5489@SysA:8304 |


