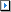
The Selected SQL/Index Set tab of the Batch Run Criteria window is used to select the SQL and index-set alternatives you want to execute. By default, all alternatives are initially selected.
Tip: To save all settings on the Batch Run Criteria dialog for subsequent batch runs, select Save setting for the next batch run.
To select or deselect an alternative
Double-click an SQL or index-set alternative.
To select or deselect all alternatives
Right-click and select Select All or Unselect All.
To select alternatives according to the cost values
Click SQL/Index Sets selection filter .
Review the DB2 LUW cost retrieved from the virtual plans.
Check the Exclude SQL/Index Set with DB2 LUW cost greater than checkbox and enter a DB2 LUW cost.
Note: The original SQL statement can be de-selected only if the Original SQL option is not selected in the SQL Termination tab of the Batch Run Criteria window and the Always run Original SQL first option is not selected.
The alternatives are ranked by DB2 LUW Cost by default, with the exception of the original SQL, which is placed at the top.
To change the execution order using the DB2 LUW cost
Click either the DB2 LUW or the SQL/Index Set column heading to reorder the alternatives for execution.
Note: High DB2 LUW Cost does not necessarily mean slower performance. If possible, it is recommended that all alternatives be tested.
To change the execution order for individual alternatives
Select the SQL or index-alternative; then click Move Up or Move Down
.
The original SQL statement can always be run first even if it does not have the lowest DB2 LUW cost.
To always run the original SQL statement first
Select the Always run Original SQL first checkbox.
This checkbox is disabled if Original SQL is selected as a termination criterion on the SQL Termination tab or the Batch Termination tab since the run time from the original SQL is going to be used to terminate the alternatives or to terminate the Batch Run itself. In this case, you must run the original SQL statement first to obtain the termination time.

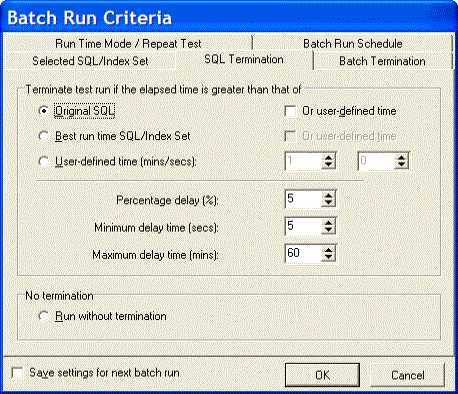
The SQL Termination tab of the Batch Run Criteria window is used to set the SQL termination criteria for each SQL and index-set alternative for which you are retrieving run times. If the current run time for a particular alternative exceeds the termination time, then the execution of the alternative terminates automatically. This will save time during testing.
Tip: To save all settings on the Batch Run Criteria dialog for subsequent batch runs, select Save setting for the next batch run.
The percentage-delay calculation adds additional time to the termination time. It is used to account for the time it takes an alternative to travel from the local computer to the database server over the network.
|
Option |
Description |
|
Percentage delay (%) |
The value entered into this box is used as a percentage to calculate the additional time that is added to the termination time. For example, if the termination time is 10 minutes and the percentage delay is 5%, then all alternatives executed are terminated if the run time exceeds 10.5 minutes. (10+ (10 * 5%)) |
|
Minimum delay time (secs) (Default = 5, Range 1 – 99) |
This is minimum number of seconds that is added to the termination time. It is necessary to factor into the overall termination time the time needed for the alternative be sent to the database server from the local computer before it starts to run. This number is only used if the percentage-delay calculation is lower than this value. |
|
Maximum delay time (mins) (Default = 60, Range 1 – 9999) |
This is the maximum number of minutes that can be added to the termination time. This number is only used if the percentage-delay calculation is higher than this value. |
|
Option |
Description |
|
Run without termination |
Executes all the alternatives until they are completed. |

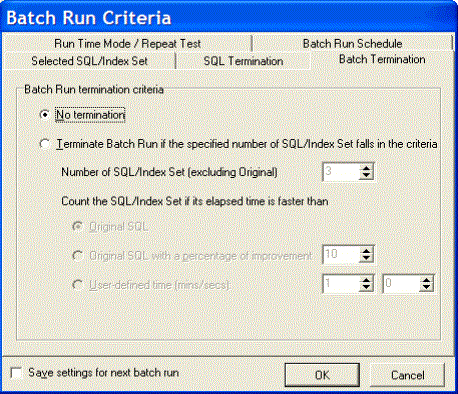
The Batch Termination page of the Batch Run Criteria window is used to determine if and when to terminate the Batch Run. It enables you to find SQL and index-set alternatives that give you performance improvement without having to execute every alternative.
Tip: To save all settings on the Batch Run Criteria dialog for subsequent batch runs, select Save setting for the next batch run.

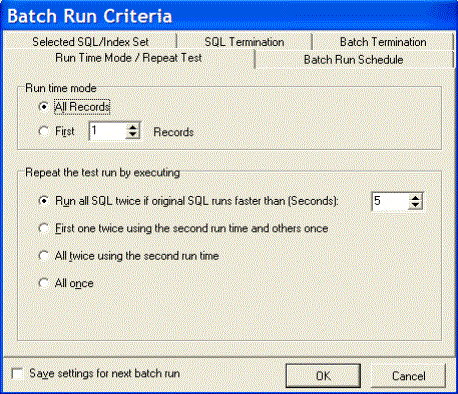
The Run Time Mode/Repeat Test tab of the Batch Run Criteria window is divided into two sections.
Tip: To save all settings on the Batch Run Criteria dialog for subsequent batch runs, select Save setting for the next batch run.
|
Run Time Mode |
Description |
|
All Records |
Specify to retrieve the run time for processing all records. |
|
First n Record(s) |
Specify to retrieve the run time for processing n records where you specify the number of records retrieved. |
|
Repeat the test run by executing |
Description |
| Run all SQL twice if original SQL runs faster than (Seconds) | This option executes the SQL and index-set alternatives twice if the run time for the original SQL is greater than the value you enter in the associated field. |
|
First one twice using the second run time and others once |
This option is suitable for SQL and index-set alternatives with normal run times. The first time you access data from table, the data is cached into memory. This process takes few moments. The next time you access that data, it is already in memory so the following alternatives will run faster. So to have a comparable test, the first SQL is run twice and the time from the second run is compared to the time from the other alternatives. |
|
All twice using the second run time |
This option is suitable for SQL and index-set alternatives that are often executed and have short running time. A significant portion of the running time of this kind of SQL is affected by the caching of index and the parsing time. To eliminate these factors, you can run all alternatives twice to use only the second run for a more comparable result. |
|
This option is suitable for long-running SQL and index-set alternatives, as it is unlikely that all the entire SQL statement is still kept in memory. There is no need to run any alternative twice since the caching of the table and the parsing time are not significant to the overall running time. |