SharePlex integrates with Oracle Clusterware cluster hardware and software to maintain the high availability of data capture and uninterrupted replication to your targets. If the node where SharePlex is running fails or must be taken out of the cluster for maintenance, SharePlex can be started on another server by the cluster software. SharePlex start and stop is controlled through the cluster.
These instructions assume that the cluster solution is already installed according to the cluster documentation, tested, and is functioning, and they are not a substitute for the documentation. Additional steps that are specific to your cluster installation may be required.
The following diagram shows SharePlex installed into an Oracle RAC cluster:
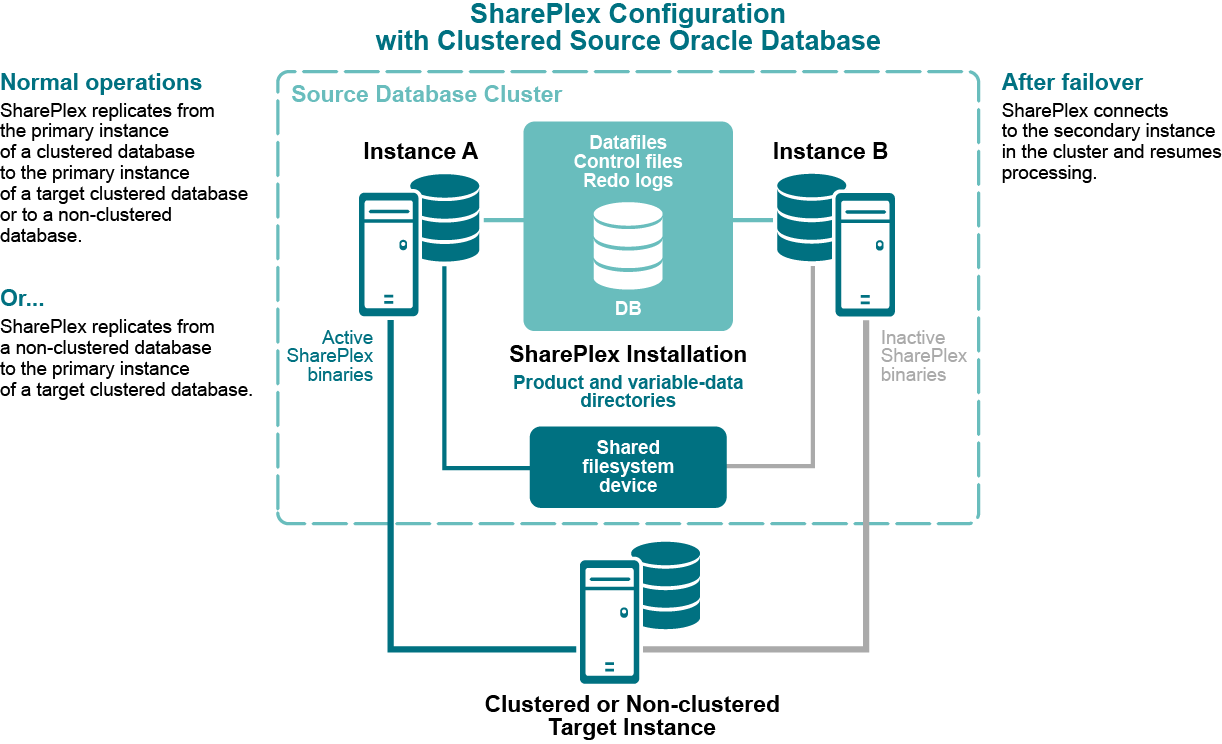
These instructions are for setting up SharePlex in an Oracle cluster.
Important! These instructions cover the parts of installing and setting up a cluster that pertain to the setup of SharePlex in the cluster. See the Oracle documentation for complete instructions for the platform that you are using.
Perform these steps on a source cluster and a target cluster, if applicable:
On one node of the cluster, create a static application Virtual IP (VIP) address for SharePlex. This VIP must point to the node where SharePlex will run and fail over to the secondary node if the primary node fails.
Notes:
Example: 123.456.0.78 splex |
Create a TNS alias for SharePlex to use to connect to the database on each node. Use the same alias on each node of a cluster. Set load balance to off and set failover to on. For example:
|
Node 1: ora_a_sp =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS_LIST =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = RAC1)(PORT = 1521))
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = RAC2)(PORT = 1521))
)
(LOAD_BALANCE = OFF)
(FAILOVER = ON)
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SERVER = DEDICATED)
(SERVICE_NAME = ora_a)
(INSTANCE_NAME = ora_a1)
)
) |
Node 2:
ora_a_sp =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS_LIST =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = RAC2)(PORT = 1521))
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = RAC1)(PORT = 1521))
)
(LOAD_BALANCE = OFF)
(FAILOVER = ON)
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SERVER = DEDICATED)
(SERVICE_NAME = ora_a)
(INSTANCE_NAME = ora_a2)
)
)
Note: A TNS alias establishes global connection information that supercedes local instance names and enables SharePlex to connect to the failover instance without requiring a configuration reactivation. SharePlex identifies the correct Oracle instance from the configuration file.
(UNIX and Linux only) Add the TNS alias to the oratab file on each node that SharePlex is expected to start on during a failover.
Example (all nodes):
ora_a:/u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0/dbhome_1:N ora_a_sp:/u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0/dbhome_1:N
If the Oracle instances in the cluster have different ORACLE_HOMEs, edit the oratab file on each node and on the DNS nameserver, if applicable, to use a symbolic link in place of the actual ORACLE_HOME path:
SID:/path_to_symbolic_link:N
In a cluster, SharePlex is installed on Unix and Linux.
To install on Unix and Linux:
On Linux and Unix, the best practice is to install both the SharePlex variable-data and product directories on a shared drive, rather than on each node. This configuration enables more efficient failover and faster upgrades of SharePlex.
If you do install these directories locally on both nodes of the cluster, do the following:
After you install SharePlex, run the Database Setup utility. The following applies in a cluster:
If you are using shared drive for variable data directory, license key added for primary node will be applicable for all other secondary nodes. If you are using local variable data directory, license need to be installed on the secondary nodes as well using the splex_add_key utility.
Perform these steps on a source cluster and on a target cluster, if applicable.
Set the SharePlex environment to point to the VIP alias and SharePlex variable-data directory.
To set the environment on UNIX and Linux:
EXPORT SP_SYS_HOST_NAME="splex"
SP_SYS_PRODDIR=/home/shareplex
SP_SYS_VARDIR="/app/shareplex/vardir"
When you create the configuration file that directs SharePlex replication, you specify the TNS alias rather than an actual ORACLE_SID, as follows.
To capture from a source cluster:
Specify the TNS alias on the o.datasource line of the file. This is the first line of the configuration file.
For example:
datasource:o.ora_a_sp
To post to a target cluster:
Specify the TNS alias as the destination in the routing map.
For example (assumes the use of wildcards to specify objects):
expand hr.% hr.% inst_c@ora_b_sp
Once a source and target cluster (if applicable) are configured, you can populate a standalone or clustered target with a copy of the source data, while replication keeps track of transactional changes made by users on the source database. Use any of the Oracle-specific copy methods for activating replication from an active source. See the procedures listed in Activate replication in your production environment in the SharePlex Administration Guide for more information.
Incorporate SharePlex as a resource in the cluster software, and include it in the cluster failover routines so that it migrates with the other applications during failover. This ensures that the sp_cop process is started on the adoptive node by the cluster software. At minimum, this includes creating a startup script for SharePlex and a cluster script for SharePlex to handle failover.
Notes:
|
Make certain your systems administrators understand that any changes or upgrades they perform to the operating system on any node in the cluster must be implemented on all nodes in the cluster so that SharePlex fails over to an identical environment.
Prework for the demonstrations
Create and activate a configuration
|
Notes:
|