Hyper-V Explorer Event Analytics tab
The Hyper-V Explorer Event Analytics tab contains details about the state of resource-related metrics for a server or virtual machine over a selected time period, and also shows any events that occur during that time frame.
This tab appears in the Hyper-V Explorer when you select a server or virtual machine on the Hyper-V Explorer Topology tab.
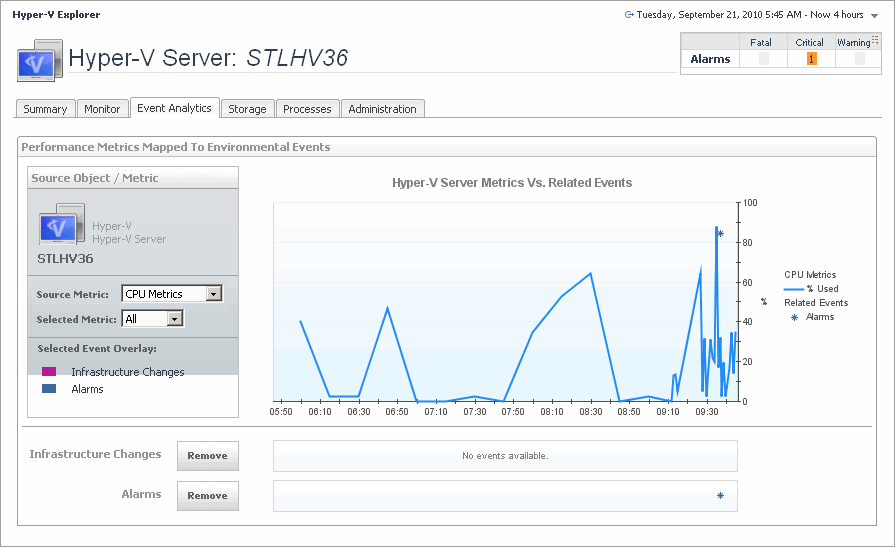
This tab is made up of the following embedded views:
|
|
Shows a chart indicating the values for one or more metric values selected in the Source Object/Metric view.
|
|
|
|
• |
Alarms. If any alarms are generated against the selected server during the selected time period, and are added as an overlay to the chart using the Infrastructure Changes and Alarms view, they also appear in the chart. | |
|
|
|
• |
CPU Metrics, % Used. The percentage of the server’s CPU utilization spent on executing system code and user programs during the selected time period. | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• |
Infrastructure changes. If any infrastructure changes occur for the selected server during the selected time period, and are added as an overlay to the chart using the Infrastructure Changes and Alarms view, they also appear in the chart. An infrastructure change is any configuration change that affects the properties of the selected server. This includes the server startup, shutdown, pause, changed shares, changes to memory settings, and similar types of changes. | |
|
|
|
• |
Memory Metrics, % Used. The percentage of the available memory that the server uses during the selected time period. | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Drill down on: |
|
|
|
• |
Alarm or infrastructure change. Displays the Event Details dialog box. |
|
|
|
Allows you to add events as overlays to the chart and correlate the resource consumption with the stability of your environment. |
|
|
|
• |
Alarms. Allows you to add and review any alarms, that are generated against the selected server, during the selected time period, to the chart. | |
|
|
|
• |
Infrastructure changes. Allows you to add and review any infrastructure changes, that occur for the selected server, during the selected time period, to the chart. An infrastructure change is any configuration change that affects the properties of the selected server or virtual machine object. This includes the object’s startup, shutdown, pause, changed shares, changes to memory settings, and similar types of changes. | |
|
|
Drill down on: |
|
|
|
• |
Alarm or infrastructure change. Displays the Event Details dialog box. |
|
|
|
Shows a chart indicating the utilization percentage for one or more metric values selected in the Source Object/Metric view.
|
|
|
|
• |
Alarms. If any alarms are generated against the selected virtual machine during the selected time period, and are added as an overlay to the chart using the Infrastructure Changes and Alarms view, they also appear in the chart. | |
|
|
|
• |
CPU Metrics, % Used. The percentage of the virtual machine’s CPU utilization spent on executing system code and user programs during the selected time period. | |
|
|
|
• |
Disk Metrics, Read Rate. The rate at which the virtual machine reads data from disk during the selected time period. | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
• |
Infrastructure changes. If any infrastructure changes occur for the selected virtual machine during the selected time period, and are added as an overlay to the chart using the Infrastructure Changes and Alarms view, they also appear in the chart. An infrastructure change is any configuration change that affects the properties of the selected virtual machine. This includes the virtual machine startup, shutdown, pause, changed shares, changes to memory settings, and similar types of changes. | |
|
|
|
• |
Memory Metrics, % Used. The percentage of the available memory that the virtual machine uses during the selected time period. | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Drill down on: |
|
|
|
• |
Alarm or infrastructure change. Displays the Event Details dialog box. |
|
Hyper-V Explorer Storage
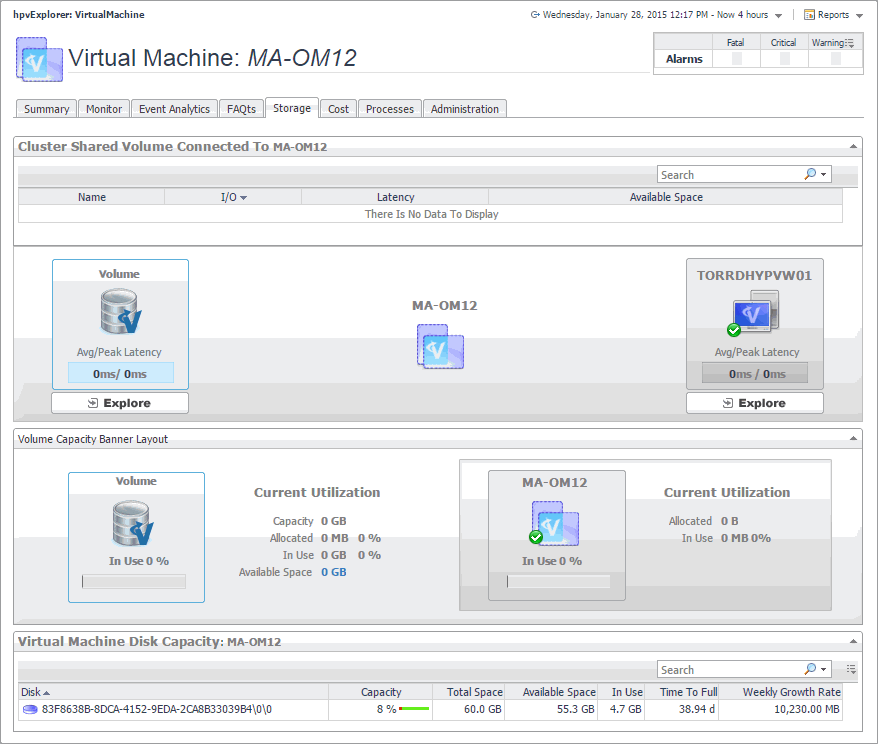
This tab only appears when you are exploring individual servers. It displays an organized view of physical drive and logical disk activity. It identifies the physical drives with the highest disk activity, and the logical drives with the lowest capacity. Use this information to fine-tune your configuration, achieve optimal results, and avoid bottlenecks. In addition, this tab lists all physical drives for the selected server, their read and write rates, along with the logical drives, the space used on each drive, data growth patterns, and related estimates.
The appearance of this tab depends on the object or group of object selected. For example, exploring a cluster shows data transfer rates for each disk volume connected to the selected cluster, among other metrics, while exploring a virtual machine reveals the current utilization of disk resources for that virtual machine.
Hyper-V Explorer Storage tab (clusters)
The Hyper-V Explorer Storage tab displays combination of embedded views displaying disk volumes associated with the selected cluster. It identifies the virtual machines that spend the highest amounts of disk resources. Use this tab to find out more about the overall consumption of disk resources for a given cluster. The information provided on this tab can help you prevent potential bottlenecks by reallocating disk resources where they are most needed.
This tab appears in the Hyper-V Explorer when you select a cluster on the Hyper-V Explorer Topology tab.
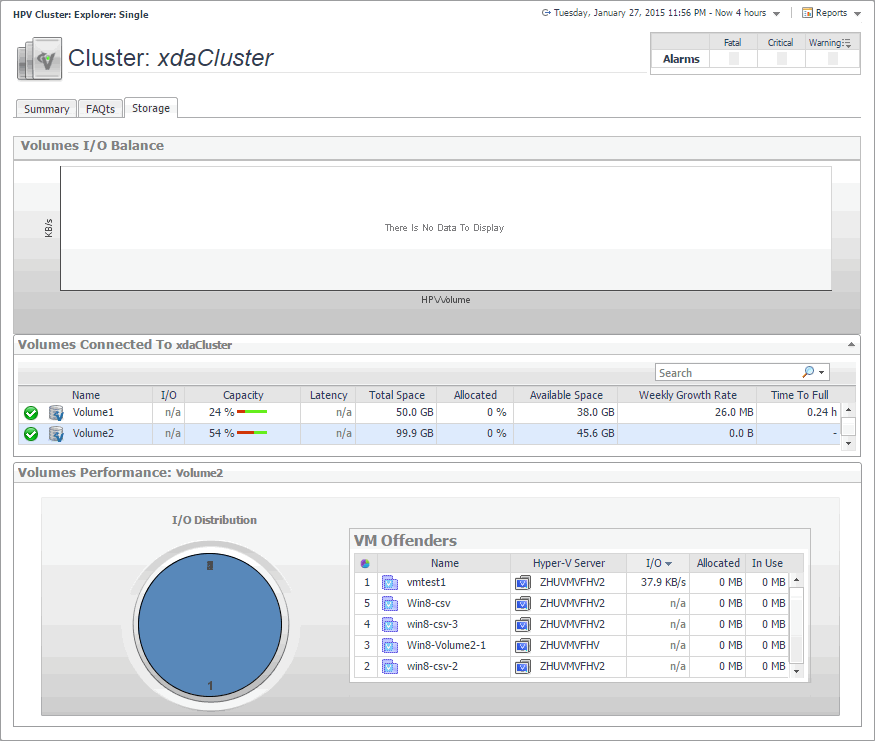
This tab is made up of the following embedded views:
Hyper-V Explorer Storage tab (Hyper-V servers)
The Hyper-V Explorer Storage tab displays combination of embedded views displaying disk volumes associated with the selected Hyper-V server. It identifies the virtual machines that spend the highest amounts of disk resources. Use this tab to find out more about the overall consumption of disk resources for a given Hyper-V server. The information provided on this tab can help you prevent potential bottlenecks by reallocating disk resources where they are most needed.
This tab appears in the Hyper-V Explorer when you select a Hyper-V server on the Hyper-V Explorer Topology tab.
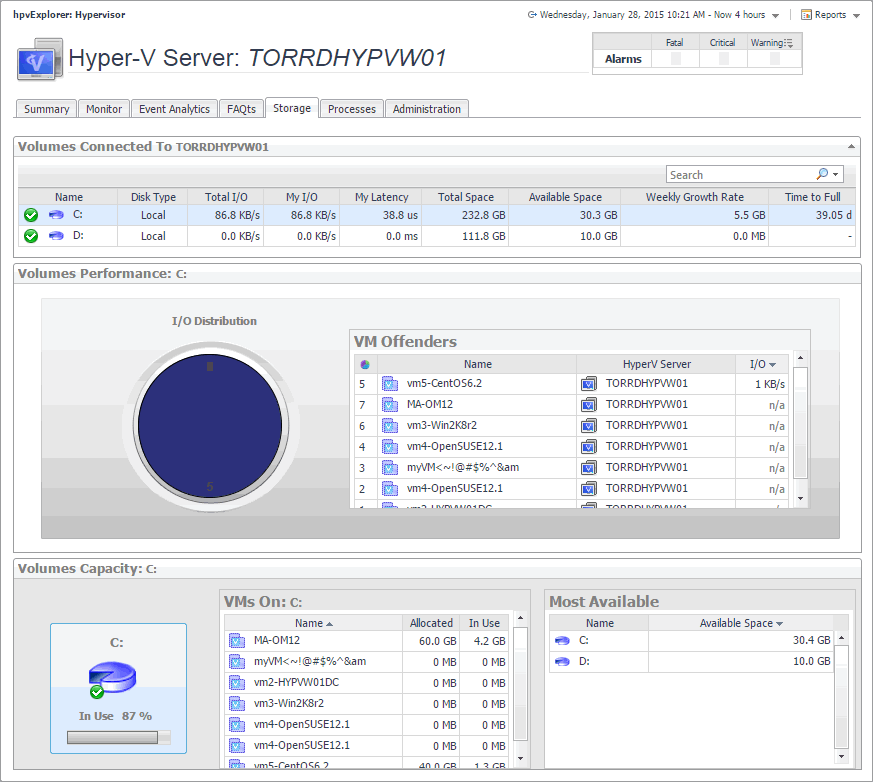
This tab is made up of the following embedded views: