Installing and enabling Foglight for Hyper-V
Foglight™ for Hyper-V is distributed in a CAR file, Virtual-HyperV-6_3_0.car. While most of Foglight for Hyper-V components are defined in this file, some of its browser interface elements are defined in two additional CAR files, DRP-6_3_0.car and Virtual-Hyper-V-Admin-6_3_0.car. The cartridge included in the Virtual-Hyper-V-Admin-6_3_0.car file provides access to Hyper-V administrative actions through the Hyper-V Explorer’s Administration tab, when your user account is granted the Hyper-V Automation User role. To enable the Administration tab, install this cartridge on the Management Server. For more information about the Hyper-V Explorer, see the Foglight for Hyper-V User and Reference Guide.
The following procedure describes the process of installing and enabling the available cartridges using the browser interface. Another way to install and enable cartridges is through the fglcmd command-line interface. For more information about the available fglcmd commands, see the Command-Line Reference Guide.
|
1 |
On the navigation panel, under Dashboards, choose Administration > Cartridges > Cartridge Inventory. |
|
2 |
On the Cartridge Inventory dashboard, click Install Cartridge. |
|
3 |
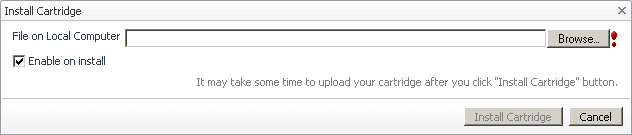
In the Install Cartridge dialog box, click Browse and navigate to the Virtual-HyperV-6_3_0.car file that you want to install. |
|
4 |
Ensure that the Enable on install check box is selected. |
|
5 |
Click Install Cartridge. |
|
6 |
|
7 |
From here, you can proceed to deploying the agent packages.
Deploying agent packages to monitored hosts
Foglight™ for Hyper-V uses Hyper-V, System Center Virtual Machine Manager (SCVMM),and Scale-Out File Server (SOFS) Agent instances to collect information from monitored hosts. Installing and enabling Foglight for Hyper-V on the Management Server makes its agent packagea available for deployment.
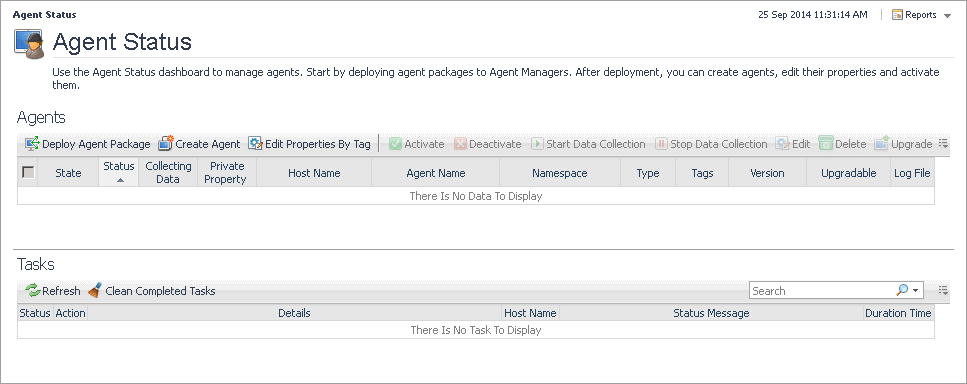
The following procedure describes the deployment process using the Agent Status dashboard. This administrative dashboard is useful for deploying the agent package one host at a time. Alternatively, for deploying the Hyper-V Agent package to multiple hosts, you can use the Agent Hosts dashboard. For more information, see the Administration and Configuration Guide.
Another way to deploy agent packages is through the fglcmd command-line interface. For more information about the available fglcmd commands, see the Command-Line Reference Guide.
|
2 |
|
3 |
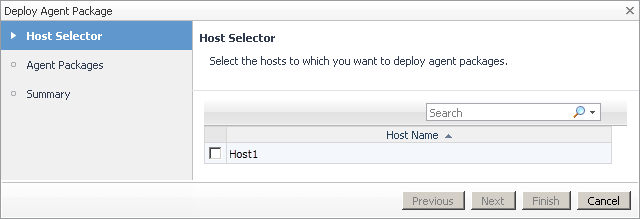
On the Agent Status dashboard, click the Deploy Agent Package button in the lower-left corner. |
|
5 |
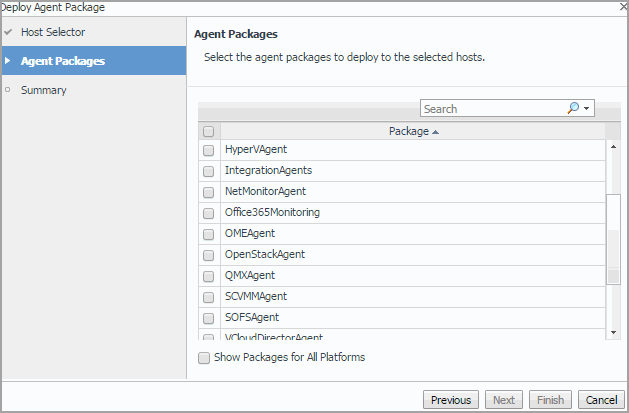
In the Deploy Agent Package wizard, on the Agent Packages page, select the HyperVAgent, SCVMMAgent,and SOFSAgent packages, and then click Next. |
|
6 |
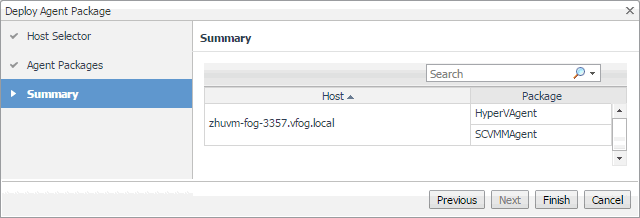
In the Deploy Agent Package wizard, on the Summary page, verify that the host name and package are correct, and click Finish. |
From here, you can proceed to create Hyper-V,SCVMM, and SOFS Agent instances to monitor hosts. For more information, see Configuring monitoring agents for data collection.
Configuring monitoring agents for data collection
Foglight™ for Hyper-V uses the Hyper-V, SCVMM,and SOFS agents to collect information about your virtual environment:
|
• |
Hyper-V Agents collect information from monitored Hyper-V servers. A Hyper-V server is a physical component required to begin building a virtual infrastructure. Hyper-V servers provide hypervisor-based architecture for controlling and managing resources for the virtual machines that run on it. |
|
• |
SCVMM Agents collect information from Virtual Machine Managers (VMM). A VMM allows you to manage host, networking and storage resources when creating and deploying virtual machines to virtual clouds. |
|
• |
SOFS Agents collect information from monitored SOFS servers. An SOFS server is a Windows Server cluster with some form of shared storage and provides highly available file-based storage for applications and general use. |
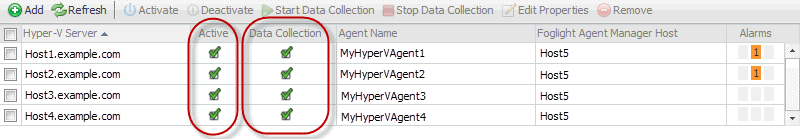
When Hyper-V, SCVMM,and SOFS agent packages are successfully deployed, you can create agent instances, activate them and start their data collection. To perform these steps in a single operation for one or more monitored hosts, use the Agents area on the Administration tab.
|
2 |
|
3 |
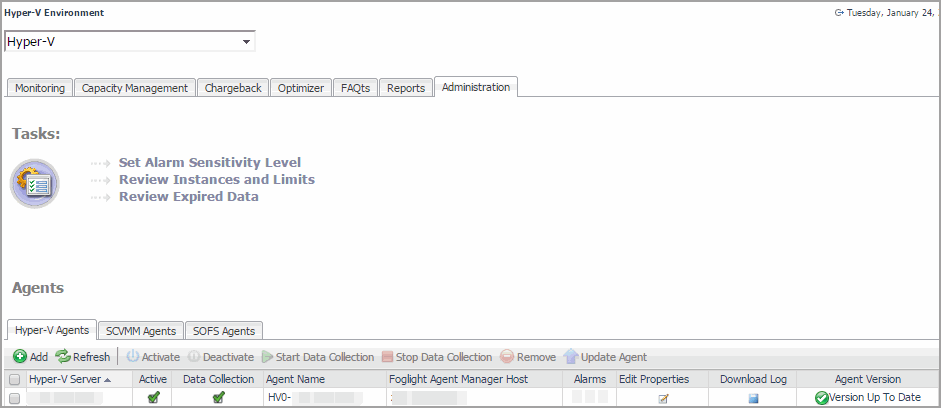
On the Hyper-V Environment dashboard that appears in the display area, open the Administration tab. |
|
4 |
On the Administration tab, under Agents, open the Hyper-V Agents, SCVMM Agents, or the SOFS Agents tab, as required. |
|
5 |
|
8 |
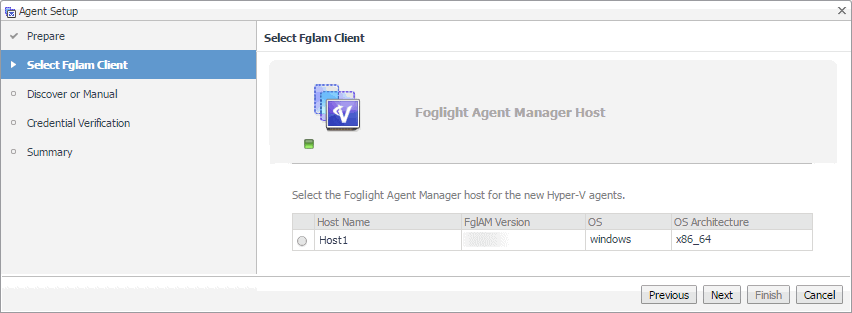
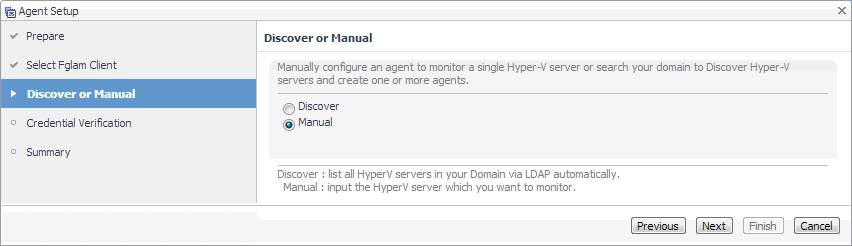
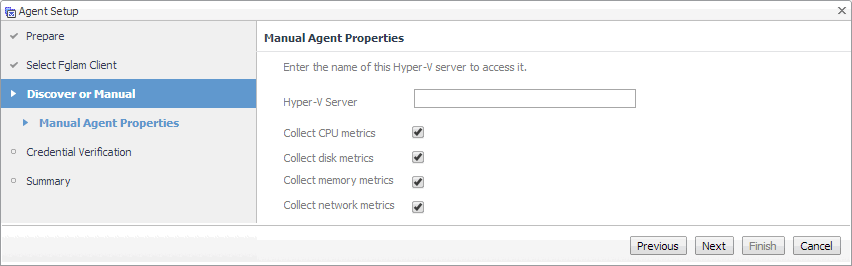
Hyper-V Agents only. On the Discover or Manual page that appears, you can indicate if you want to manually specify the Hyper-V Server that you want to monitor, or to choose between the servers running in a given domain. |
|
a |
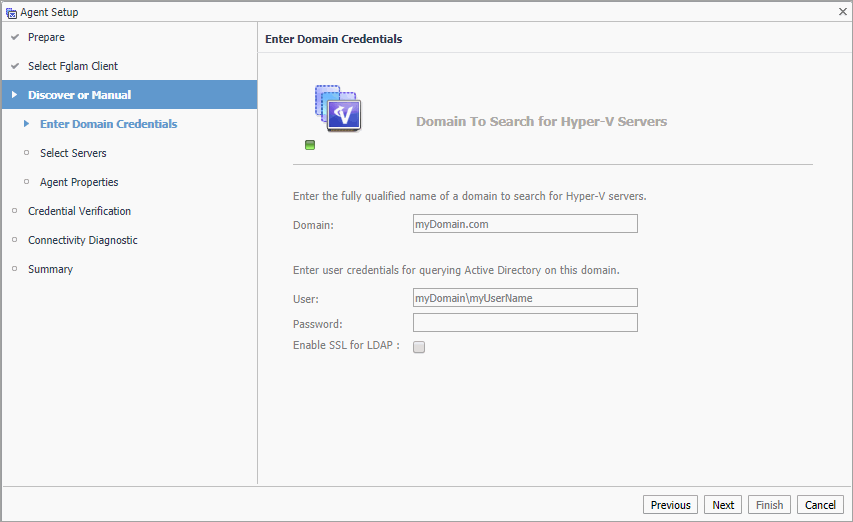
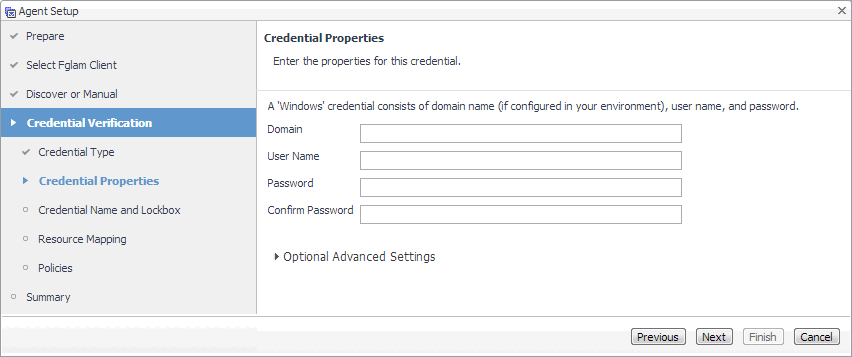
Discovering Hyper-V Servers only. On the Enter Domain Credentials page that appears, specify the information needed to search for the running Hyper-V Servers. |
|
• |
Domain: Type the fully qualified name of a domain to search for the Hyper-V Server. For example, myDomain.com. |
|
• |
User: Type the user name to be used by the agent to be used to query Active Directory on the selected domain using the syntax Domain\UserName. For example, myDomain\myUserName. |
|
• |
Password: Type the password associated with the above user name. |
|
d |
|
b |
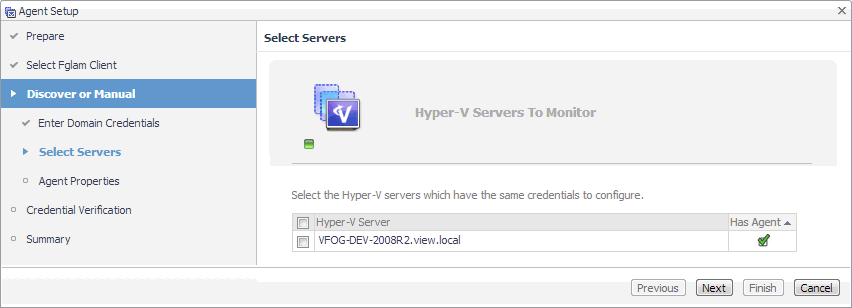
Manually specifying a Hyper-V Server only. On the Manual Agent Properties page that appears, specify the information needed to search for the running Hyper-V servers. |
|
c |
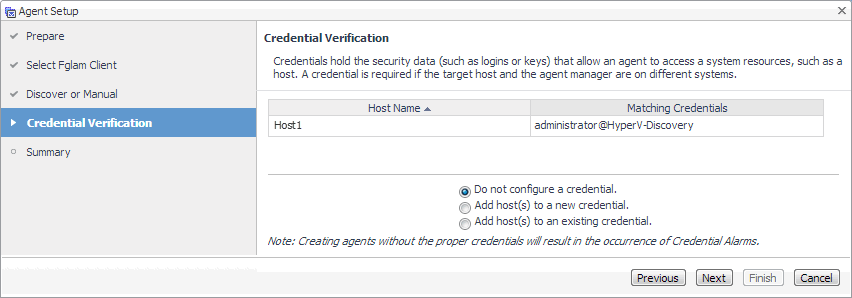
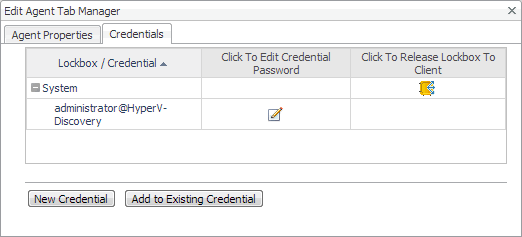
On the Credential Verification page that appears, review the existing set of credentials. If the wizard determines that the selected Agent Manager has any credentials configured for the host on which the Hyper-V Server is running, they appear listed on this page. |
|
9 |
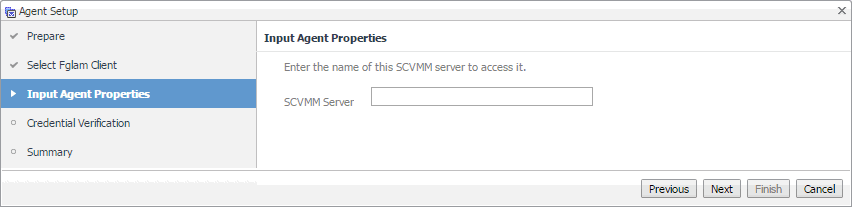
SCVMM Agents only. On the Input Agent Properties page that appears, type the name of the SCVMM server, and click Next. |
|
10 |
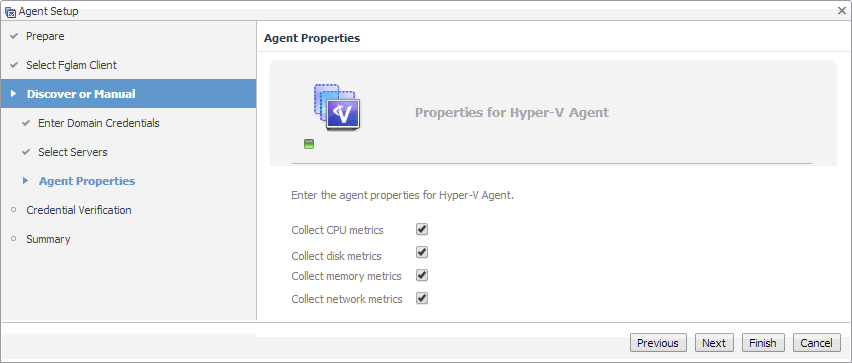
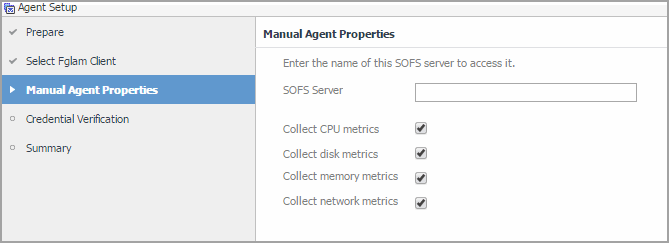
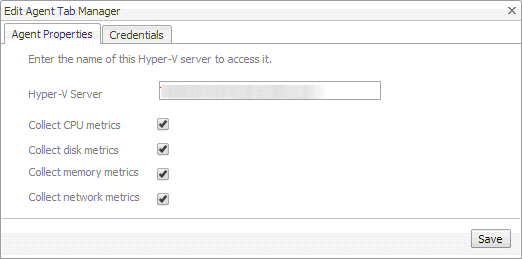
SOFS Agents only. On the Manual Agent Properties page that appears, type the name of SOFS Server, specify whether or not this SOFS Server collects CPU/disk/memory/network metrics, and click Next. |
|
11 |
On the Credentials Verification page, select one of the following options: |
|
• |
Do not configure a credential: Select this option if you want to configure the credential for this resource at a later time. Click Next and continue with Step 14. |
|
• |
Add host(s) to a new credential: Select this option if you want to add the host to a new credential. This option is suitable if none of the existing credentials have the connection details needed to access the new host. Click Next and continue with Step 12. |
|
• |
Add host(s) to an existing credential: Select this option if you want to add the host to an existing credential. This option is suitable if an existing credential has the security data needed to access the new host, but you need to edit its resource mappings to include this host. Click Next and continue with Step 13. |
|
a |
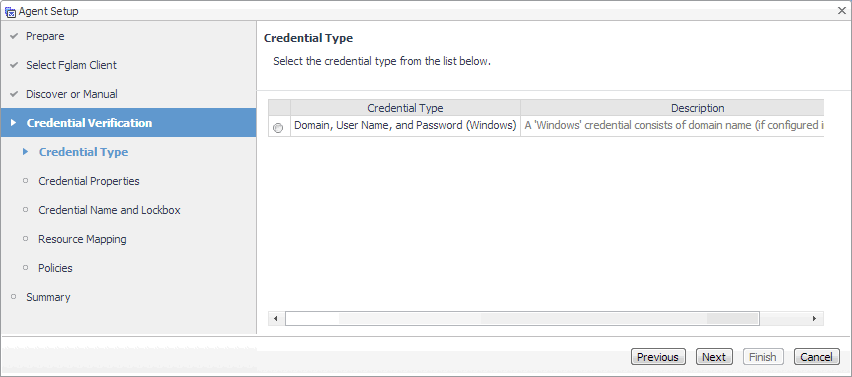
On the Credential Type page that appears, select the credential type from the available options. |
|
b |
Click Next. |
|
c |
|
d |
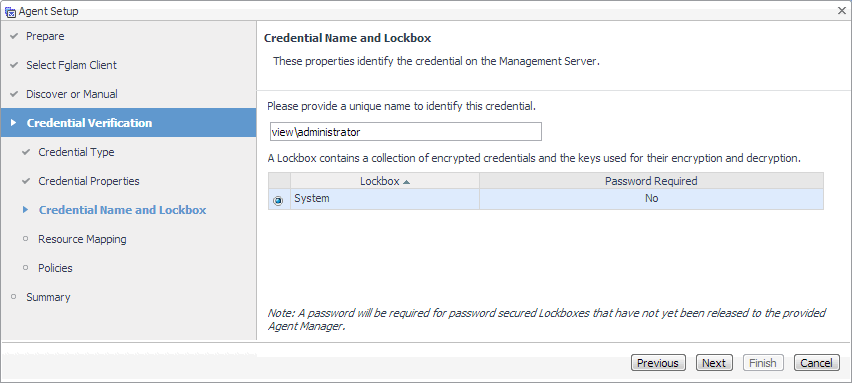
On the Credential Name and Lockbox page, provide a name to uniquely identify the credential, and select a lockbox in which you want to keep the credential. A lockbox can be used to group credentials for access and/or security. In smaller Foglight installations, using the default System lockbox should be sufficient. |
|
e |
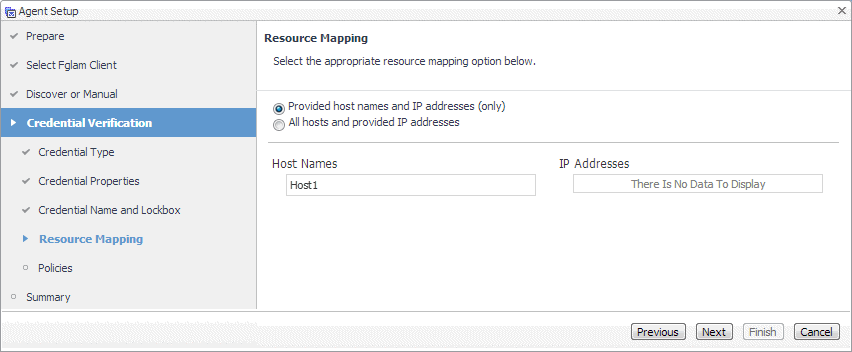
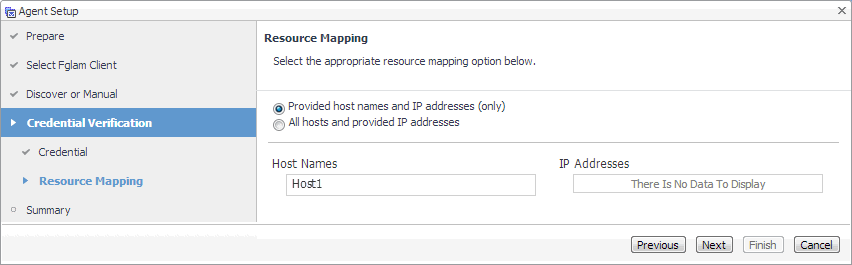
On the Resource Mapping page, indicate which hosts you want to associate with this credential. Click Next. |
|
f |
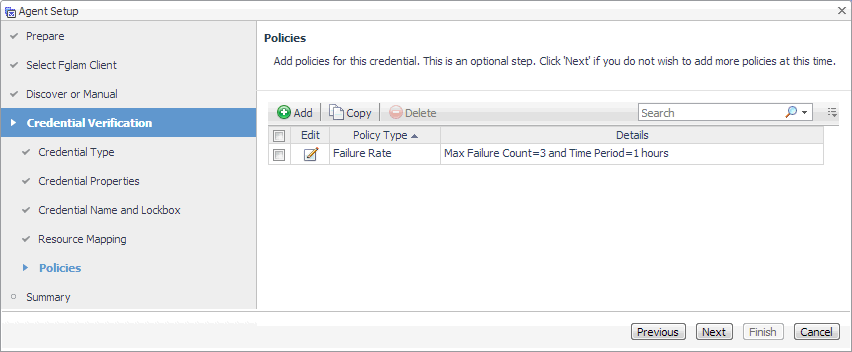
Optional—On the Policies page, define one or more policies for this credential. A policy defines the number of times a credential can be used, the number of allowed authentication failures, the time range during which the credential is valid, or the length of time the credential data can be cached on the client. For example, you can specify the number of times the credential can be used, or the time period during which it can be used. For complete information about the available credential policies, see the Administration and Configuration Help. |
|
a |
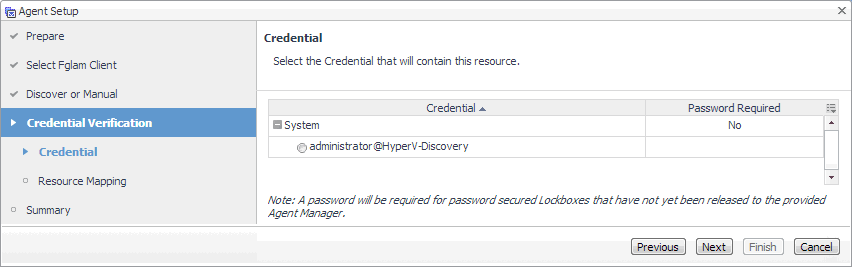
On the Credential page that appears, select an existing credential to contain this host. |
|
b |
Click Next. |
|
c |
On the Resource Mapping page, indicate which hosts you want to associate with this credential. You can either select the host that you are about to start monitoring, all monitored hosts, or hosts whose name contains a specific text string. |
|
14 |
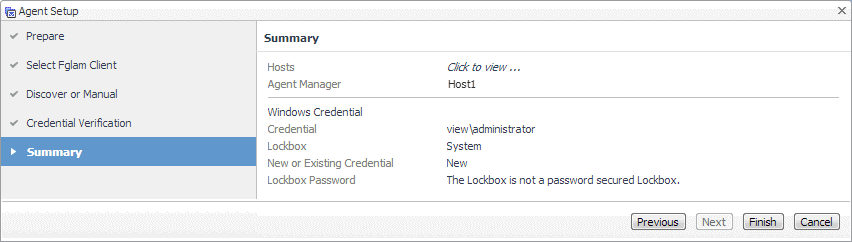
On the Summary page that appears, review the information provided about the host and the monitoring agent. |
|
15 |
Click Finish. |
|
a |
Select an agent and click Edit Properties. |
|
c |
Open the Credentials tab, and review the available credentials. |
|
19 |
Click Refresh. |
Using an alternative method to create and activate agent Instances, and to start their data collection
Another way to create agent instances is using the fglcmd command-line interface. For more information about the available fglcmd commands, see the Command-Line Reference Guide.
|
2 |
|
3 |
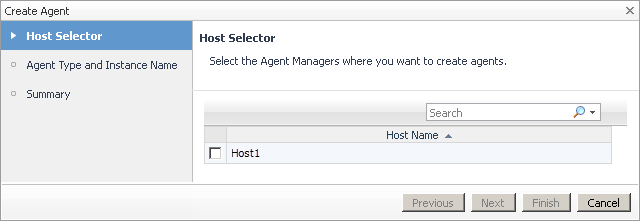
On the Agent Status dashboard, click Create Agent. |
|
5 |
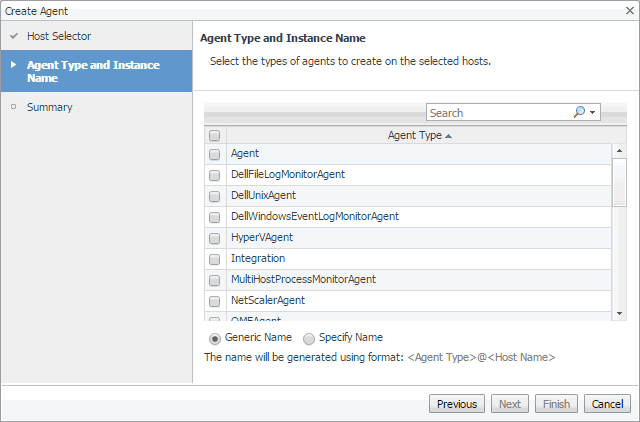
On the Agent Type and Instance Name page, select HyperVAgent, SCVMMAgent, or SOFSAgent, as required. |
|
• |
To have Foglight for Hyper-V assign a generic name, ensure that Generic Name is selected. |
|
• |
To use a specific agent name, select Specify Name, and in the Name box that appears, type the agent name. |
|
7 |
Click Next. |
|
8 |
In the Create Agent wizard, on the Summary page, verify that the host name and agent name are correct, and click Finish. |
|
a |
On the Agent Status dashboard, select the newly created Hyper-V, SCVMM,or SOFS agent instance, click Edit, and chose Edit Properties from the menu that appears. |
|
b |
Click Modify the private properties for this agent. |
|
d |