What Is Oracle RAC?
Real Application Clusters (RAC) is a clustering technology. Oracle RAC is a “shared disk” clustering solution that is significantly different from the architectures offered by Microsoft SQL Server and IBM DB2. Each node in an Oracle RAC cluster has equal access to all of the database data through a shared disk subsystem. Data is neither partitioned to specific nodes, nor replicated across nodes. A high-speed network interconnect allows each node to keep its in-memory view of data consistent.
An Oracle RAC configuration has the following architectural characteristics:
- Many instances of Oracle run across several nodes.
- Many instances share a single physical copy of a shared Oracle database.
- All instances have common data and control files.
- Every instance has individual redo logs and undo segments.
- Every instance can simultaneously execute transactions against the same database.
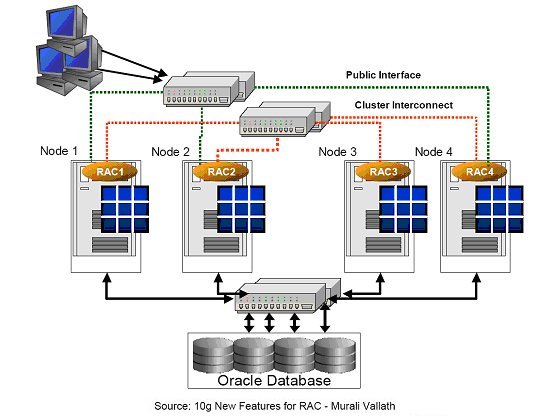
The following diagram illustrates the basic components of an Oracle RAC cluster.
A user should find an Oracle RAC database operationally identical to a database hosted on a single server. From top to bottom, the important features represented are:
- Cluster interconnect - A high-speed, high-bandwidth communication facility that connects the nodes in an Oracle RAC cluster.
- Multiple nodes/instances - Oracle instances run on the nodes (host machines) in the Oracle RAC cluster. Each instance comprises an Oracle System Global Area (SGA) plus the corresponding Oracle background processes that retain and process Oracle database requests.
- Shared disk subsystem - Database files in Oracle RAC systems are stored on multiple disks that are shared by all the nodes in the cluster, and all nodes must be able read and write to those disks.