Step 1: Registering source storages
The first step is to register source storages from which to retrieve data. As source storages you can use:
- Offline Exchange Server databases. Recovery Manager for Exchange can register the following:
- databases held in regular backups of Exchange Server, recovery databases on an online Exchange Server,
- databases in a recovery storage group on an online Exchange Server, or databases held in a folder.
- Offline Lotus Domino databases. Recovery Manager for Exchange is capable of registering Lotus Domino databases from a specified folder.
- Personal Folders (.pst) files. Recovery Manager for Exchange can register multiple .pst files from different folders at a time.
- Online Exchange mailboxes. Recovery Manager for Exchange enables you to selectively register multiple online mailboxes hosted on on-premises Exchange Servers or in Exchange Online in Office 365.
- Online public folder hierarchies hosted on Exchange Servers or Exchange Online in Office 365. You can selectively restore data from any folder in an online public folder hierarchy registered as a storage.
- Online Archive Manager instances. You can register multiple Archive Manager instances as source storages.
Items that are supported as source and/or target storages depend on the Recovery Manager for Exchange edition you are using. For more information, see Comparison of Recovery Manager for Exchange editions.
Extracting Exchange databases from backups
To restore individual messages from a backed up Exchange Server database, Recovery Manager for Exchange first extracts the database to a specified folder.

Recovery Manager for Exchange can extract entire Exchange Server databases (including log files) from regular Exchange Server backups. All backup types are supported: full, differential, and incremental. Recovery Manager for Exchange supports backups created with native Exchange or third-party backup tools. For a complete list of supported third-party backup software, please see the Release Notes supplied with Recovery Manager for Exchange.
In Exchange Server 2000 or 2003, each Exchange store database includes a properties database (.edb) file and a streaming database (.stm) file that is used for storing native Internet content. An Exchange Server store database originating from Exchange Server 2010 or later only includes an .edb file. The .edb file contains folders, tables, and indexes for messaging data, and MAPI messages and attachments.
The log files of an Exchange Server database store the changes made to the database, thus providing a way to restore transactions that were committed but not written to the database. While in Exchange Server 2010 storage groups are discontinued, in Exchange Server 2000, 2003, or 2007 each storage group includes a set of log files that apply to all the Exchange store databases within that storage group.
Accessing Exchange backups through existing backup software
Recovery Manager for Exchange can integrate with third-party backup software to locate and access Exchange backups. Recovery Manager for Exchange employs the capabilities of an existing backup management infrastructure, such as:
- Backup management across multiple operating systems and heterogeneous storage devices.
- Access to backups that span multiple media.
- Retrieval of backups by using multiplexing and multi-streaming storage techniques.

To provide interoperability with backup software, Recovery Manager for Exchange uses the following methods:
- Exchange Server emulation. The computer running Recovery Manager for Exchange appears as an Exchange Server to the backup software. Exchange backups can be restored to Recovery Manager for Exchange by redirecting the restore to the Recovery Manager for Exchange computer.
- Access to backup server. Recovery Manager for Exchange connects to a backup server that is part of the backup infrastructure, issues requests for backups stored on that server, and uses standard protocols to retrieve and restore data from the backup server.
Exchange Server emulation
Recovery Manager for Exchange emulates Microsoft Exchange Server in order to retrieve data from backups created with such software as:
- Quest® NetVault Backup®
- CA ARCserve Backup
- EMC NetWorker
- HP Data Protector
- IBM Tivoli Storage Manager
- Microsoft Windows Backup
- Symantec Backup Exec
- Symantec NetBackup
For supported versions of third-party backup software, see the Quest® Recovery Manager for Exchange Release Notes.
When it is running in Exchange Server emulation mode, Recovery Manager for Exchange provides all the services required for your backup software to restore Exchange data to the computer running Recovery Manager for Exchange.
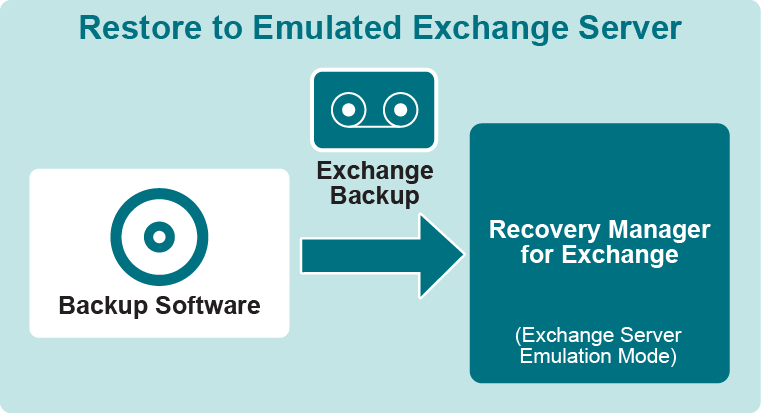
The Exchange Server emulation option allows you to restore backups using your backup software, redirecting the restore to the emulated Exchange Server. After you restore a backup to the computer running Recovery Manager for Exchange, Recovery Manager for Exchange registers the database files extracted from that backup, so that you can search and selectively restore data.
Access to backup server
Recovery Manager for Exchange makes use of an open application programming interface (API) when retrieving data from backups created with the following software:
- Quest® Rapid Recovery® (AppAssure®)
- Quest® vRanger®
- EMC NetWorker
- IBM Tivoli Storage Manager
- Microsoft Data Protection Manager
- Microsoft Windows Server Backup
For these backup software products, Recovery Manager for Exchange prompts you to specify the backup server that manages the backups from which you want to extract and register databases. Recovery Manager for Exchange then establishes a connection to the server and displays a list of backups managed by that server. You can then select one or more backups to be extracted.
For supported versions of third-party backup software, see the Quest® Recovery Manager for Exchange Release Notes.
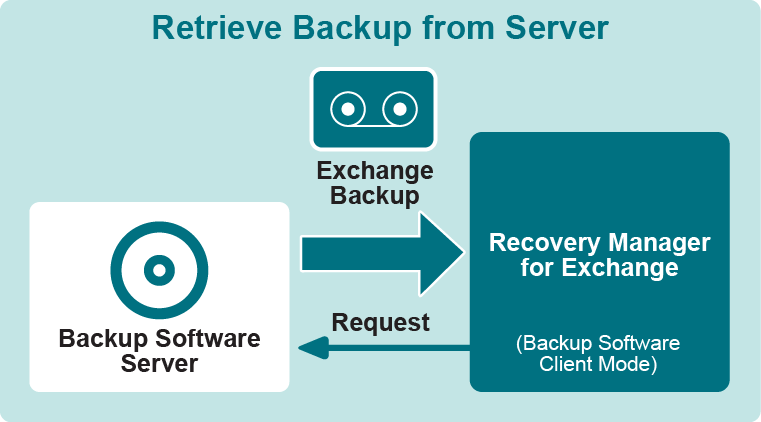
Recovery Manager for Exchange sends requests to the backup server for the backups you selected and processes data provided by the server, extracting Exchange Server database files from the backups to the computer running Recovery Manager for Exchange. After that, Recovery Manager for Exchange works with the extracted database files to register them as storages.
Accessing offline Exchange or Domino databases, or Personal Folders (.Pst) files
Accessing offline Exchange or Domino databases, or Personal Folders (.Pst) files
Recovery Manager for Exchange can access offline Exchange Server and Lotus Domino databases in any location. For example, you can copy database files from an Exchange Server or Lotus Domino computer to an alternate location—a network share, local folder or drive—and then have Recovery Manager for Exchange access the database there to search and restore specific data. Likewise, you can access .pst files to search and selectively restore folders, messages, or attachments these files contain.
Accessing recovery databases and databases
Recovery Manager for Exchange can access recovery databases (Exchange Server 2010 or later) and databases located in a recovery storage group (Exchange Server 2003 and 2007) on an online Exchange Server computer. Recovery Manager for Exchange is particularly useful when you need to restore specific email messages in a recovery database or database held in a recovery storage group. By using Recovery Manager for Exchange, you can connect to the database that holds the data you want to restore, search the database for specific messagelevel items, optionally preview the found items and/or their attachments, and then selectively recover them. Alternatively, you can use Recovery Manager for Exchange to restore the entire database.
